

Context
Recently, State Bank of India, ICICI Bank, Axis Bank, IDFC First Bank, Kotak Mahindra Bank, HDFC Bank, IndusInd Bank and Federal Bank have joined the Aggregator Account (AA) network) which will enable customers to easily access and share their financial information.
What is an Account Aggregator (AA)?
- AA is a framework that facilitates the distribution of financial information in real time and blindly (AA data flow encrypted) between regulated entities (Banks and NBFCs).
- The RBI (Reserve Bank of India) in 2016 approved the AA as a new component of NBFC (Non-Banking Financial Companies), whose main responsibility is to facilitate the transfer of user financial data with their explicit consent.
- AAs enable data flow between financial information providers (FIPs) and financial information users (FIUs).
- The structure of AA is based on the Data Empowerment and Protection Architecture (DEPA) framework.
- DEPA is an organization that allows users to securely access their data and share it with third-party users.
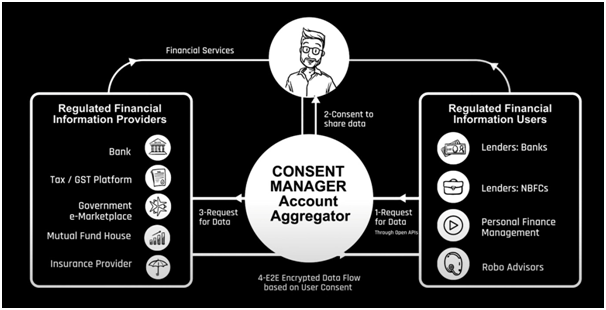
- DEPA is an organization that allows users to securely access their data and share it with third-party users.
Issues with India’s current financial system
- India’s financial system today involves many hassles for consumers –
- sharing physical signed and scanned copies of bank statements
- running around to get documents notarized or stamped
- having to share personal username and password to give a financial history to a third party
How is AA different from Aadhaar eKYC data sharing, and other platforms?
- Aadhaar eKYC and CKYC allow sharing of four ‘identity’ data fields only for KYC purposes (such as name, address, gender, etc.).
- Similarly, credit bureau data only show loan history and credit score.
- The AA network allows sharing of transaction data or bank details from savings/deposit/current accounts.
It’s Significance
- For Consumers: The AA framework allows customers to access a variety of financial services from a number of providers on a single site depending on the consent process, where consumers can choose which financial data to share and which organization.
- Less physical Interaction: It allows users to control who gets access to their data, track and access its own traffic and reduce the risk of leaks on the move.
- Banking: As an addition to India's digital infrastructure, it will allow banks to access the flow of approved data and verified data. This will help banks reduce transaction costs, which will enable them to offer low-size ticket loans and products and services tailored to their customers.
- Minimize fraud: AA reduces fraud associated with virtual data by introducing secure digital signatures and end-to-end data sharing encryption.
Way forward
Going forward, a large number of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) can be reached outside the portable branches and will change the inflow of credit. As we delve deeper into this, the opening of banks works surprisingly well as India is not well-kept when it comes to debt and other financial products. Significant pressure will arise from information and acquisition at the ecosystem level.
The AA framework can be expanded to manage data from other domains as well, such as health-related data and telecom. However, if licensed entities are to be approved it is important to have a data privacy framework as the RBI currently aims to protect only financial data within its mandate.


