

Context
Recently, the World Health Organization (WHO) has released it’s first-ever report on the global impact of high blood pressure.
|
Hypertension is the most important risk factor for death and disability in India, according to a paper in The Lancet, regional health (South-east Asia), published late last year. |
Highlights of the Report:
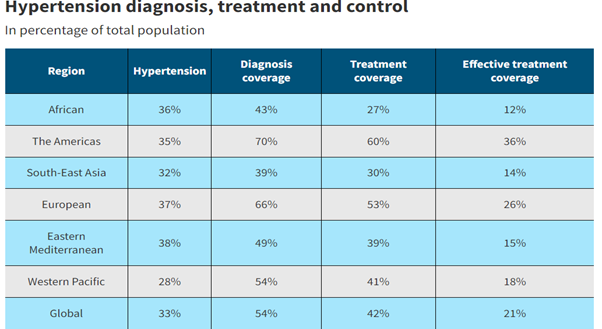
- The WHO report states that hypertension affects one in three adults worldwide. This common, deadly condition leads to stroke, heart attack, heart failure, kidney damage and many other health problems.
- Approximately four out of every five people with hypertension are not adequately treated, but if countries can scale up coverage, 76 million deaths could be averted between 2023 and 2050.
- The number of people living with hypertension (blood pressure of 140/90 mmHg or higher or taking medication for hypertension) doubled between 1990 and 2019, from 650 million to 1.3 billion.
- Nearly half of people with hypertension globally are currently unaware of their condition.
- More than three-quarters of adults with hypertension live in low- and middle-income countries.
- The world organisation states that lifestyle changes such as eating a healthier diet, quitting tobacco and being more active can help lower blood pressure.
|
The economic benefits of improved hypertension treatment programmes outweigh the costs by about 18 to 1. |
What is Hypertension?
- Hypertension (high blood pressure) is when the pressure in your blood vessels is too high (140/90 mmHg or higher).
- It is common but can be serious if not treated.
- People with high blood pressure may not feel symptoms. The only way to know is to get your blood pressure checked.
- Blood pressure is written as two numbers;
- The first (systolic) number represents the pressure in blood vessels when the heart contracts or beats.
- The second (diastolic) number represents the pressure in the vessels when the heart rests between beats.
- Hypertension is diagnosed if, when it is measured on two different days, the systolic blood pressure readings on both days is ≥140 mmHg and/or the diastolic blood pressure readings on both days is ≥90 mmHg.
- Things that increase the risk of having high blood pressure include:
- older age
- genetics
- being overweight or obese
- not being physically active
- high-salt diet
- drinking too much alcohol
|
Key facts
|
Government Initiatives
- Hypertension Control Initiative Programme: It is a large-scale hypertension intervention under the National Health Mission and has been recognised for its positive work done within the country’s existing primary healthcare system.
- Indian Hypertension Control Initiative (IHCI) is a 5-year initiative involving the Ministry of Health & Family Welfare, Indian Council of Medical Research, State Governments, and WHO-India.
- By December 2021, the IHCI program was implemented in 101 districts across 19 states and enrolled more than 20 lakh patients in 13,000+health facilities.
- In the 26 initial Phase I districts, nearly one-fifth (22%) of the estimated total number of people with hypertension in the district were enrolled.


