12th March 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
The construction of the ‘Away From Reactor’ (AFR) facility at the Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project (KKNPP) site for storing nuclear waste.
- The Kudankulam Village Panchayat, under which the project site falls, has passed a resolution against setting up the facility.
About
History
- In 1988, during the Rajiv Gandhi period a MOU (Memorandum of Understanding) for construction of a nuclear power plant in India was signed between two countries India and Soviet (Russia).
- But due to several factors from political and economic crisis the project has been put on hold since there was a breakup in Soviet and moreover with the objection from US stating that the agreement signed didn’t meet up with the current Terms and Conditions from the group of nuclear suppliers.
- Previously before 2004 the water reactor equipment was brought through roads as their mode of transport from Tuticorin port and due to various difficulties of damages incurred during its transportation.
- It decided to select a Naval point base and come up with an idea to develop a small port near the tip of the country and they felt the best place would be Koodankulam in southern part of Tamil Nadu and then a small port become operational on January 14, 2004.
- The main purpose of its construction is to receive baggage carrying oversized light water reactors from ships anchored at a distance of half a km from its port.
- In 2007 a MOU was signed between India and Russia and when Russian president Vladimir Putin visited India he had discussion with Manmohan Singh and both countries have planned to promote the use of nuclear energy to certain heights.
About Kudankulam Nuclear Power Project (KKNPP)
- In the resolution, the ward members also condemned the KKNPP administration for going ahead with the construction of the facility despite opposition from the State government to storing highly radioactive nuclear fuel waste.
- Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant is the largest nuclear power station in India, situated in Kudankulam in the Tirunelveli district of Tamil Nadu.
- Construction on the plant began on 31 March 2002, but faced several delays due to opposition from local fishermen.
- KKNPP is scheduled to have six VVER-1000 reactors built in collaboration with Atomstroyexport, the Russian state company and Nuclear Power Corporation of India Limited (NPCIL), with an installed capacity of 6,000 MW of electricity.
|
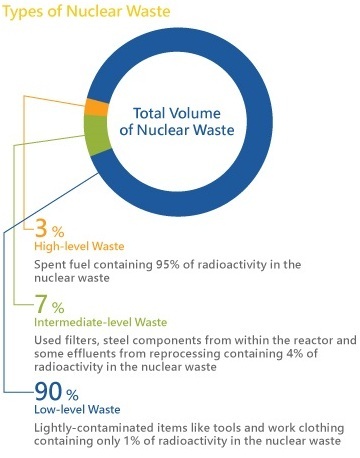
Radioactive (or nuclear) waste
|