About
About Lithium:
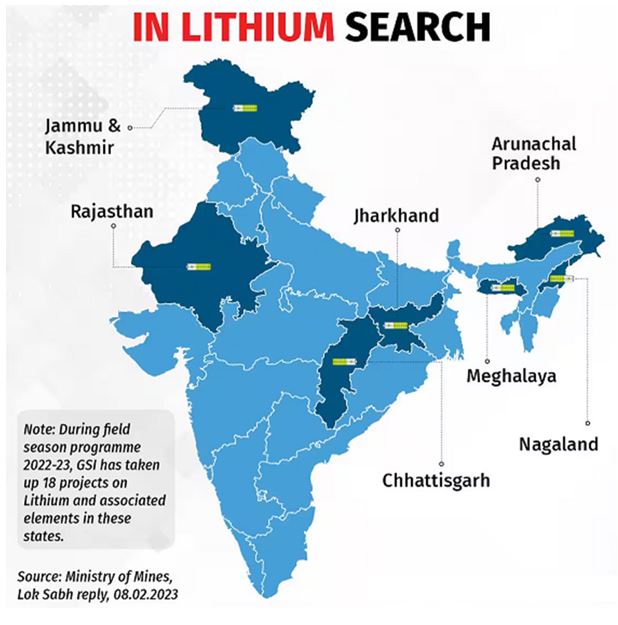
Lithium is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal that is highly reactive and flammable. It is the lightest metal and the least dense solid element. Lithium is widely distributed across the world, with the largest reserves found in Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile. In India, the Geological Survey of India has discovered lithium deposits in Salal village, Reasi district, Jammu & Kashmir.
Uses of Lithium:
Lithium has a wide range of uses, including in the production of ceramics, glass, and aluminum, as well as in the manufacture of batteries, lubricants, and pharmaceuticals. Lithium-ion batteries are used in electric vehicles, mobile phones, laptops, and other electronic devices. The demand for lithium is expected to rise significantly in the coming years due to the increasing popularity of electric vehicles and the shift towards renewable energy.
I. Lithium Distribution: India and World
Lithium, often referred to as the "white gold" of the 21st century, has become a vital component in powering our modern world.
i. Global Lithium Landscape:
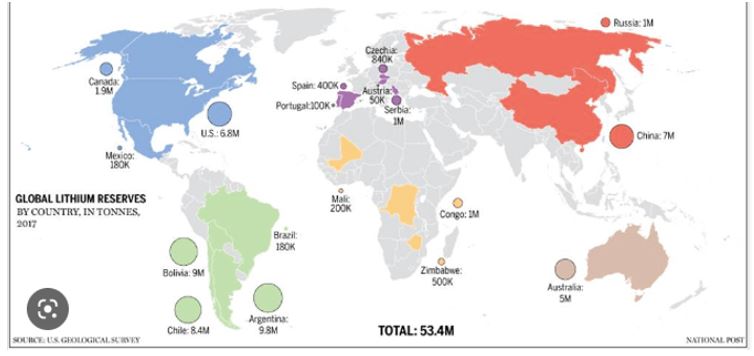
- Distribution Overview: The global distribution of lithium resources is not uniform, with key deposits concentrated in specific regions. One of the largest lithium-producing countries is Australia, home to the Greenbushes lithium mine, which holds a substantial share of the world's lithium reserves.
- South America's Lithium Triangle: The Lithium Triangle, encompassing parts of Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile, stands out as a major lithium-producing region. Salar de Atacama in Chile, for instance, hosts significant lithium brine deposits, contributing substantially to the global lithium supply.
- China's Dominance: China, a major player in the lithium-ion battery market, has developed a robust lithium industry. With extensive lithium resources in provinces like Jiangxi and Sichuan, China plays a pivotal role in the global lithium supply chain.
ii. Lithium Landscape in India:
- Current Scenario: India, despite being a major consumer of lithium-ion batteries, is yet to tap into significant lithium resources domestically. The exploration and extraction of lithium in India are in nascent stages, and the country relies heavily on lithium imports to meet its growing demand.
- Pegmatite Reserves in Rajasthan: Recent exploration activities have identified lithium-bearing pegmatite reserves in the Marwar region of Rajasthan, marking a potential breakthrough for India's lithium resources. The extraction of lithium from pegmatites is gaining traction as a feasible option.
- Collaborations for Lithium Exploration: India is actively seeking collaborations with lithium-rich nations and private entities to secure a sustainable lithium supply chain. Partnerships with countries like Bolivia and Australia aim to facilitate exploration and extraction initiatives.
III. Case Studies:
- Greenbushes Lithium Mine (Australia): The Greenbushes mine in Western Australia is a standout example of a lithium-rich resource. It contributes significantly to global lithium production, emphasizing the strategic importance of Australia in the lithium market.
