23th January 2024 (6 Topics)
Context
The report on the Future of Work highlights that Gen Zs and millennials prefer gig roles due to flexible work locations and a emphasis on specialized skills.
Key Highlights
Key Highlights of the report –
- Future job landscape: Firms are focusing on geographical expansion for talent exploration and strategic partnerships for competitive advantage and market access.
- Tier 2/3 city prominence: Expansion into smaller cities gains traction for harnessing untapped innovation potential and diverse talent pools.
- Drivers for expansion: Small organizations prioritize talent availability and cost savings, while larger tech firms focus on diverse skill sets and untapped talent in emerging technology hubs.
- Industry transformation: The tech industry in India undergoes significant transformation, shifting from traditional offices to exploring remote work and adapting to evolving workspace dynamics.
- Balance in the future of work: The evolving work landscape will be defined by a dynamic balance between efficiency improvements from automation and the expansive potential of creativity through continuous innovation.
|
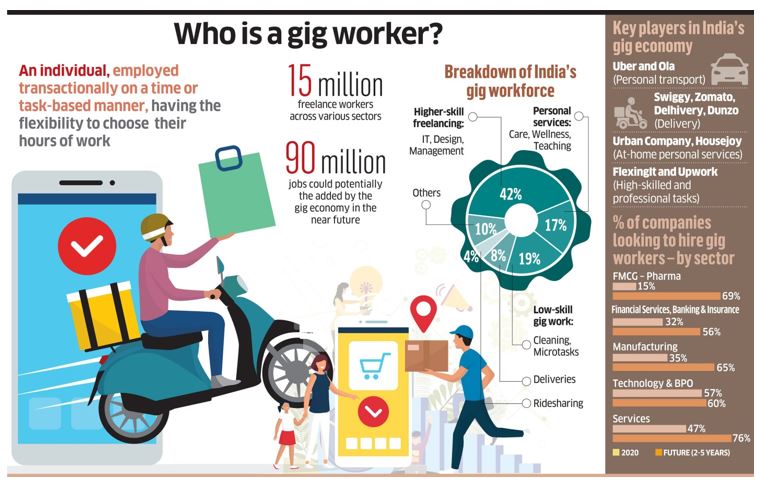
What is gig economy?
Benefits of Gig Economy:
|
Current trend in the Indian Economy-
- about 47% of gig work is in medium skilled jobs
- about 22% in high skilled
- about 31% in low skilled jobs
The trend shows the concentration of workers in medium skills is gradually declining and that of the low skilled and high skilled is increasing.
Expected trend
- While in 2020-21, the gig workforce constituted 2.6% of the non-agricultural workforce or 1.5% of the total workforce in India, by 2029-30, gig workers are expected to form 6.7% of the non-agricultural workforce or 4.1% of the total livelihood workforce in India.
Significance of Gig Economy in India
- Boosting Employment Opportunities: In India's quest to provide employment opportunities, the gig economy plays a crucial role by expanding job availability and enhancing labor force participation.
- Addressing Skill Diversity: Approximately 47% of gig work involves medium-skilled jobs, 22% in high-skilled roles, and 31% in low-skilled positions, catering to a diverse range of skills in the workforce.
- Youthful Demographic Advantage: With a large population of educated and tech-savvy youth, India leverages its demographic dividend, as many millennials seek the gig economy for its flexibility and work-life balance.
- Empowering Female Labor Force: The gig economy benefits female workers by providing income-generating opportunities, choice, and flexible work arrangements, leading to an increase in women's participation from 18% to 36%.
- Post-Retirement Opportunities: Contract work's flexibility attracts retirees, enabling them to continue working on their terms even after retirement.
- Democratization of Job Opportunities: The gig and platform sector, characterized by low-entry barriers, holds significant potential for democratizing job opportunities and fostering inclusive job creation in India.
- Technological Advancements Driving Change: Rapid technological advancements, especially in AI, robotics, and data analytics, eliminate workplace limitations, enhancing productivity and improving the living standards of gig workers.
- Revolutionizing Last-Mile Delivery: The gig economy has revolutionized the last-mile delivery industry, making it more accessible, affordable, and efficient through innovative work models.
- Facilitating Remote Work: Telecommunications have made work more dynamic, enabling collaboration irrespective of geographical constraints, fostering the growth of remote work.
- Enabling Start-Up Culture: Gig workers serve as a cost-effective alternative for businesses, allowing project-by-project hiring without the obligation of providing traditional employee benefits.
More Articles