

Context
As outsourcing/contractual has become the dominant mode of working in the government, from highly specialized tasks to the most routine ones.
Background
- The government has been worried about unequal remuneration and treatment of contract workers, but it continues to hire them in bigger numbers.
- As many as 3 million people working in the government sector — or 43% of the total government workforce — are engaged in temporary jobs, according to a study by the Indian Staffing Federation (ISF), an apex body of staffing companies in the country.
- At least 9 million of these people are engaged in key flagship government programs and are deprived of minimum wages with limited to nil social security cover.
|
Nature of Jobs in the Government Sector They may be classified into three categories;
|
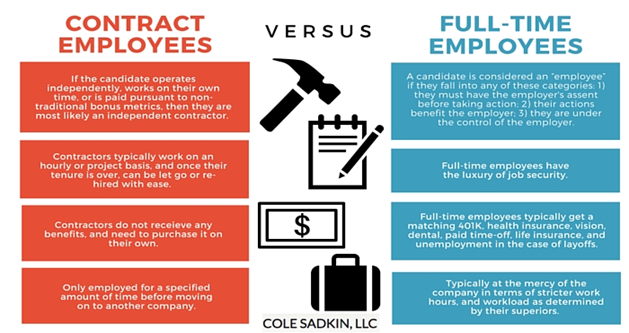
Analysis
Who are Gig Workers of the Government?
- The term "gig" is a slang word for a job that lasts a specified period of time. Traditionally, the term was used by musicians to define a performance engagement.
- Examples of gig workers include freelancers, independent contractors, project-based workers, and temporary or part-time hires.
How they are supporting the economy?
- The gig economy is based on flexible, temporary, or freelance jobs, often involving connecting with clients or customers through an online platform.
- The gig economy can benefit workers, businesses, and consumers by making work more adaptable to the needs of the moment and the demand for flexible lifestyles.
- At the same time, the gig economy can have downsides due to the erosion of traditional economic relationships between workers, businesses, and clients.
- In a gig economy, large numbers of people work in part-time or temporary positions or as independent contractors.
- The gig economy has many benefits for both the employee and employer. An employer has access to a wide range of talent that they can hire. If the talent proves to be less than acceptable, there is no contract to keep the employee on or issues of letting them go.
Why it is not recommended to employee contractual employees?
Despite it is not recommended to employ more gig workers, the government is expanding its scope. So, what are the reasons behind it?
- Lack of job security, irregular wages, and uncertain employment status
- Rising stress due to uncertainty associated with regularity in available work and income
- Limited access to the internet and digital technology
- The contractual relationship between the platform owner and gig worker denies the latter access to many workplace entitlements.
- Stress is due to pressure from algorithmic management practices and performance evaluation based on ratings.

Constitutional Provisions
|
Article |
Title |
Description |
|
21A
|
Right to Education
|
The State shall provide free and compulsory education to all children of the age of 6 to 14 years in such manner as the State, by law, may determine. |
|
24
|
Prohibition of Employment of Children in Factories |
No child below the age of fourteen years shall be employed in work in any factory or mine or engaged in any other hazardous employment. |
|
39 |
The state shall in Particular direct its policy toward securing |
That the health and strength of workers, men, and women, and the tender age of children are not abused and that citizens are not forced by economic necessity to enter avocations unsuited to their age or strength |
What can be done to safeguard their interest?
- Increase access to institutional credit for platform workers and those interested in setting up their own platforms.
- Unsecured loans extended to first-time borrowers in the platform economy may be classified as Priority Sector Lending.
- Skill development of youth and workforce to make them employable.
- Government can ensure universal coverage of platform workers through the Code on Social Security.
- Paid Sick Leave, Health Access, and Insurance for gig workers.
- Occupational Disease and Work Accident Insurance to all delivery and driver partners.
- Retirement/Pension Plans and Other Contingency Benefits.
Conclusion
Fixed-term contractual stints with the government with safeguards against sheer exploitation can be a major source of employment. However, such modes of recruitment will have to assimilate the principles of affirmative action, in line with the vision of social justice enshrined in our Constitution.