- Salar de Atacama (Chile): Chile's Salar de Atacama is renowned for its vast lithium brine deposits. The sustainable extraction of lithium from brines has become a model for environmentally conscious mining practices.
- Lithium Exploration in Rajasthan (India): Ongoing exploration activities in the Marwar region of Rajasthan showcase India's potential as a lithium resource. Pilot projects and collaborative ventures are crucial in establishing a sustainable lithium industry within the country.
IV. Recent Data and Future Prospects:
- Global Demand and Supply (2023): Recent data indicates that the global demand for lithium is soaring, driven by the expanding electric vehicle market and renewable energy projects. As of 2023, the lithium supply chain faces challenges to meet the increasing demand, necessitating investments in exploration and extraction.
- India's Lithium Roadmap (2023): In India, the government's push for electric mobility and renewable energy integration has elevated the significance of lithium. The nation is devising a comprehensive lithium roadmap, focusing on sustainable extraction, recycling, and strategic collaborations to secure its lithium future.
II. Impacts of Lithium Mining:
1. Mining: The two primary methods for extracting lithium—open-pit mining and lithium brine extraction—pose distinct environmental challenges.
- Open-pit mining, often used for lithium-bearing minerals like spodumene, results in habitat disruption and extensive land clearance.
- On the other hand, brine extraction involves diverting water from natural sources, altering local ecosystems.
|
Case Studies: Real-world Impact 1. Salar de Atacama, Chile: Chile's Salar de Atacama, a key player in the global lithium market, illustrates the environmental trade-offs. The extraction of lithium from brines in the region has led to concerns about water scarcity and ecosystem disruption. The delicate balance of the Atacama Desert's unique flora and fauna is under threat as lithium production intensifies. 2. Greenbushes Lithium Mine, Australia: The Greenbushes lithium mine in Western Australia, a major global supplier, exemplifies the environmental impact of open-pit mining. The disruption of local ecosystems, dust pollution, and the energy-intensive extraction process contribute to the mine's environmental footprint. |
2. Water Scarcity: A Critical Concern
Lithium Brine Extraction and Aquifer Depletion: One of the significant environmental concerns linked to lithium brine extraction is water scarcity. In regions like Argentina's Salar del Hombre Muerto, the extraction process involves diverting water from local aquifers, leading to depletion and threatening the livelihoods of nearby communities.
3. Carbon Footprint: The Hidden Challenge
Energy-Intensive Extraction and Processing: Lithium extraction and processing demand significant energy inputs, contributing to the industry's carbon footprint. The carbon intensity of lithium production is particularly pronounced in areas where fossil fuels power the extraction process, offsetting the clean energy narrative associated with electric vehicles.
III. Mitigation Strategies and Sustainable Practices
1. Recycling Initiatives: To address the environmental impact of lithium mining, recycling initiatives are gaining momentum. Recovering lithium from used batteries reduces the need for new mining, lessening the strain on ecosystems.
2. Technological Innovations: Advancements in lithium extraction technologies are crucial for minimizing environmental impact. Sustainable methods, such as direct lithium extraction technologies, aim to reduce water usage and habitat disruption.
IV. Lithium and Geopolitics
i. Uneven Distribution: The global distribution of lithium resources is characterized by regional disparities, with key reserves concentrated in countries like Australia, Chile, China, and Argentina. This uneven distribution sets the stage for geopolitical competition over access to lithium, a crucial element for electric vehicles and renewable energy storage.
|
II. Case Studies: 1. Australia-India Collaboration: Australia, home to significant lithium reserves, has emerged as a key partner for India. In a recent agreement, Indian companies entered partnerships with Australian counterparts to explore and develop lithium assets. This collaboration aims to secure a stable lithium supply for India's burgeoning clean energy initiatives. 2. India's Engagement with Bolivia: Bolivia, home to vast lithium resources in the Salar de Uyuni, has become a focal point for India's lithium diplomacy. Recent agreements between India and Bolivia involve joint ventures for lithium exploration and extraction. Bolivia's lithium-rich salt flats present a strategic opportunity for India to diversify its lithium sources. |
ii. China's Dominance and India's Strategic Response:
Lithium Triangle Diplomacy: China's influence in the Lithium Triangle (Argentina, Bolivia, and Chile) has prompted India to adopt a strategic approach. India's engagement with these South American nations involves diplomatic efforts to counterbalance China's stronghold and secure lithium resources for its ambitious clean energy plans.
iii. Africa's Lithium Reserves and India's Outreach:
Partnerships in Africa: Africa, with untapped lithium reserves, has become a focus for India's lithium outreach. Recent agreements involve collaboration with African nations to explore lithium resources. This proactive engagement aims to diversify India's lithium supply chain and reduce dependency on specific regions.
