

Context
Recently PM Narendra Modi made a nationwide launch of the Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission with the introduction of Health ID, which is going to revolutionize the way health services are being provided in our country.
Background
- It is an extension of the Nation Digital Health Mission (NDHM), which was launched from the rampart of Red Ford on August 15th
- Presently it is been functional in six Union Territories and is in its pilot phase.
- It has the potential to change the functioning of healthcare facilities.
- This Mission is aimed at creating interoperability within the digital health ecosystem, this will do the same role the Unified Payments Interfacedid in revolutionizing digitals payments in India.
Analysis
What is Ayushman Bharat Digital Mission (ABDM)?
- It is aimed at developing astructural framework necessary to support the integrated digital health infrastructure of the country. This will help the government to bridge the gap among the various stakeholders of the healthcare ecosystem through digital means.
- IndiaEnterprise Architecture Framework (IndEA)shall be adopted for developing the ABDM.
- The National Health Authority (NHA) under the Ministry of Health and Family Welfare is the implementing agency for ABDM.
- Under the mission, every citizen shall be provided with a digital health ID in a digitally protected environment.This digital Health ID shall be a repository of all health-related information.
- It will enable the access and exchange of health records of citizens with their consent.
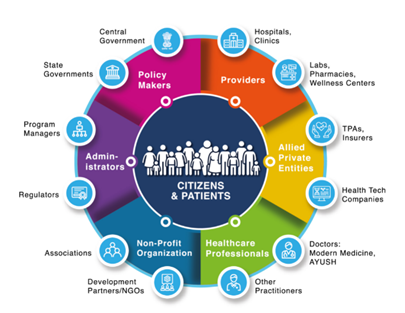
ABDM Ecosystem
Building Blocks of the ABDM:
- Health ID: The Health ID will be used to uniquely identify persons, validate them, and organisingtheir medical records (with the informed consent of the patient) across multiple systems and stakeholders.
- Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR): It is a repository of all healthcare professionals involved in the delivery of healthcare services across both modern and traditional systems of medicine. Healthcare Professionals Registry will enable healthcare professionals to get connected to India’s digital health ecosystem and the certain outcome of it shall be, ensure the ease of doing business for doctors/hospitals and healthcare service providers.
There currently exists no nationally recognized source of data on Healthcare Professionals in India that is trusted, digitally enabled and widely adopted by healthcare ecosystem stakeholders. The Healthcare Professionals Registry (HPR). CAQH (Council for Affordable Quality Healthcare) in the USA and General Medical Council (GMC) in the UK are examples where such a repository system is functional.
- Healthcare Facilities Registries (HFR): It is a repository of health facilities of the country across different systems of medicine. It will provide extensive coverage by including both public and private health facilities including hospitals, clinics, diagnostic laboratories and imaging centres, pharmacies, etc.
- Personal Health Records (PHR): A PHR is an electronic record of health-related information on an individual that adheres to the nationally recognized interoperability standards and that can be drawn from multiple sources while being managed, shared, and controlled by the individual.
|
The salient features of the Health Records (PHR):
|
Management of Health Records in ABDM:
- Use of the Aadhaar is voluntary. One can also use one’s mobile number for registration instead of Aadhaar.
- The records shall be stored with healthcare information providers as per their “retention policies”, and are “shared” over the ABDM network in encrypted formats only after the beneficiary express consent.
- The user can either permanently delete or temporarily deactivate her health ID.
How will this help citizens?
- The new system will ensure the safety of the medical records of the patients as the records will be stored in encrypted digital formats.
- It can also remove the unnecessary repetition of tests and procedures and bring standardisation in the healthcare facilities.
- The digital ecosystem will enable the host to provide facilities like remote or online consultation, diagnosis and delivery of medicines. This will be a boon to patients residing in small and rural areas, where they have limited access to healthcare facilities.
- With the data in hand, the government can motivate people towards a healthy lifestyle, which also mean that people will have to pay a lower for amount towards their health insurance premiums.
What are the concerns?
- Risk to Adoption:As it is going to follow the centralized data governance model, the States or other bodies that have robust data sets and digitalsystems may not be willing to release control of the same, which might lead to resistance. As health is a state subject and we have a federal structure, it could bring possible legal hurdles which need to be addressed beforehand.
- Operational Challenges: Mechanisms, committees and processes may have to be built to manage such a vast dataset.This may require significant investments in technology, human resources, communicationsefforts and process design. We have to increase the number of PHC and the number of skilled staff to cater for all Indians.
- Data Privacy: The data privacy processes will need to be carried out with utmost care. Implementation of stringent data protection measures will be crucial to preserving personal information. Though the government is saying that no medical practitioner will be able to access a citizen’s health data without his consent, the clouds of concern remain there.
- Digital divide: Though India has 118 active mobile users but to make the scheme function to its full potential, it is important to have seamless pan-India internet coverage. In addition, digital illiteracy is still prevalent in rural India and among the tribal population.
Conclusion:
The outcomes of the mission will be far wider than what is being perceived today. It can be related to a neural system where the entire ecosystem where the signals will get connected. By establishing an integrated digital health ecosystem, NDHM is going to achieve the goals of National Health Policy 2017 and the Sustainable development goals (SDG) related to health. NDHM will be adding a new chapter in the Indian digital healthcare ecosystem, enabling more effective delivery of healthcare services and moving towards health to all.Itis going to provide efficient, accessible, inclusive, affordable, timely and safe disbursal of healthcare services.


