

16th August 2023 (7 Topics)
Context
According to a recent update, Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) has charted out a four-month-long trajectory for its solar spacecraft set for launch by September this year.
Evolution of ISRO’s Solar Mission:
- Since a decade now to India’s sun observatory Aditya L1, is now going to further add to sun’s exploration.
- Indian Institute of Astrophysics has been working to assemble Aditya L1’s primary payload–a 90-kg Visible Line Emission Coronagraph (VERC) which will drive ISRO’s first-ever scientific mission to the sun.
- The final satellite consisting of seven different payloads has now been successfully integrated at UR Rao Satellite Centre (URSC).
- Though the sun is about 150 million kilometres from the Earth, the spacecraft would be put into a halo orbit around the Lagrange point (L1)–1.5 million km from the Earth, so it can view the mighty sun without any eclipses.
- Objectives of the mission:
- The scientific mission will also look to gather more data on understanding the coronal mass ejection.
- It also aims to study the photons and the solar wind ions and electrons emitted by the sun, as well as the interplanetary magnetic field created in space.
|
Coronal mass ejections (CMEs) are large expulsions of plasma and magnetic fields from the Sun’s corona.
|
Significance of Aditya L1 mission in India’s journey:
- Advancement in Solar Physics: Data collected by the suite of instruments in this mission will help to advance our understanding of the sun's activity.
- Understanding the sun's activity and its influence on Earth's climate can help in space weather forecasting space as events such as solar flares and coronal mass ejections can disrupt communication and navigation systems.
- It will help better predict sunspot cycles thus the sun’s energy output and contribute to the harnessing of renewable energy as a source to meet our energy demands.
- A better understanding of the impact of the sun on earth’s climate contributes to the better development of strategies for mitigation and adaptation to climate change.
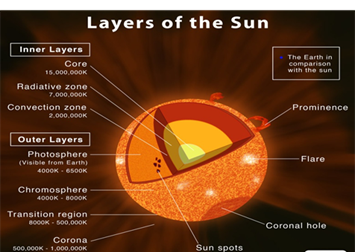
Visible Line Emission Coronagraph (VERC):
- It is the largest payload that would fly on the Aditya-L1 mission. It is an internally occulted solar coronagraph capable of simultaneous imaging, spectroscopy and spectro-polarimetry close to the solar limb.
- The VELC consists of a coronagraph, spectrograph, polarimetry module and detectors, aside from auxiliary optics.
|
Interesting Facts about Sun:
|


