

Context
Ministry of Environment, Forest and Climate Change has notified the Battery Waste Management Rules, 2022 to ensure environmentally sound management of waste batteries.
- New rules will replace the Batteries (Management and Handling) Rules, 2001.
About
Key highlights:
- The rules cover all types of batteries namely;
- Electric Vehicle batteries
- Portable batteries
- Automotive batteries
- Industrial batteries
- It is based on the concept of Extended Producer Responsibility (EPR) where the producers of batteries are responsible for the collection and recycling of waste batteries and the use of recovered materials from wastes into new batteries.
|
Extended producer responsibility:
|
- Based on Centralized Online Portal: The portal will help in the exchange of EPR certificates between producers and recyclers to fulfill the obligations of producers.
- Promoting new industries: It promotes the setting up of new industries and entrepreneurship in the collection and recycling of waste batteries.
- Committee for monitoring: Online registration & reporting, auditing, and a committee for monitoring the implementation of rules is done.
- Follows Polluter Pays Principle: Environmental compensation will be imposed for non-fulfilment of Extended Producer Responsibility targets, responsibilities and obligations set out in the rules.
- Funds: The funds collected under environmental compensation shall be utilised in the collection and refurbishing or recycling of uncollected and non-recycled waste batteries.
What is the need for Battery management?
- Flourishing EV industry:Increasing push for the adoption and production of electric vehicles (EVs).
- To become self-dependent: India aims to reduce carbon emissions and hence targeted the installation of renewable sources of power generation, which are crucial to batteries.
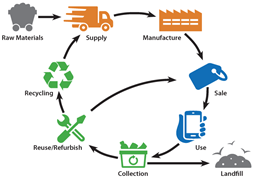
How informal recycling sector is harmful?
- Release of toxins: In informal recycling sector, old batteries tend to release toxins into the air, water, and soil.
- Against the rules: Transportation of batteries to the informal recycling sector is in direct contravention of the Batteries Management and Handling Rules (2001).
- Lack of regulation by authorities such as the CPCB and the SPCBs.
- Polluting nature of recycling in the informal sector, in which lead is melted on furnaces and the acid in the batteries is often dumped in nearby drains or fields — polluting water as well as soil.
|
Lithium-ion batteries:
|
Impacts:
- On Environment: The impacts can be water pollution, degradation of soil health, etc.
- On Fauna: More long-term effects on the environment include signs of mutation in animals.
- On Health: Eye and skin irritation, Chemical burns, Cancer, Genetic mutations, etc.
Other Government Initiatives:
- E- MOBILITY- National policy on transformative mobility and Battery storage.
- Waste to Energy initiative


