

29th November 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
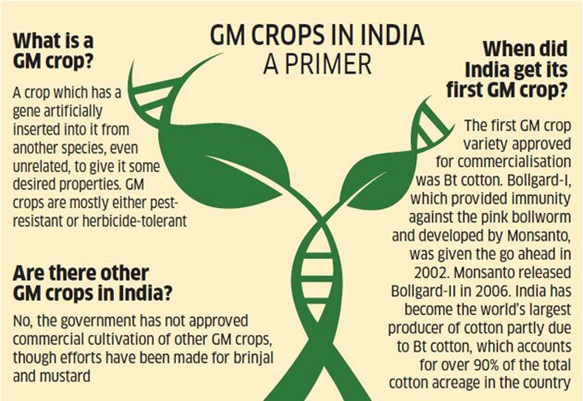
Recently, the Genetic Engineering Appraisal Committee (GEAC) approved the environmental release of genetically engineered (GE) mustard (DMH-11 hybrid) in India which has drawn criticism for damaging the Environment and Ecology and does not follow adequate approval provisions.
About
GM Mustard Crop:
- The hybrid mustard DMH-11 has been produced which contains two alien genes isolated from a soil bacterium called Bacillus ‘amyloliquefaciens’.
- The first gene (‘barnase’) codes for a protein that impairs pollen production and renders the plant into which it is incorporated male-sterile.
|
The Approving Body:
|
- This plant is then crossed with a fertile parental line containing, in turn, the second ‘barstar’ gene that blocks the action of the barnase gene.
- The resultant F1 progeny is both high-yielding and also capable of producing seed/ grain.
- This system was used to develop DMH-11 by crossing a popular Indian mustard variety ‘Varuna’ (the barnase line) with an East European ‘Early Heera-2’ mutant (barstar).
Concerns associated:
- The presence of a third ‘bar’ gene, makes GM mustard plants tolerant to the spraying of glufosinate ammonium, a chemical used for killing weeds. This will cause displacement of manual labor engaged in weeding by promoting the use of chemical herbicides.
- The deployment of herbicide-resistant or HT crops has been accompanied by deleterious outcomes in several places including the US, Australia, and Canada as well as Argentina.
- The most well-established harmful consequence has been the spread of herbicide-resistant weeds across large tracts of agricultural land, which can spell disaster for the normal crop.
- The GM mustard can threaten the population of honey bees as the Mustard flowers are a source of nectar for honey bees and many other pollinator insects.
Loopholes in governance:
- The potentially harmful long-term ecological and economic consequences of releasing DMH-11 have not received sufficient consideration.
- Second, details of the mandatory trials to ensure food and environmental safety which is a prerequisite before environmental release have not been made public.
- Finally, a detailed long-term assessment of the potential social and economic benefits of using DMH-11, vis-à-vis its potential drawbacks, remains to be made.
- It is not enough for GEAC to merely refer it for chemical registration since the (Central Insecticide Board and Registration Committee) CIB&RC is not the competent body for recommending approval of GM crops.
- GEAC assumes that farmers will use DMH-11 without adding herbicide even though they know that it carries a gene for herbicide resistance.
- It ignores the known fact that there have been numerous recent reports in the Indian media of the illegal use of unapproved herbicide-resistant crops, which has been brought to the notice of the government.
- It ignores the known fact that there have been numerous recent reports in the Indian media of the illegal use of unapproved herbicide-resistant crops, which has been brought to the notice of the government.


