

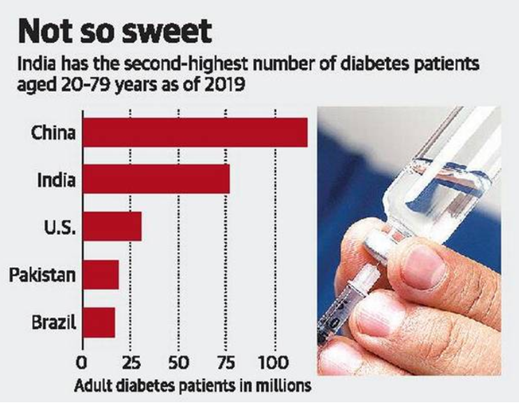
One in six people with diabetes in the world is from India. The numbers place the country among the top 10 countries for people with diabetes, coming in at number two with an estimated 77 million diabetics. China leads the list with over 116 million diabetics.
Context
One in six people with diabetes in the world is from India. The numbers place the country among the top 10 countries for people with diabetes, coming in at number two with an estimated 77 million diabetics. China leads the list with over 116 million diabetics.
Background/Highlights of the report
- On International Diabetes Day, the International Diabetes Foundation Diabetes Atlas makes it clear India needs to pause and re-evaluate its strategy to combat diabetes.
- The ninth edition of the IDF Diabetes Atlas offers projections that continue to put India at the second slot right up to 2045.
- Every sixth diabetic in the world is an Indian, making the country the world's diabetes capital.
- And the numbers are staggering; just over 134 million Indians will be diabetics in the next 25 years.
- India is on the top of the table of a clutch of countries in from Southeast Asia — Bangladesh, Sri Lanka, Nepal and Mauritius.
- Bangladesh, which is second on the list of top five countries with diabetes (20-79 years), however, has only 8.4 million diabetics.
- China, India and the United States had the largest number of adults with diabetes.
- More than half the world's total diabetics are aged between 20 and 60.
- It is projected that the number of adults with diabetes in Pakistan will exceed that in the United States of America, and it will move to third place by 2045.
- Diabetes-related health expenditure in the South East Asia, at $8.1 billion in 2019, was the lowest total of all IDF regions.
- In the SEA Region, 8.4 percent of total health expenditure was allocated to diabetes. The highest percentage was in Mauritius (16.9 per cent), and the lowest was in Nepal (4.2 per cent).
- Type 2 diabetes accounted for around 90 percent of all people with diabetes.
- The rise in the number of people with type 2 diabetes was driven by a complex interplay of factors, including urbanisation, an ageing population, decreasing levels of physical activity and increasing levels of overweight people and obesity.
About Diabetes
- Diabetes is a disease that occurs when your blood glucose, also called blood sugar, is too high.
- Blood glucose is your main source of energy and comes from the food you eat.
- Insulin, a hormone made by the pancreas, helps glucose from food get into your cells to be used for energy.
- Sometimes your body doesn’t make enough or any insulin or doesn’t use insulin well. Glucose then stays in your blood and doesn’t reach your cells.
- Although diabetes has no cure.
- Sometimes people call diabetes “a touch of sugar” or “borderline diabetes.” These terms suggest that someone doesn’t really have diabetes or has a less serious case, but every case of diabetes is serious.
What are the different types of diabetes?
- Type 1 diabetes: If you have type 1 diabetes, your body does not make insulin. Your immune system attacks and destroys the cells in your pancreas that make insulin. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in children and young adults, although it can appear at any age. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day to stay alive.
- Type 2 diabetes: If you have type 2 diabetes, your body does not make or use insulin well. You can develop type 2 diabetes at any age, even during childhood. However, this type of diabetes occurs most often in middle-aged and older people. Type 2 is the most common type of diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: Gestational diabetes develops in some women when they are pregnant. Most of the time, this type of diabetes goes away after the baby is born. However, if you’ve had gestational diabetes, you have a greater chance of developing type 2 diabetes later in life. Sometimes diabetes diagnosed during pregnancy is actually type 2 diabetes.
What health problems can people with diabetes develop?
- Heart disease
- Stroke
- Kidney disease
- Eye problems
- Dental disease
- Nerve damage
- Foot problems
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
- Increased thirst and urination
- Increased hunger
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
- Numbness or tingling in the feet or hands
- Sores that do not heal
- Unexplained weight loss


