

The fourth industrial revolution is conceptualized as an upgrade on the third revolution and is marked by a fusion of technologies straddling the physical, digital and biological worlds. It will mark out as a new phase rather than a prolongation of the current revolution - velocity, scope, and systems impact and lead to the transformation of entire systems of production, management, and governance.
About
What is 'Fourth Industrial Revolution'?
The fourth industrial revolution is conceptualized as an upgrade on the third revolution and is marked by a fusion of technologies straddling the physical, digital and biological worlds. It will mark out as a new phase rather than a prolongation of the current revolution - velocity, scope, and systems impact and lead to the transformation of entire systems of production, management, and governance. In simple words, the new revolution can be said to be the advent of cyber-physical systems which, while being "reliant on the technologies and infrastructure of the third industrial revolution represent entirely new ways in which technology becomes embedded within societies and even our human bodies".
Background:
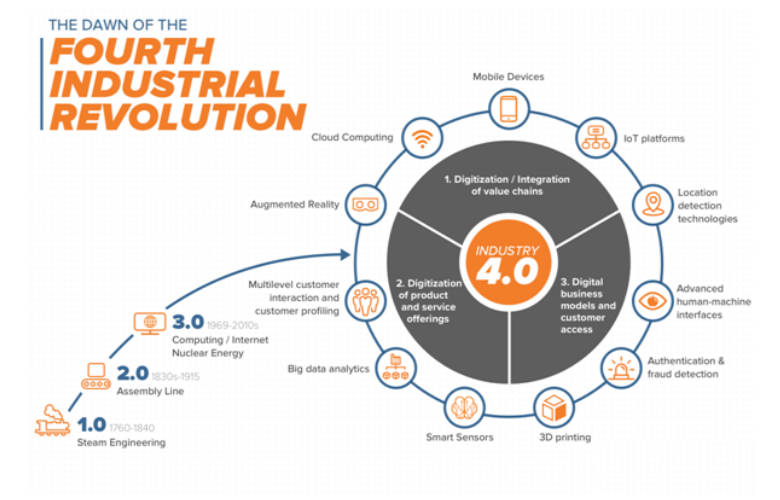
- The 1st Industrial Revolution which occurred in 18th century in Britain used water and steam power to mechanize production, harnessing of steam power and birth of modern factory.
- The 2nd Industrial Revolution, from the last 3rd of the 19th century to the outbreak of World War I, was powered by developments in electricity, transportation, chemicals, steel, and mass production and consumption.
- Now a 4th Industrial Revolution is building on the 3rd, the digital revolution that has been occurring since the middle of the last century. It is characterized by a fusion of technologies that is blurring the lines between the physical, digital, and biological spheres.
How will it be different from 3rd revolution?
There are 3 reasons why today's transformations represent not merely a prolongation of the 3rd Industrial Revolution but rather the arrival of a 4th and distinct one: velocity, scope, and systems impact. The speed of current breakthroughs has no historical precedent. When compared with previous industrial revolutions, the 4th is evolving at an exponential rather than a linear pace. Moreover, it is disrupting almost every industry in every country. And the breadth and depth of these changes herald the transformation of entire systems of production, management, and governance.
Impacts of fourth industrial revolution:
On Business:
The Technologies that underpin the 4th Industrial Revolution will have a major impact on businesses. On the supply side, many industries are seeing the introduction of new technologies that create entirely new ways of serving existing needs and significantly disrupt existing industry value chains. It will improve the quality, speed, or price at which value is delivered. It will also lead to major shifts on the demand side are as growing transparency, consumer engagement, and new patterns of consumer behaviour (increasingly built upon access to mobile networks and data) force companies to adapt the way they design, market, and deliver products and services.
It will enable development of technology-enabled platforms that combine both demand and supply to disrupt existing industry structures of sharing or on demand economy. These technology platforms will create entirely new ways of consuming goods and services in the process. It will lower the barriers for businesses and individuals to create wealth, altering the personal and professional environments of workers. The main effects that the 4th Industrial Revolution have on business are-on customer expectations, on product enhancement, on collaborative innovation, and on organizational forms.
On Government:
New technologies and platforms will increasingly enable citizens to engage with governments, voice their opinions, coordinate their efforts, and even circumvent the supervision of public authorities. Though, the governments will gain new technological powers to increase their control over populations, based on pervasive surveillance systems and the ability to control digital infrastructure. But they will increasingly face pressure to change their current approach to public engagement and policymaking.
On Security:
The 4th Industrial Revolution will profoundly impact the nature of national and international security, affecting both the probability and the nature of conflict. The advances in technology will create the potential to reduce the scale or impact of violence, through the development of new modes of protection, for example, or greater precision in targeting.
Impact on people:
The 4th Industrial Revolution will change not only what people do but also who they are. It will affect identity and all the issues associated with it: sense of privacy, notions of ownership, consumption patterns, the time people devote to work and leisure, and how they develop careers, cultivate skills, meet people, and nurture relationships. Constant connection may deprive people of one of life's most important assets: the time to pause, reflect, and engage in meaningful conversation.
