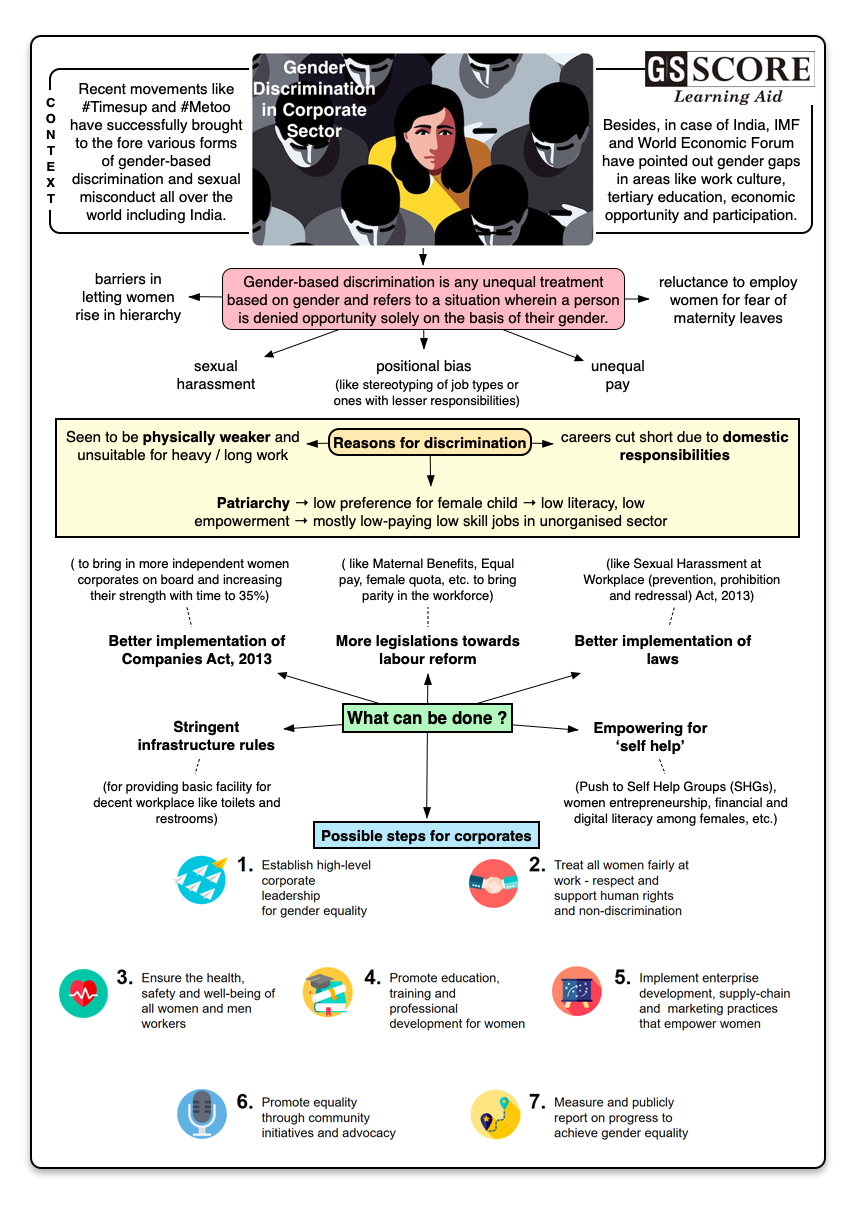
2018 has been about the women-led movements like #Timesup and #Metoo calling out on various forms of gender-based discrimination and sexual misconduct, respectively. The persistent gender pay-gap is one of the harsh realities of the 21st century and has been a grave concern worldwide for over a century now. Although industrialised nations have
Issue
Context:
2018 has been about the women-led movements like #Timesup and #Metoo calling out on various forms of gender-based discrimination and sexual misconduct, respectively. The persistent gender pay-gap is one of the harsh realities of the 21st century and has been a grave concern worldwide for over a century now. Although industrialised nations have this problem too, but, in case of countries like India, the gender wage disparity is far more worrisome.
Background:
Data on gender disparity:
2018 began with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) nudging India to ensure gender parity for better GDP growth (27% increase) and ended with the World Economic Forum’s (WEF) annual Gender Gap Index (GGI) pointing out the areas India needs to improve on. India had a rank of 108th on the latter with some areas of improvement like wage equality for similar work and closing of tertiary education gender gap.
The WEF measures Gender gap across four key pillars - economic opportunity, political empowerment, educational attainment, and health and survival. India ranks higher (rank 15) than the USA and the UK on the parameter of political empowerment but much lower (142nd among 149) on the parameter of economic opportunity and participation.
About:
Gender based discrimination in the corporate sector:
Gender-based discrimination is any unequal treatment based on gender and refers to a situation wherein a person is denied opportunity solely on the basis of their gender.
Women population constitutes almost half (48.18%) of the country’s population. Women play a very important role in country’s development yet the women population in India is characterized by low literacy rate (65.46%) and female labour participation rate (FLPR) of 25.51%. Studies, also, show that only two-thirds of women graduates are employed. A very few companies have women at the helm and even fewer women-led start-ups are being promoted and funded.
Large majority of women across the spectrum have started speaking out against the discrimination including the wage pay-gaps and demanding equality, including the leading actresses from both Hollywood and Bollywood.
Forms of gender-based discrimination:
Direct
- Unequal pay: It is very common form of discrimination, wages earned by women are generally lesser than their male counterparts.
- Glass ceilings: It’s an invisible barrier to keep the females from rising beyond a certain level in a hierarchy. It is mostly concerned with high-achieving women in the corporate sector.
