

Context
At the beginning of the pandemic, vaccine companies stated that they would make sure low-income countries will have the same access to the vaccine as the rest of the world. A massive global disparity in the allocation of available vaccines is still evident today.
Background
What is a vaccine patent?
- A patent gives the vaccine manufacturers exclusive rights to prevent others from manufacturing, using, offering for selling or importing the shot/vaccine they develop.
What is bioethics?
- Bioethics is concerned with the questions related to the ethical implicationsofbiological research, and the biological andmedical applications of research.
Four commonly accepted principles of Bioethics are:
-
- Principle of respect for autonomy,
- Principle of nonmaleficence,
- Principle of beneficence, and
- Principle of justice.
- Issues like freedom of research, access to health care and distribution of health resources, and equitable access to the outcomes of biological researchare closely related to Bioethics.
What is intellectual property protection?
- Intellectual property refers to those legal rights, arising from any intellectual activity in the industrial, scientific, literary and artistic fields.
- IP systems provide safeguards to specific well-defined subject matter by giving limited entitlements to the right holders to exclude others from certain uses of the protected material. But an IP right does not give its holder the entitlement to use or market a product.
The mechanism for Waivers under WTO Agreements
- The Marrakesh Agreement, which had led to the establishment of WTO provides that a waiver under WTO treaties, such as TRIPS, can be only be decided at the WTO Ministerial Conference.
- The waiver must contain a justification based on the exceptional circumstances. Waivers that are longer than one year will get reviewed by the Ministerial Conference onannual basis until itgets terminated.
Key points:
- The 1995 agreement on Trade-Related Aspects of Intellectual Property Rights (TRIPS) asks the ratifying countries to adopt the standard of intellectual property rights to protect creators and promote innovation.
- South Africa and India have proposed a waiver from the application of certain provisions of the TRIPS Agreement (waiving IP rights like patents, copyright, and trademarks) for prevention, containment or treatment of Covid-19.
- If the proposal for waiver is granted or approved, WTO member countries will not be under any obligation by the law, for a temporary period, to either grant or enforce patents and other IP-related rights to Covid-19 medications, vaccines, and other related treatments.
- This will provide safeguard to the measures adopted by countries to vaccinate their populations from claims of breach under WTO law.
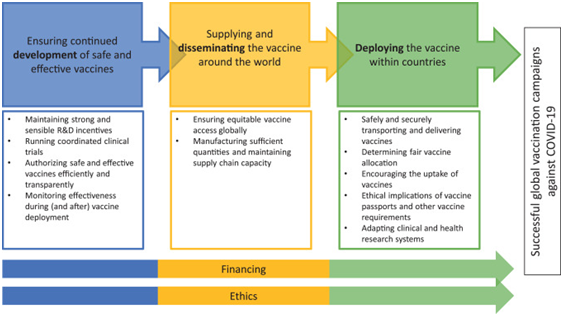
Analysis
- At the beginning itself, the wealthy countries such as the U.S., Canada, and others figured out the severity of COVID-19, as a result, they proactively engaged in bilateral agreementswith the vaccines producing companies. This ensured that they will be standing in the front of the line well even before the vaccines were out of the production units.
- The biggest problem is that vaccine manufacturing, R&Dtakes place in a concentrated group of high-income countries. Companies that arebased in these countries, which also happen to be the main IP holders, have sold the bulk of vaccine doses to their own governments, and to governments of other high-income nations which are able to buy it.
- Efforts to ensure vaccines for poorer nations, such as pledges to COVAX, came to existence only after the wealthy countries had secured more than enough for them. As a result, the robust vaccine distribution agreements (COVAX) that came were too little and too late.
Vaccine-divide and its Ethical acceptability:
- The pharmaceutical companies putting in years of R&D aresupported by high-income countries. With a tunnelled or self-centric approach these countries have the exclusive right to receive their products first.
