

Context:
Recently, the Prime Minister inaugurated the first leg of the Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS), India’s first mass rapid system dedicated to regional connectivity.
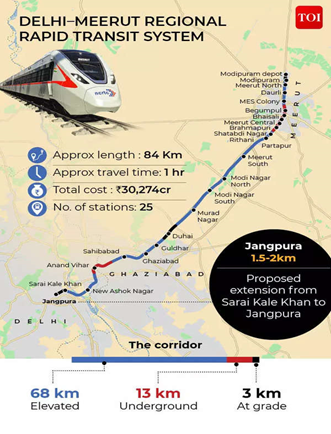
- Trains on the first section will eventually cut the journey time between Delhi and Meerut to less than an hour.
About
- India’s first regional rapid train, between Delhi and Meerut, has been named “Namo Bharat”.
- The events held: The projects which got the green signal includes;
- inaugurate the priority section of the Delhi-Ghaziabad-Meerut Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS) corridor and
- Flag off the “RapidX train” connecting Sahibabad and Duhai Depot.
- Construction:
- The National Capital Region Transport Corporation (NCRTC) has constructed the RRTS also known as Namo Bharat.
- NCRTC is a joint venture company of the Central government and the governments of Delhi, Haryana, Rajasthan and Uttar Pradesh.
- NCRTC, under the Ministry of Housing and Urban Affairs, is mandated with implementing the RRTS project across the National Capital Region.
The Regional Rapid Transit System (RRTS):
- With semi high-speed rail connectivity at its core, the RRTS is an integrated, mass transit network.
- It aims to ensure balanced and sustainable urban development through better connectivity and access across the NCR.
Origin
- The idea of such a network lies in a study which the Indian Railways was commissioned to carry out in the year 1998-99.
- The study identified the possibility of an RRTS network to connect various locations in the NCR through fast commuter trains.
- The proposal was re-examined in the year 2006 with the extension of the Delhi Metro lines to some NCR towns such as Gurgaon, Noida and Ghaziabad.
- It was soon taken up by the National Capital Region Planning Board (NCRPB) while developing its Functional Plan on Transport for NCR-2032.
- NCRPB identified and recommended eight RRTS corridors to connect NCR towns with high speed rail-based commuter transit services.
Objective
- It seeks to unlock the entire potential of the NCR in various ways in addition to enhancing multi-modal connectivity at the existing transportation hubs.
- One of the most significant aims of the project is to nudge commuters towards public transportation.
- Hence, it will have a positive impact on relieving the congestion both on its road/highways as well as existing metro and railway networks.
- The project aims to give a push to employment generation and the opening up of newer commercial hubs along the current contours of the NCR.
- Shorter travel times are expected to increase the overall economic productivity of the region.
Features
- RRTS trains will travel significantly faster than metro trains.
- These will operate at a speed of 160 km/hour but are designed to be able to run at speeds up to 180 km/hour.
- The RRTS is modelled on systems such as the RER in Paris, Regional-Express trains in Germany and Austria as well as the SEPTA Regional Rail in the United States, among others.
How is the RRTS different from existing metro or railways systems?
- When compared with metros, the RRTS network is faster.
- Compared with the Indian Railways, though the RRTS train will cover relatively smaller distances. It will do so at higher frequency and provide relatively more comfort than the average Railways coach.
Role of Science and Technology in Economic Growth:
In economics, it is widely accepted that technology is the key driver of the economic growth of countries, regions and cities. Technological progress allows for the more efficient production of more and better goods and services, which is what prosperity depends on.
- Time is Money: Technology can save the time it takes to produce a good or deliver a service, contributing to the overall profits of a business.
- Efficiency: Technology can contribute to the efficiency of a business's output rate, allowing for larger quantities of products to be moved or of services to be rendered.
- Specialization: Technology has to lead to an increase in the division of labour and specialization of jobs within a business, further contributing to the efficiency with which a business can run.
- Natural Resources: Technology has a huge effect on the ability of businesses and governments to access natural resources and use them in the most effective ways possible to benefit both the business and the economy.
- Industrial Expansion: Thanks to the increased efficiency of labour with the ever-improving state of technology, businesses can increase total output, which in turn leads to higher profits and greater economic development.
- Research: Better technology has led to further research into nearly every sector of business and science, meaning businesses can benefit from all sorts of technological advancements.
- The Internet and International Trade: Information technology is the single most important element in the success and growth of international trade and job market growth, allowing businesses to share information and conduct trade in less time than the blink of an eye.
|
Benefits |
Consequences |
|
|
Conclusion
In conclusion, the expansion of railway infrastructure brings about a range of consequences, both positive and negative. While railways significantly improve accessibility, reduce traffic congestion, and contribute to environmental sustainability, they also pose challenges like land displacement, environmental disruptions, and potential safety concerns. Striking a balance between reaping the economic and societal benefits and addressing the associated drawbacks requires meticulous planning, community engagement, and a commitment to sustainable development


