Recently Prime Minister Modi laid the Foundation Stones of City Gas Distribution (CGD) Projects in 65 Geographical Areas (GAs) in 129 Districts under the 9th CGD Bidding Round in New Delhi.
Issue
Context:
- Recently Prime Minister Modi laid the Foundation Stones of City Gas Distribution (CGD) Projects in 65 Geographical Areas (GAs) in 129 Districts under the 9th CGD Bidding Round in New Delhi.
- According to the Minister of Petroleum and Natural Gas, the Government is working to move India towards a Gas-based economy.
Background
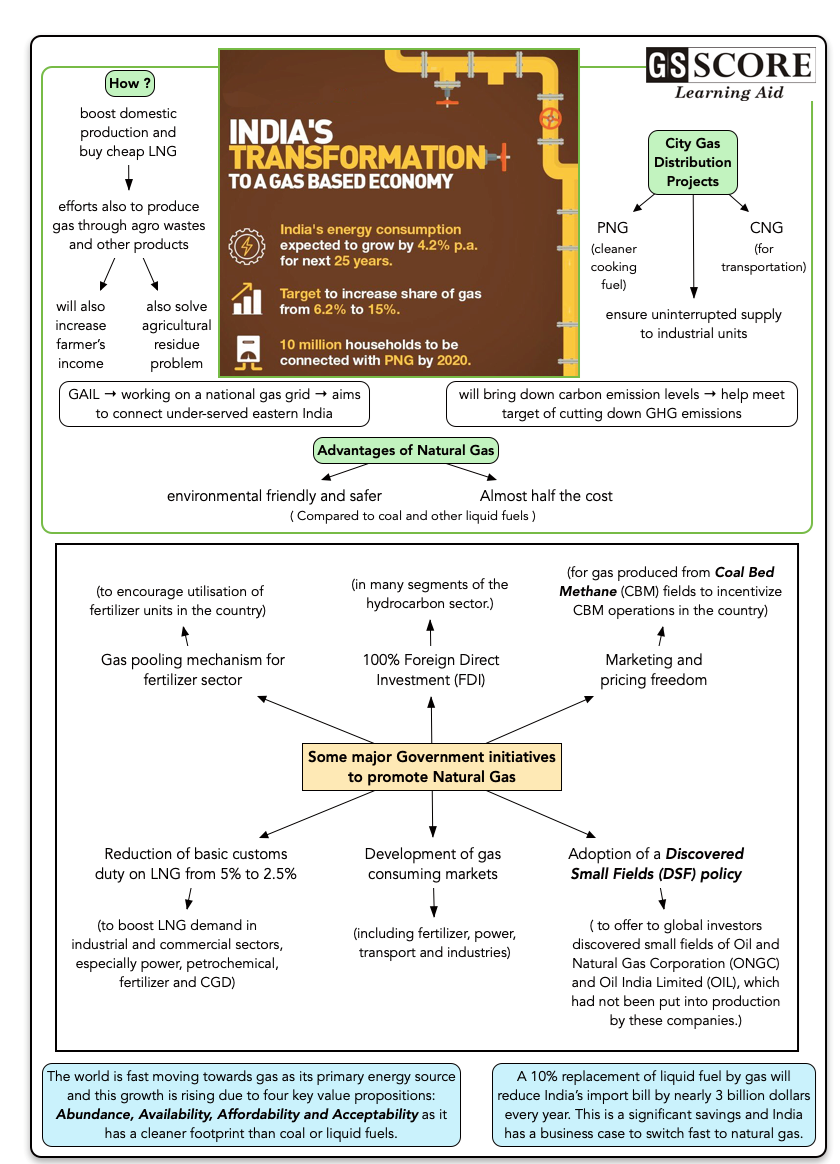
- Presently, the share of gas in the country’s energy mix is just over 6% and the aim is to reach the 15%, while the world average is 24%.
- India aims to bring down its carbon emission level and number of initiatives has been taken in this direction such as LED bulbs, BS VI fuel, Bio-energy, International Solar Alliance, Pradhan Mantri Ujjawala Yojana, and providing clean piped gas supply to more cities.
- The Government is also focusing on enhancing the LNG terminal capacity, renegotiating Indo-Qatar Gas deal, and positive Indo-US engagement in this direction.
- Efforts are not only being made to increase the use and supply of Gas, but also to produce gas through agro-wastes and other products and including the same into the CGD network.
- Government of India has put thrust to promote the usage of environment friendly clean fuel i.e. natural gas as a fuel/feedstock across the country to move towards a gas based economy.
- Accordingly, development of CGD networks has been focused to increase the availability of cleaner cooking fuel (i.e. PNG) and transportation fuel (i.e. CNG) to Indian citizens. The expansion of CGD network will also benefit to industrial and commercial units by ensuring the uninterrupted supply of natural gas.
About
Gas Based Economy
- The Government of India wants to make India a gas-based economy ‘by boosting domestic production and buying cheap LNG’.
- India has set a target to raise the share of gas in its primary energy mix to 15% by 2022. Achieving this would mean that annual gas consumption would increase from about 50 bcm to above 200 bcm in the future.
- Keeping the pursuit of gas-based economy in mind, India has invested heavily in creating LNG import facilities, CGD infrastructure and pipelines to supply the gas across the country to cater to supply of piped cooking gas and for powering vehicles.