Pros and cons of Fourth Industrial revolution:
- Positives:
- World Economic Forum report on FIR concludes that it will have an undeniable impact on job scenarios across the world disrupting erstwhile, well-established businesses, bringing sweeping changes to labour markets, and changing business models on the foundation of emerging economic theories.
- Fourth Industrial Revolution has the potential to raise global income levels and improve the quality of life for populations around the world.
- In the future, technological innovation will also lead to a supply-side miracle, with long-term gains in efficiency and productivity.
- Transportation and communication costs will drop, logistics and global supply chains will become more effective, and the cost of trade will diminish, all of which will open new markets and drive economic growth.
- Negatives:
- Revolution is likely to increase inequality in the world as the spread of machines increases markets and disrupts labour markets.
- Inequality represents the greatest societal concern associated with the Fourth Industrial Revolution.
- The largest beneficiaries of innovation tend to be the providers of intellectual and physical capital the innovators, shareholders, and investors which explains the rising gap in wealth between those dependent on capital versus labour.
- As automation substitutes for labour across the entire economy, the net displacement of workers by machines might exacerbate the gap between returns to capital and returns to labour.
- With this revolution, it is also possible that in the future, talent, more than capital, will represent the critical factor of production. This will give rise to a job market increasingly segregated into low-skill/low-pay and high-skill/high-pay segments, which in turn will lead to an increase in social tensions.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution will change not only what we do but also who we are. It will affect our identity and all the issues associated with it: our sense of privacy, our notions of ownership, our consumption patterns, the time we devote to work and leisure, and how we develop our careers, cultivate our skills, meet people, and nurture relationships.
India and fourth industrial revolution:
- Potential:
- India provides a potentially huge market access.
- There is the very appealing demographic dividend with Indian youth representing approximately 20% of the global workforce by 2020. With more than 50 per cent of its population is under the age of 27, India can play a pivotal role in shaping the global fourth Industrial revolution in a responsible, scalable and inclusive manner.
- There is a rising middle class
- India is expected to become the fifth largest consumer market in two decades. Within this context, any form of consumption, entrepreneurship, startup or industry, can be viewed as a scaling opportunity.
- The subcontinent has already taken steps to become an e-government. For example, the government has made efforts to enroll its citizens into a national database. Aadhaar is the world's largest biometrics database, with 1.2 billion Indian residents enrolled so far.
- India also wants to become an AI hub with the government recently announcing its National Programme on AI to encourage the development of AI-related technology in the country.
- India is also quickly rising up the ranks in terms of innovation. Last year, the country moved up five spots on the Global Innovation Index, ranking 57th out of 125 countries. In the category of ICT service exports, India was ranked first.
- India also has a robust start-up scene, which reportedly has more firms than anywhere else in the world except for the US and the United Kingdom (UK).
- With one of the youngest labour forces in the world, a sizeable technical aptitude, the second largest number of internet users on mobile devices and the second largest English speaking population, India is well positioned to enhance its global leadership in a post fourth industrial revolution era.
- With the right mix of accelerators - including regulatory frameworks, educational ecosystems and government incentives - India can lead the fourth industrial revolution, while simultaneously enhancing the quality, equity and sustainability of its own growth and development outcomes
- The enablers to actualize India’s sustainable transformation to fourth industrial revolution includes
- Creation of an enabling ecosystem through incubators and accelerators to develop and scale innovations in ‘Future Now’ Cleantech sectors like clean energy, climate-smart agriculture, circular economy, green buildings and e-mobility is critical from the Indian context, to achieve transformative goals.
- Proactive initiatives and policies to build on the positive aspects of the new industrial revolution and preventing further widening of the inequality gap are necessary. The Government of India, through its unique initiatives like Digital India, Startup India and Make in India Initiative is bolstering the opportunities for industry 4.0 and green entrepreneurs.
- Participation of relevant ministries (like MoEFCC, MNRE) and Government-led coalitions (like International Solar Alliance) must be leveraged to champion this on-going movement.
- World Economic Forum, in partnership with the Government of India has set up the Center for the Fourth Industrial Revolution India to design and pilot practical tools for specific technologies. Such platforms and coalitions must be leveraged to assess the feasibility and scale innovative business models
- Access to finance commensurate with maturity of the business model and beginning stage of the start-up lifecycle is extremely important to scale innovations. While Government-led initiatives like Start-Up Sangam will play a key role in crowding capital, private sector participation through grants, seed funding, equity capital and mainstream debt is necessary to scale innovations
- Corporates will have a key role in championing this on-going movement, leveraging the ART Model – Alliances, Relationships enabled through Technology.
- India is currently at a cusp of technovation revolution and the transition to a sustainable and inclusive growth trajectory will be accelerated by path-breaking innovations, enabling policies and availability of finance. These developments will lead to the emergence of ‘new-Gen’ business models, characterized by DICE – Design, Innovation and Creativity led Entrepreneurship to create social, environmental and economic positive impact.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
1. The fourth industrial revolution can not only disrupt labour market, but fundamentally alter them. Elaborate.
2. Examine the steps taken by government of India to address the challenges posed by the fourth industrial revolution.


