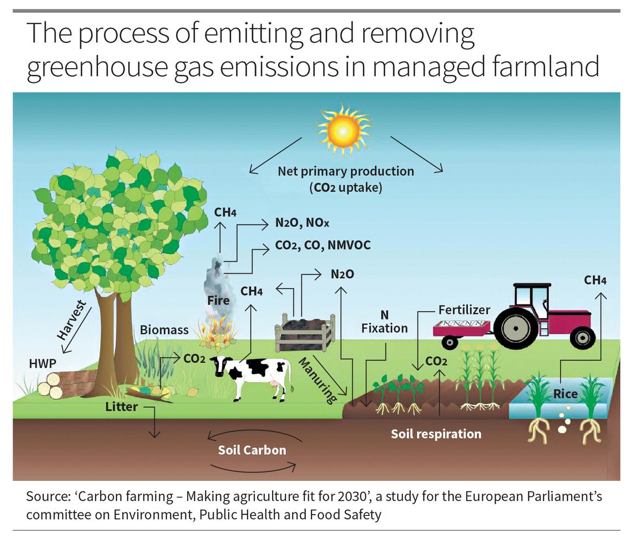
Context
Carbon farming, which integrates regenerative agricultural practices with carbon sequestration techniques, has gained attention due to its potential to address climate change while enhancing soil health and agricultural productivity.
1: Dimension- Significance of Carbon Farming
- Conservation Agriculture: Techniques like zero tillage, crop rotation, and cover cropping enhance soil health and minimize disturbance.
- Integrated Nutrient Management: Promotes soil fertility and reduces emissions using organic fertilizers and compost.
- Agro-ecology: Encourages crop diversification and intercropping for ecosystem resilience.
- Livestock Management: Strategies like rotational grazing and waste management reduce methane emissions and increase carbon storage.
2: Dimension- Challenges to Carbon Farming:
- Geographical Variation: Effectiveness depends on factors like soil type, water availability, and biodiversity.
- Water Scarcity: Hot and dry regions face challenges due to limited water resources, hindering plant growth and carbon sequestration.
- Financial Assistance: Small-scale farmers may lack resources to invest in sustainable practices, requiring financial support for adoption.
- Limited Awareness: Awareness about carbon farming needs to be increased among farmers and policymakers.
- Inadequate Policy Support and financial assistance: Policies need to incentivize and support carbon farming adoption and financial assistance are limited.
- Technological Barriers: Access to appropriate technologies is essential for effective implementation.
Fact Box:Carbon Farming Techniques:
Global Carbon Farming Initiatives:
|
UPSC PYQQ: What is/are the advantage/advantages of zero tillage in agriculture? (UPSC 2020)
Select the correct answer using the code given below:
Solution: (d) |