

Context
The steering committee of the UNFPA-UNICEF Global Programme to End Child Marriage is on a visit to India to witness State interventions which have helped reduce the prevalence of child marriage.
What is the situation in the world?
|
Child marriage can be described as a formal marriage or an informal union entered into by an individual before attaining the prescribed eligible age. |
- According to data from UNICEF, the total number of girls married in childhood stands at 12 million per year.
- Without further acceleration, more than 150 million additional girls will marry before they turn 18 by 2030.
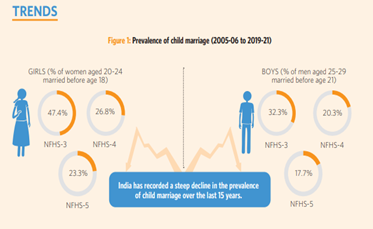
- Situation in India: There is a growing trend for a decline in the overall prevalence of child marriage, but 23.3% is still a disturbingly high percentage in a country with a population of 141.2 crore.
- Eight States have a higher prevalence of child marriage than the national average — West Bengal, Bihar and Tripura top the list with more than 40% of women aged 20-24 years married below 18.
- Eight States have a higher prevalence of child marriage than the national average — West Bengal, Bihar and Tripura top the list with more than 40% of women aged 20-24 years married below 18.
|
Reasons responsible for child marriage |
Effects of Child Marriage |
|
|
UNFPA-UNICEF Global Programme to End Child Marriage:
- The UNFPA (United Nations Population Fund)-UNICEF Global Programme to End Child Marriage is the first United Nations-led joint initiative designed with a focus on promoting the rights of adolescents to delay marriage.
- It highlights the need for targeted and focused interventions to accelerate progress to end child marriage.
|
Role played by the Government of India: |
What are the laws and policy interventions? |
|
|
|
Innovative Schemes:
|
What needs to be done?
- Engaging gram panchayats
- Empowering girls
- Creating proper public infrastructure
- Addressing societal norms
Pathways for Change:
- Addressing poverty as a driver: We need inclusive economic growth that reaches the most marginalized communities and families to tackle poverty as a key driver of child marriage.
- Enhancing education opportunities: The need of the hour is investments in quality secondary and higher education to enable girls to gain knowledge and skills, and expand their life options.
- Access to right-based health information and services: There is an urgent need for targeted delivery of essential life skills, including sexual and reproductive health information to enable informed choice and reduce unintended pregnancy.
- Addressing internalized inequitable values and attitudes: We need to tackle harmful gender norms and power dynamics to ensure that girls are empowered to make their own decisions about their lives and regarding if, when and whom they want to marry.
- Promoting positive masculinity and engaging men and boys: Men and boys are key stakeholders in addressing harmful practices and gender-based violence – working with them is critical to advance empowerment-oriented pathways for all


