

- Recently, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) organised a conference on “Cyber Security – Challenges and Innovations.”
- The conference focused on the current trends, need and future requirements of innovation in the field of cyber security for a secured cyber space and will help in understanding the challenges and the way ahead for the country through home-grown technological research and innovation.
Issue
Context
- Recently, Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) organised a conference on “Cyber Security – Challenges and Innovations.”
- The conference focused on the current trends, need and future requirements of innovation in the field of cyber security for a secured cyber space and will help in understanding the challenges and the way ahead for the country through home-grown technological research and innovation.
Background
- In the twentieth century, India saw an impetus in Information Technology (IT) and an enormous growth in e-commerce. Both these sectors ride on and reside in cyberspace involving electronic transactions, software, services, devices and networks which are highly susceptible to cyber-crimes. Hence to ensure its safety, cyber-security has become one of the most compelling priorities for the country.
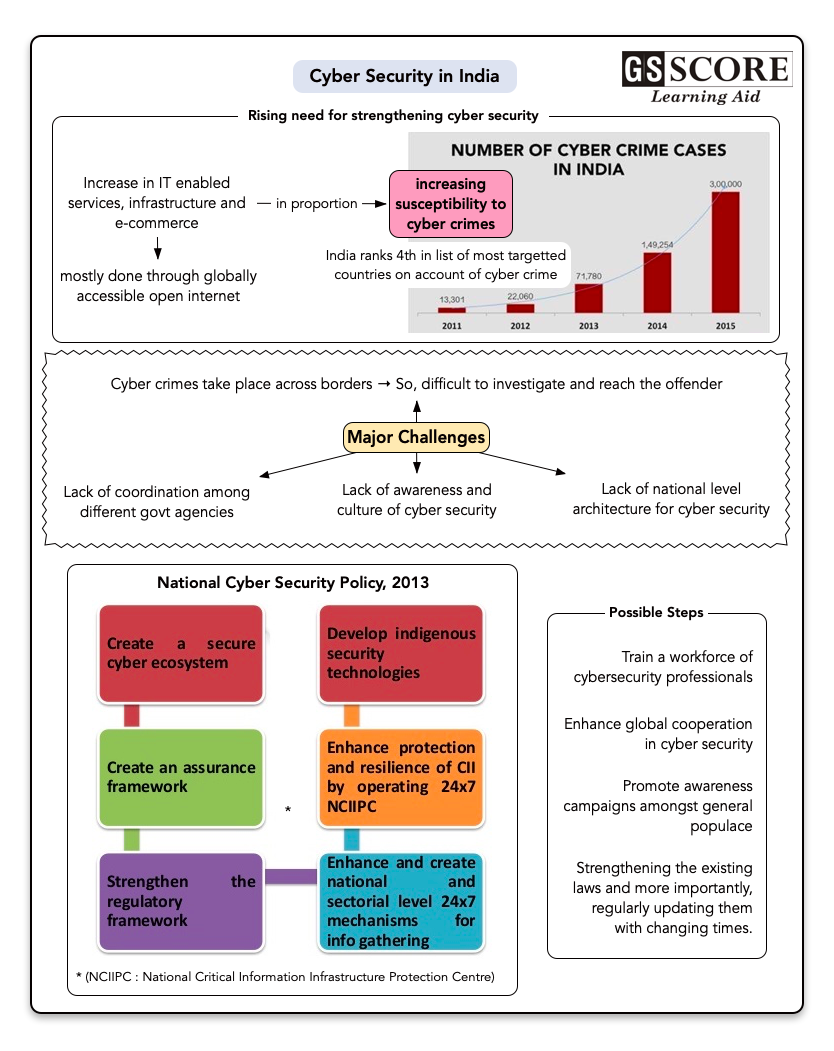
- Out of the top 10 most targeted countries by cyber attackers in 2017, India ranks fourth and cyber-security defenders are facing a lot of threats from these cyber criminals.
- A report, prepared by the Indian Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) analysing cyber-attacks from April-June 2018 said that the maximum numbers of cyber-attacks on official Indian websites are from China, US and Russia. It has also flagged the possibility of malicious actors from Pakistan using German and Canadian cyberspace for intruding into Indian cyberspace and carrying out malicious activities.

- CERT-In is the nodal agency which deals with cyber security threats like hacking and phishing. It collects analyses and disseminates information on “cyber incidents,” and also issues alerts on “cyber security incidents.”
About
Cyber Space
- It is a domain characterized by the use of electronics and the electromagnetic spectrum to store, modify, and exchange data via networked systems and associated physical infrastructures. It is a term associated with application of the Internet worldwide.
- Unlike the physical world that is limited by geographical boundaries in space — land, sea, river waters, and air — cyberspace is continuing to expand and has no geographical limitation. A nation’s cyberspace is part of the global cyberspace; it cannot be isolated to define its boundaries since cyberspace is borderless. This is what makes cyberspace so unique.
Cyber Security
- It is a broad spectrum phrase and relates to preventing any form of unauthorized and malafide access to a personal computer, laptop, smartphone or a major network like the national banking system or the railways network or a national information technology asset that also has military implications. Whether it is for the email, social networking, net-banking or mobile banking, almost everyone is dependent on the internet and hence potentially vulnerable.
- It is, thus, a complex issue that cuts across multiple domains and calls for multi-dimensional, multi-layered initiatives and responses. It has proved a challenge for governments all around the world. The task is made difficult by the inchoate and diffuse nature of the threats and the inability to frame an adequate response in the absence of tangible perpetrators.
Analysis
Need For Cyber Security
- To ensure critical infrastructure systems do not collapse under any situation.
- To ensure business continuity.
