Context
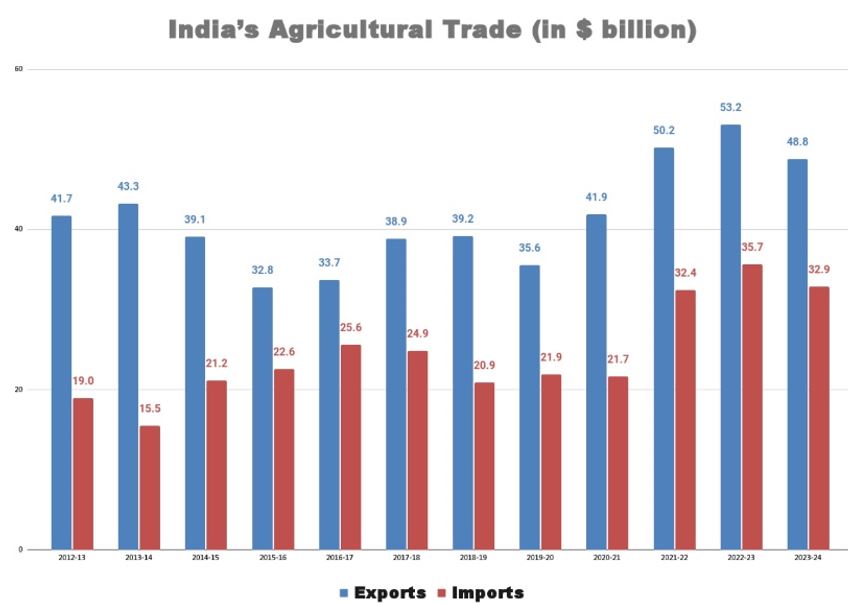
India's agricultural exports experienced an 8.2% decline, primarily due to restrictions on various commodities such as cereals, sugar, and onions. The total value of agricultural exports stood at USD 48.82 billion, a decrease from the record high of USD 53.15 billion in the previous fiscal year.
Factors Impacting Exports
- The decline in exports was led by sugar and non-basmati rice. Restrictions on sugar exports resulted in a significant drop in its export value, while a ban on non-basmati rice exports contributed to the overall decline in this segment.
- Wheat and onion exports were also affected by export restrictions imposed due to domestic shortages and rising prices.
- Discrepancy between government's objectives (promoting crop diversification) and its policies on import tariffs. While import duties on most pulses have been eliminated, promoting their cultivation, the low tariffs on certain imported items contradict the goal of reducing dependence on imports for items like pulses and edible oils.
Export Drivers and Import Trends
- Exports: Despite the overall decline, certain agricultural export items such as basmati rice and spices experienced growth. However, exports of oil meals, and raw cotton remained below their previous records.
- Imports: On the import side, the decrease in overall agricultural imports in 2023-24 was mainly due to a reduction in edible oil imports. Lower global prices led to a decrease in the import bill for vegetable oils. However, imports of pulses nearly doubled, reaching the highest levels since 2015-16.
Policy Implications
- There needs urgent recognition of importance of policy stability and predictability for farmers and agri-traders.
- Policies favoring consumers over producers, such as sudden export bans or restrictions, can have significant negative impacts on agricultural producers.
- A more predictable and rules-based policy approach, such as temporary tariffs instead of outright bans, is recommended.
- There is a need for a more rational export-import policy that balances the interests of producers and consumers, as well as short- and long-term goals for the agricultural sector. This may involve revisiting export and import restrictions and tariffs to ensure a more sustainable and equitable agricultural trade environment.
Fact Box:Agriculture in India
Schemes promoting Agricultural Export
|