Analysis
Significance of a Gas based economy
- There is immense scope for use of gas in the Indian economy in a range of areas- from generating power to producing quality steel.
- Enhancing the share of gas would help India meet its target of cutting down greenhouse gas emission from petrol, diesel and kerosene under the global climate deal of 2015 commitment.
- A gas based-economy would have a positive impact on the environment, when automobiles would be run on CNG and industries would get uninterrupted gas supplies.
- An economically-growing India, the third largest energy consumer and fourth biggest LNG importer in the world, is dependent on imports to meet 45 per cent of its gas needs.
- The availability of gas will be crucial for the government plans to provide free cooking gas connections to 80 million poor families under the Pradhan Mantri Ujjwala Yojana.
- Apart from this, India’s gas demand is expected to be driven by requirements of the fertiliser, power and steel sectors.
- Gas Authority of India Limited (GAIL) is also working on a national gas grid that is aimed at connecting the under-served eastern part of the country to the rest of the nation and LNG will play a key role here.
- To promote clean energy, 5,000 compressed bio-gas plants would be set up in five years to convert agricultural waste into bio-CNG. This would not only address the problem of agricultural residue but also increase farmers' income.
- Securing energy supplies is also required to ensure country’s military security.
Why Natural Gas?
- It is a superior fuel as compared with coal and other liquid fuels being an environment friendly, safer and cheaper fuel.
- It is supplied through pipelines. There is no need to store cylinders in the kitchen and thus saves space.
- As per WHO database released in May 2018, India has 14 out of 15 world’s most polluted cities in terms of PM 2.5 concentration. Large number of industries also consumes polluting fuels like pet coke and furnace oil which emit polluting CO2. Some of the high courts have recently ordered for banning use of pet coke in states within their jurisdiction.
- Natural Gas (as CNG) is cheaper by 60% as compared with petrol and 45 % w.r.t. Diesel. Similarly, Natural Gas (as PNG) is cheaper by 40 % as compared with market price LPG and price of PNG almost matches with that of subsidised LPG (based on prices in Delhi). An auto-rickshaw owner can save Rs. 7000-8000 on his monthly fuel bill by conversion from petrol to CNG. Thus, even on cost front as well, natural gas is preferable to petrol, diesel and LPG.
- India made a commitment in COP21 Paris Convention in December 2015 that by 2030, it would reduce carbon emission by 33% of 2005 levels. Natural gas, as domestic kitchen fuel, as fuel for transport sector as well as a fuel for industries and commercial units, can play a significant role in reducing carbon emission.
Government initiatives to promote Natural Gas
The GoI has adopted a systematic approach to focus on all aspects of the gas sector:
- Development of gas sources either through domestic gas exploration & production (E&P) activities or through building up facilities to import natural gas in the form of LNG.
- Development of adequate gas pipeline infrastructure including nationwide gas grid and CGD network.
- Development of gas consuming markets including fertilizer, power, transport and industries
Some important specific initiatives taken to enhance the domestic natural gas production, expand the gas pipelines and secondary infrastructure and develop the gas consuming markets are as under:
- 100% Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) in many segments of the hydrocarbon sector.
- Notification of a new Hydrocarbon and Exploration Licensing Policy (HELP) in March 2016.
- Adoption of a Discovered Small Fields (DSF) policy to offer to global investors discovered small fields of Oil and Natural Gas Corporation (ONGC) and Oil India Limited (OIL), which had not been put into production by these companies.
- Linkage of gas prices to the market/important hub prices under the New Domestic Natural Gas Price Guidelines of 2014.
- Marketing and pricing freedom for new gas production from Deep-water, Ultra Deep-water and High Pressure-High Temperature areas, subject to certain conditions.
- Marketing and pricing freedom for gas produced from Coal Bed Methane (CBM) fields to incentivize CBM operations in the country.
- A capital grant of 40% for development of 2,650 km-long Jagdishpur-Haldia & Bokaro-Dhamra natural gas pipeline to ensure supply of natural gas to eastern India.
- Reduction of basic customs duty on LNG from 5% to 2.5% in the 2017 budget to boost LNG demand in industrial and commercial sectors, especially power, petrochemical, fertilizer and CGD, and also help in reviving stranded capacity of power and fertilizers plants.
- Gas pooling mechanism for fertilizer sector to encourage utilisation of fertilizer units in the country.
- Priority for allocation of domestic gas accorded to Piped Natural Gas (PNG)/Compressed Natural Gas (CNG) segments to meet 100% of their demand and faster roll out of PNG connections and CNG stations to promote the use of natural gas in the transport sector, households and small industries.
Conclusion
- The world is fast moving towards gas as its primary energy source and this growth is rising due to four key value propositions: Abundance, Availability, Affordability and Acceptability as it has a cleaner footprint than coal or liquid fuels.
- A 10% replacement of liquid fuel by gas will reduce India’s import bill by nearly 3 billion dollars every year. This is a significant savings and India has a business case to switch fast to natural gas.
Learning Aid
Practice question:
The Government is working to move India towards a Gas-based economy. What is the significance of a gas based economy? Discuss the initiatives taken by the Government in this regard so far.