

Context
Recently, WHO’ Science Council has released a report “Accelerating access to genomics for global health” advocating for passing on Genomic Technologies to developing countries.
About
About the Report
- The report was published by the World Health Organization’s Science Council.
- The report followed WHO’s 10-year strategy for genomic surveillance of pathogens.
- Genomic surveillance has played a crucial role in the global COVID-19 response.
|
What is WHO Science Council?
|
What are the Highlights WHO's Report?
- Access to genomic technologies needs to be expanded, especially for Low- and Middle-Income Countries (LMIC).
- It is not ethically or scientifically justifiablefor countries with fewer resources to gain late access to such technologies.
- Shortfalls in financing, laboratory infrastructure, materials and highly trained personnel need to be addressedto expand access to genomic technologies.
- The benefits will not be fully realizedunless deployed worldwide.
- Only through equity can science reach its full potential impact and improve health for everyone, everywhere.
- The report recommended addressing four themes:
- Advocacy, implementation, collaboration and associated ethical, legal and social issues.
- The report also recommended WHO create a Genomics Committeeto take forward the recommendations and monitor their applications.
|
TOOLS: There are several tools to make genomic technologies more affordable:
|
|
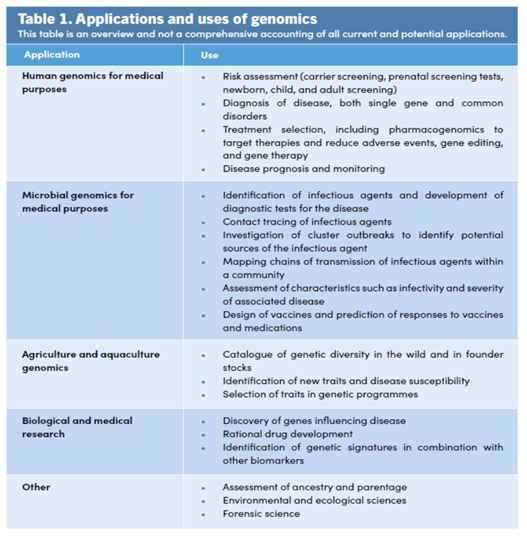
What is Genomics?
|
RECOMMENDATIONS OF WHO REPORT:
|
RECOMMENDATIONS OF REPORT |
HOW WHO CAN CONTRIBUTE |
|
Promote the adoption or expanded use of genomics in all Member States through advocacy by many parties. |
WHO should use its leadership role in global public health to advocate for the expanded use of genomics in its Member States.
WHO should promote affordable access to genomic technology globally so that all Member States, especially Low and Middle-Income Countries (LMICs), can adopt and expand the use of genomics for better health and other benefits. |
|
Identify and overcome the practical issues that impede the implementation of genomics through local planning, financing, training of essential personnel, and the provision of instruments, materials, and computational infrastructure. |
WHO should provide guidance to Member States on best practices for implementation of national or regional genomic programmes.
Member States should establish national programmes for building or expanding genomic capabilities or join a regional programme. |
|
Foster commitments to collaborative activities to promote all aspects of national and regional programmes that advance genomics in the Member States. |
WHO should promote international collaborations on genomics by strengthening effective existing collaborative arrangements and by helping form new ones for specific needs.
Industry, academia, and civil society should collaborate on the use of genomics to help solve important health problems, especially those prevalent in LMICs. |
|
Promote ethical, legal, and equitable use and responsible sharing of information obtained with genomic methods through effective oversight and national and international rules and standards in the practice of genomics. |
WHO’sGenomics Committee should be the custodian of guidance on how to deal with the ethical and social ramifications of genomics, including the global governance of genomic information.
Organizations in Member States, especially funding agencies, academic institutions, and governmental units should be attentive to ELSIs and to efforts being made by WHO and other international bodies to develop solutions to outstanding issues related to genomic ELSIs. |