- If we look at the U.S. which has already vaccinated most citizens is now planning to vaccinate its teenagers, who pose a much lower risk from COVID-19. At the same time, most countries don’t even have enough vaccines to protect their frontline workers and their vulnerable elderly populations. To add more, these countries often lack robust health care systems. There exists a moral imperative for equitable vaccine distribution among everyone.
- Ethical allocation of health care resources is important for the principle of justice.The principle of justice talks about the moral-obligation to act on the basis of fair judgement between available options. It is related to fairness, equality and entitlement.
Supporters of a patent waiver make the following argument:
- Vaccine patent waivers shall allow other countries to produce generic copies of vaccines and this will result in an increase in the global availability of vaccines.
- Increasing the global supply would give developing nations access to vaccines.
- Increasing vaccine access would save lives and decrease the prevalence of future Covid variants, which could prolong the pandemic.
- By looking at this, it appears that maintaining patents violates the principle of beneficence,by knowingly refusing to help countries in the times of need.
- It also violates the principle of non-maleficence, avoiding harm to others, as patents can demotivate the innovators from other countries from developing a novel vaccine due to the fear of copyright suits.
- The sole aim is to reduce the barriers to countries producing their own vaccines, particularly for low-income countries.
Precedents for patent waivers:
- In 2001, the “Doha Declaration on TRIPS and Public Health” eliminated patents on drugs for HIV, which resulted in cost-effective production.
- In the 1980s similar thing happened with the hepatitis-B vaccines. By handing over the formulation/procedure for then existing vaccines, other companies started producing their own versions.
- Doing away with IP (Intellectual property) protections could also free innovators across the globe to develop new vaccines without worrying about copyright infringement issues.
Concerns:
The method of using a patent waiver to increase the global supply is debatable.
- Patent waivers are not enough: Critics argue that the waiver would not result in an immediate increase in supply, as establishing production facilities for a new type of vaccine would take months and would ultimately require further assistance from companies in addition to the waiver.
- Jeopardizing the supply chains: The waivers have the potential of jeopardizing the existing supply chains. The Pfizer-BioNTech vaccine, for example, requires 280 components from 86 suppliers in 19 countries. This competition for the raw material could possibly slow down the net production.
- Setback for innovation: A waiver would discourage future innovation. The mRNA technology utilized by the Pfizer-BioNTech and Moderna vaccines is only possible due to the years of R&D from the public and private sectors.
- Disincentivise Pharmaceutical Companies: With no profit incentive to create new vaccines, we may see investments in the industry drop. This could result in a decline in new technologies, leaving humanity underprepared for the next pandemic.
- Vaccine Quality may get Compromised: Waiving of patents might result in losing control over the safety and quality standards for vaccine manufacturing.
It's easy to get caught in the debate of a patent waiver, as there are strong arguments for both sides. What remains relevant is that the issues of:
- justice (equitable distribution)
- beneficence (helping other countries)and
- non-maleficence (avoiding harm to other countries)
Significance for India:
- Help in increasing the vaccine production: The bulk of the vaccine doses produced in India are taken up by foreign countries which are paying more for the doses. This move can in making the vaccines more affordable and scaling up their production to meet the demand.
- Preparation for the Third Wave: Indian authorities have stated that the third wave of the pandemic is possible. Addressing shortages of vaccines and making them affordable could be the best way to prepare for the third wave.
Conclusion:
Every nation should have the right to make its own vaccines during the times of pandemics. This principle is pushing the campaign to temporarily waive intellectual property (IP) protection on coronavirus vaccines.
At the same time waiving of the IP protections alone will not do enough to increase the availability of vaccines across the globe. Waiving patent protections is not to be mistaken as apanacea.The countries must work together to increase their manufacturing capabilities and provide a boost to the global supply of vaccines.
It’s important for the manufacturers, the government and the various stakeholders to address the concerns of patent holders, to make sure that the global vaccination drive is not compromised in any way. It is of immense importance that we need to be on the right side when the history of the pandemic comes to be written.