- To ensure disaster recovery plans are tested regularly and upgraded.
For the success of government initiatives like Digital India, Make in India and Smart Cities.
India’s Cyber Security Challenges
- With India carving a niche for itself in the IT sector, dependence on technology is also increasing. With Indians using the internet for all their needs, ranging from shopping to banking, studying to storing data, cyber-crimes have also increased in proportion to usage.
- Cyber space crimes can be diverse, multi-domain, multi-location, multilingual and multicultural and therefore it is difficult to investigate the crime and reach the offender.
- Threats from online radicalization have been on the rise.
- With the advent of IT revolution and growing penetration of the Internet and smartphones, India has recently emerged as one of the favourite countries among cyber criminals.
- The major security threat lies to the critical infrastructure of the nation wherein the attackers can gain control of vital systems such as nuclear power plants, financial, transportation or health systems that can lead to dire consequences.
- Despite having a National Cyber Security Policy in place, risks to our critical infrastructure remain.
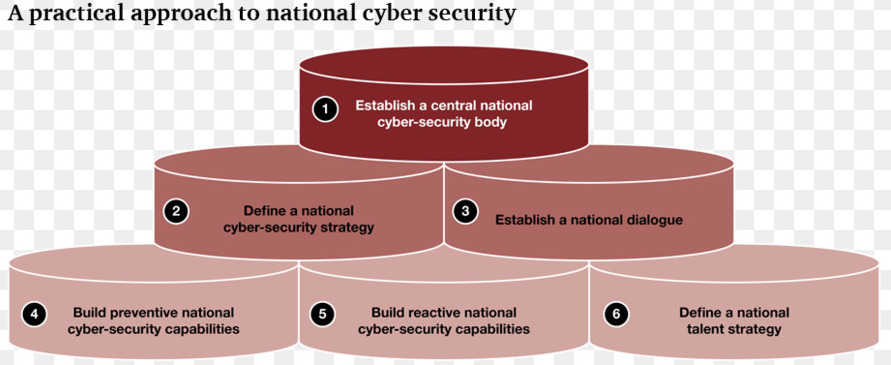
- There is lack of coordination among different government agencies. So, in spite of instituting a National Cyber Security Coordinator in 2014, the tussle between the National Technical Research Organisation (the nodal agency for cyber security) and the Ministry of Communications and Information Technology impede coordination.
- Lack of National level architecture for Cyber-security - Critical infrastructure is owned by private sector, and the armed forces have their own fire-fighting agencies. However there is no national security architecture that unifies the efforts of all these agencies to be able to assess the nature of any threat and tackle them effectively. The Prime Minister’s Office has created a position towards this cause but there is a long way to go before India has the necessary structure in place.
- Lack of uniformity in devices used for internet access. With varying income groups in India, not everyone can afford expensive phones. In the US, Apple has over 44% market share. However, in India the iPhones with their higher security norms are used by less than 1% of mobile users.
- Lack of trained and qualified manpower to implement the counter measures.
- Lack of awareness and the culture of cyber security at individual as well as institutional levels. As there is no National regulatory policy in place for cyber-security there is a lack of awareness at both company level as well as individual level. Domestic netizens can protect and be protected from the cyber-attacks only if there is a guided and supervised legal framework.
National Cyber Security Policy, 2013
With primary aim to monitor and protect information and strengthen defences from cyber-attacks, the National Cyber Security Policy, 2013 was released by the Government of India.
It aims to achieve through:
- Creating workforce of 5, 00,000 professionals skilled in next five years through capacity building, skill development and training.
- Developing suitable indigenous technologies in ICT sector.
- Providing fiscal benefits to corporate sector for adoption of cyber security.
- Safeguarding the privacy of citizens' data.
- Enabling effective prevention, detection and investigation of cybercrimes.
- Creating and promote the culture of cyber security.
- Enhancing global cooperation in cyber security.
Important features of the policy are:
- A national and sectoral 24X7 mechanism has been envisaged to deal with cyber threats through National Critical Information Infrastructure Protection Centre (NCIIPC).
- Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT-In) has been designated to act as a nodal agency for coordination of crisis management efforts. CERT-In will also act as umbrella organization for coordination actions and operationalization of sectoral CERTs.
- A mechanism is proposed to be evolved for obtaining strategic information regarding threats to information and communication technology (ICT) infrastructure, creating scenarios of response, resolution and crisis management through effective, predictive, prevention, response and recovery action.
Way Forward
- There is a need to stress upon the areas of strategic importance including Artificial Intelligence, Robotics, Virtual reality & augmented reality, Internet of things (IOT) which would be the backbone of the country in future.
- There is also a need to sensitize the common citizens about the dangers of cyber threats. CERT-In should engage academic institutions and follow an aggressive strategy.
- There should be increased partnership of government and private sector since the majority of the country’s cyber resources are controlled by entities outside of the government.
- Agreements relating to cyber security should be given the same importance as other conventional agreements.
- More investment in this field in terms of finance, skill training and manpower is required. There is a need to increase the number of cyber security experts and IT security auditors, in which the nation is facing a crisis at present.
- Indian agencies working after cyber security should also keep a close vigil on the developments in the IT sector of our potential adversaries.
- Explicit privacy laws in the country must be enacted addressing the concerns regarding encroachment on citizens' privacy and civil-liberties.
- India’s legal system needs to be upgraded towards enhanced cyber laws as its present form is still dwelling on the IT Act, 2000 (IT Amendment Bill 2006 and IT Amendment Bill 2008) which are unable to cover the holistic issues in a field which is changing every day.
Learning Aid
Question
“Cyber security poses bigger threat than any other spectrum of technology.” Examine the given statement in light of increasing India’s cyber security challenges.