- Diminished responsibilities: The sex differences are exaggerated to treat men and differently as the latter are given jobs with less responsibility like house-keeping, organising events, etc. whereas men are entrusted with leadership roles.
- Positional bias: Women are stereotypically considered for the posts of secretaries, HR (human relations), receptionist, etc.
- Sexual harassment: Women are also victim of various forms of sexual harassment at workplace affecting their work productivity and is a grave safety concern.
- Restrooms: Workplaces, especially in unorganized sector (e.g. Salt farming) do not have adequate facilities of restrooms subjecting women workers to undergo long work-hours without relieving themselves impairing their health.
- Victimization: When the prejudiced or biased treatment translates into victimization of the women workers.
- Terminations: There are cases of females being dismissed on account of speaking against sexual harassment or for asking for equality even in companies like Wipro. Also, females are being terminated on account of taking maternity leaves as well.
Indirect
- Interview questions: Women candidates are often put to questioning in terms of their work commitment due to their familial responsibilities and the choices they make in their personal lives which male candidates aren’t asked about.
- Conversations: Due to the deeply seated discriminating attitude towards women, they are talked to differently than their male counterparts.
- Outdated views: There are outdated views regarding the dressing, working, and how they must carry themselves, etc., which affect their productivity.
Other issues:
Lack of proper grievance redressal mechanism for female workers to register their complaints and get them redressed properly. Often, there are biased enquiries and unfair and wrongful dismissal of women who speak up against the discrimination.
In India, despite the law being in place for appointing an Internal Complaints Committee under the Women at Workplace (prevention, prohibition and redressal) Act, 2013, there are many companies without such a committee in place; who have it, are in a dysfunctional state.
Analysis
Reasons for the discrimination:
General factors:
- Most of the women (about 94%) work in unorganized sector where the wages tend to be very low.
- Lack of knowledge, awareness and illiteracy among the rural women who make the majority of the female workforce. Due to these reasons they’re confined to low-paying low-skilled jobs.
- Physically women are considered weaker than male and seen as unsuitable for longer work hours resulting in their reduced wage rate.
- Male workers improve their productivity by undergoing on-job trainings; women due to familial priorities like child care, are unable to do so.
- Women’s careers are cut-short due to the domestic responsibilities which fall upon their shoulders much more than men.
Societal factors:
- Patriarchal mindset and deep-seated patriarchy which seeks to confine women to the domestic sphere and the four walls of the household only.
- Prejudice and stereotypical attitude towards women by not considering them as equals which leads to biases against women in various areas like work assessment, job assignment, etc.
- Socialisation process which has entrenched the patriarchy deeply into the minds of people including the women.
- Seeing women as an object of male satisfaction rather than an equal participant in the economy.
- Seeking to maintain the age-old gendered power roles in the society which favour the males over females.
Other factors:
Religion, history, media, socialisation process, etc. are also responsible for perpetuation of discriminating mindset against women.
Ethical issue with discrimination:
Discrimination is against the basic human law of equality and humanity which seeks to treat a fellow human as inferior and second-class citizens .The most fundamental moral principle of civilised societies i.e. equality, which forms the basis of Article 1 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR).
Gender-based discrimination is a serious form of injustice and is based on ill-founded logic which have no authentic proof, whatsoever, and is largely an attitudinal issue.
Widespread discrimination can lead to intolerance and conflict in the society. Discrimination at workplace results in breeding of ill feelings at work, and reduced productivity.
Factors which make women better suited to the leadership roles:
Studies have shown that women have more patience and high emotional quotient so they are well-suited for the leadership role as they are able to better communicate and handle the work-relations. Women are also good at management and have better sense of ethics.
There are a number of successful women corporate leaders like Ela Bhatt, Indira Nooyi, Arundhati Roy, etc. who have time and again proved the naysayers wrong when it comes to proving the mettle of women-power.
How to improve the situation?
Policy intervention:
- Better implementation of Companies Act, 2013 to bring in more independent women corporates on board and increasing their strength with time to 35%.
- Better implementation of laws like Sexual Harassment at Workplace (prevention, prohibition and redressal) Act, 2013 for maintaining a safe environment for women to work in.
- More legislations to bring parity in the workforce such as labour reform, Maternal Benefits, Equal pay, female quota, etc.
- Push to Self Help Groups (SHGs), women entrepreneurship, financial and digital literacy among females, etc. to give them decision-making power and working towards women empowerment.
- Stringent infrastructure rules for providing basic facility for decent workplace like toilets and restrooms.
By Challenging social attitude:
The attitudinal issue associated with patriarchy can only be tackled with the socialisation process in which education plays a major role. Education increases the awareness among the population regarding their rights and gives them opportunity for becoming economically independent which increases their status in society, their confidence, and gives them voice. For example, in urban areas women are getting education and thus are becoming more and more aware of their rights and thus the disparity has, somehow, shown a declining trend. But the literacy rate and awareness is low among rural women.
The importance of change-agents and role models, also, become important to break the notional problems surrounding the working women.
The role of media including social media, in promoting the positive stories about the working women giving impetus to the womenfolk is also very crucial. Social media also provides a voice to the women which was hitherto not available to her. The recent movements like #Timesup and #Metoo have shown the decisive role social media can play in garnering support and solidarity for the causes of women.
Thus, increasing participation levels of women in the various arenas, like paid labour market activities which bridges the hiatus in the crucial sphere of economic involvement, is important for improving the overall status of women in society.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
Analyse, how gender parity is positive for the development of country. Also discuss the initiatives taken by government to bridge the wide gender pay gap in India.