

|
Overview
|
Context
The Union Cabinet has approved the auction of airwaves capable of offering fifth generation, or 5G, telecom services, including ultra-high-speed Internet, and gave its nod for setting up of captive 5G networks by big tech firms.
- The auction of over 72 GHz of the spectrumwill be held by 2022 July-end.
Background
- Devices such as cell phones and wire line telephones require signals to connect from one end to another.
- These signals are carried on airwaves, which must be sent at designated frequencies to avoid any kind of interference.
- The Union government owns all the publicly available assets within the geographical boundaries of the country, which also include
- With the expansion in the number of cell phone, wire line telephone and internet users, the need to provide more space for the signals arise from time to time.
- To sell these assets to companies willing to set up the required infrastructure to transport these waves from one end to another, the central government through the DoT auctions these airwaves.
- These airwaves are called spectrum, which is subdivided into bands which have varying frequencies.
- All these airwaves are sold for a certain period of time, after which their validity lapses, which is generally set at 20 years.
5G Spectrum
- About 5G Technology:
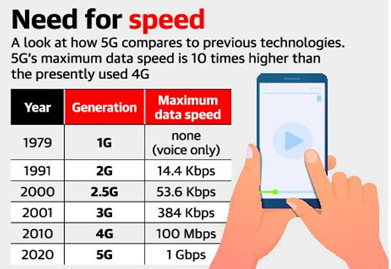
- It is the latest upgrade in the Long-Term Evolution (LTE) mobile broadband networks with reduced latency than 4G.
- 5G technologies offer an extremely low latency rate, the delay between the sending and receiving information.
- From 200 milliseconds for 4G, 5G brings it down to 1 millisecond (1ms).
- It works in three bands of the spectrum with their respective pros and cons.
- Low Band Spectrum:
- It shows great promise in terms of coverage and speed of internet and data exchange with a maximum speed limited to 100 Mbps (Megabits per second).
- Telcos can use and install it for commercial cellphone users who may not have specific demands for very high-speed internet.
- It may not be optimal for the specialised needs of the industry.
- Mid-Band Spectrum:
- It offers higher speeds compared to the low band but has limitations in terms of coverage area and penetration of signals.
- It may be used by industries and specialised factory units for building captive networks that can be molded into the needs of that particular industry.
- High-Band Spectrum:
- It offers the highest speed of all three bands, but has extremely limited coverage and signal penetration strength.
- Internet speeds have been tested to be as high as 20 Gbps (gigabits per second).
- Importance: Operators will use a combination of different spectrum bands to deliver 5G services, and it will play a critical role in determining the speed and range of coverage.
- Benefits of 5G Technology:
- Healthcare:Healthcare providers can create sensor networks to track patients and share information faster than ever before.
- Public Safety:A vast network and rapid response times mean that public works can respond to incidents and emergencies in seconds rather than minutes, and municipalities can react fast and with reduced costs.
- Autonomous Vehicles:5G will allow vehicles to communicate between them and with infrastructure on the road, improving safety and alerting drivers to travel conditions and performance information.
|
Regulating Body: Telecom Regulatory Authority of India (TRAI)
|
Global scenario
- More than governments, global telecom companies have started building 5G networks and rolling it out to their customers on a trial basis.
- In countries like the US, some companies have taken the lead when it comes to rolling out commercial 5G for their users.
- A South Korean company, which had started researching on 5G technology way back in 2011, has, on the other hand, take the lead when it comes to building the hardware for 5G networks for several companies.
Where does India stand in the 5G technology race?
- On par with the global players, India had, in 2018, planned to start 5G services as soon as possible, with an aim to capitalize on the better network speeds and strength that the technology promised.
- Indian private telecom players have been urging the DoT to lay out a clear road map of spectrum allocation and 5G frequency bands so that they would be able to plan the rollout of their services accordingly.
- One big hurdle, however, is the lack of flow of cash and adequate capital with some companies due to their AGR dues.
Benefits for India after auction of 5G services
- Revenue generation: The auction process will generate revenue for the government as well as make companies to involve in contributing for societal benefits.
- Less departmental burden: Work load of technological advancements in every field has made the departments full with less time for other developmental projects.
- Privatization of Infrastructure
- More Bidders availability
- More efficient services of 5G
- Better implementation: The implementation of 5G technologies will now be included to rural areas also with the help of private players.
Conclusion
The decision to auction spectrum by the government is determined by various factors- technological, regulatory as well as economic factors. It can be influenced by the prevailing policy conditions, advances in the technology, the conditions associated with auction and the price of the spectrum. The auction therefore can be graded successful or failure due to many attributes.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION: Q1) Discuss the concerns and challenges related to 5G technology. Where does India stand in the 5G technology race as compare to other global players? |

