16th February 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
India and Australia have announced that they are set to conclude an interim trade agreement in March and a Comprehensive Economic Cooperation Agreement (CECA) 12-18 months thereafter.
About
About interim trade agreement:
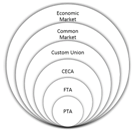
- An interim or early harvest trade agreement is used to liberalise tariffs on the trade of certain goods between two countries or trading blocs before a comprehensive FTA (Free Trade Agreement) is concluded.
- It will cover “most areas of interest for both countries” including goods, services, rules of origin, sanitary and phytosanitary measures and customs procedures.
Status of India’s current trade with Australia:
- Bilateral trade between the two countries stood at about USD 12.5 billion in Financial Year (FY) 21 and has already surpassed USD 17.7 billion in the first 10 months of FY22.
- India has imported merchandise worth about USD 12.1 billion from Australia in the first 10 months of the fiscal and has exported merchandise worth USD 5.6 billion in the same period.
- Key imports from Australia include coal, gold and Liquified Natural Gas while key exports to the country from India include diesel, petrol and gems and jewellery.
About Free Trade Agreement:
- A free trade agreement (FTA) is an agreement where two or more countries agree to provide preferential trade terms, tariff concession etc. to the partner country.
- In this agreement, a negative list of products and services is maintained by the negotiating countries on which the terms of FTA are not applicable hence it is more comprehensive than preferential trade agreement.
India and Australia interim trade agreement:
- The agreement with Australia was set to bring opportunities across sectors including mining, pharmaceuticals, health, education, renewables, railways, gems and jewellery, tourism, defence and textiles.
- India is also likely to seek easier visa access for both students and professionals visiting Australia.
- Australia is likely to seek market access for wines and agricultural products which are not produced on a large scale in India.
- The agreement would lead to deeper cooperation between the two countries in critical minerals and rare earth elements which are critical to future industries including renewable energy and electric vehicles.
Impact of QUAD:
- India and Australia are both members of the Quad (Quadrilateral Security Dialogue) along with the US and Japan.
- The coalition has given impetus to increasing trade relations between all members of the Quad.
- Australia already had FTAs with both the US and Japan and that all four countries could start building a framework for economic cooperation within the countries of the Quad after they announced a deal with India.
|
Types of Regional Trading Agreements: Regional trading agreements vary depending on the level of commitment and the arrangement among the member countries.
|