V. Pioneering the Shift: From Oil to Lithium - A Transformative Economic Journey
The global transition from fossil fuels to clean energy sources has spurred a paradigm shift, with lithium emerging as a linchpin in the journey towards a sustainable future. The Indian government has set a target of achieving 30% electric vehicle penetration in private cars, 70% in commercial vehicles, and 80% in two and three-wheelers by 2030. The development of a domestic lithium-ion battery industry is expected to create jobs and reduce India’s dependence on imports.
i. The Fossil Fuel Era: A Foundation in Oil
- Historical Dependence: For decades, the global economy has been anchored in the extraction, refinement, and consumption of oil. Fossil fuels, primarily oil, have powered industries, transportation, and economies, shaping the geopolitical landscape.
ii. Lithium's Ascent: A Catalyst for Change
- Clean Energy Imperative: As concerns over climate change escalate, nations are compelled to shift towards clean and renewable energy sources. Lithium-ion batteries have emerged as a transformative technology, powering electric vehicles (EVs) and serving as storage solutions for renewable energy.
- Transportation Revolution: The rise of electric vehicles is a striking example of the shift from oil to lithium. Major automotive players are investing heavily in EV technologies. Companies like Tesla, with its groundbreaking electric cars, have disrupted the traditional automotive industry and set the stage for a lithium-centric transportation sector.
|
Case Studies: 1. Norway's EV Revolution: Norway provides a compelling case study of a nation embracing the lithium-based economy. With aggressive incentives for EV adoption, Norway has transformed its transportation sector. Electric vehicles now dominate the market, showcasing the potential of lithium-powered mobility. 2. China's Lithium Dominance: China, a global leader in lithium-ion battery production, exemplifies the economic implications of the shift. The country's commitment to electric mobility and renewable energy has positioned it at the forefront of the lithium-based economy, influencing global supply chains. |
iii. Economic Impact and Job Creation:
Emergence of New Industries: The lithium-based economy has sparked the rise of new industries. Battery manufacturing, lithium extraction technologies, and renewable energy projects are generating employment opportunities and fostering economic growth in regions strategically investing in the clean energy transition.
iv. Challenges and Opportunities:
Resource Geopolitics: As nations vie for lithium resources, a new form of resource geopolitics is unfolding. Lithium-rich countries gain economic leverage, potentially altering the global power dynamic. This shift demands astute diplomacy and strategic alliances to secure a stable lithium supply.
Technological Innovation: The transition to a lithium-based economy necessitates continuous technological innovation. Research and development in battery technologies, energy storage solutions, and lithium extraction methods present opportunities for economic advancement and global leadership.
VI. Significance of Lithium for India:
- Lithium as the Enabler of Clean Energy: Lithium-ion batteries, powered by the metal lithium, have become the backbone of clean energy solutions. In India, the significance of lithium lies in its pivotal role in the electrification of transportation, renewable energy storage, and the overall transition towards a greener and more sustainable economy.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs) Revolution: India, with its ambitious goals for electric mobility, sees lithium as a critical component for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density and longer life, making them ideal for powering the EV revolution in the country.
VII. Challenges Faced by India:
- Limited Domestic Lithium Reserves: India's lithium landscape is characterized by limited domestic reserves. The nation is heavily dependent on lithium imports, primarily from countries like China and Australia. Ensuring a stable and diversified lithium supply chain is a paramount challenge for India.
- Exploration and Extraction Hurdles: The exploration and extraction of lithium reserves within India present challenges. While potential lithium-bearing regions like Rajasthan have been identified, the scaling up of extraction operations involves overcoming technological and infrastructural barriers.
- Global Competition and Resource Geopolitics: The global demand for lithium has led to intensified competition among nations for securing stable supplies. India faces the challenge of navigating this resource geopolitics to safeguard its lithium interests and mitigate the risk of supply chain disruptions.
VIII. Indian Government Initiatives for Lithium:
- National Mission on Transformative Mobility and Battery Storage (NMTM&BS):
- Objective: Launched as part of the National Institution for Transforming India (NITI) Aayog's efforts, the mission aims to promote clean and sustainable mobility and advance energy storage solutions.
- Focus on Lithium: The NMTM&BS places a significant emphasis on the development of advanced battery technologies, including lithium-ion batteries, for electric vehicles and energy storage applications.
- Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles (FAME) Scheme:
- Objective: The FAME scheme, initiated by the Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises, provides financial incentives to promote the adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles.
- Focus on Lithium: The scheme incentivizes the manufacturing and adoption of lithium-ion batteries and electric vehicles, contributing to the growth of the domestic lithium ecosystem.
- Lithium Exploration in Rajasthan:
- Initiative: The Geological Survey of India (GSI) identified lithium reserves in the Marwar region of Rajasthan.
- Objective: This exploration initiative aims to assess the lithium potential in the region and lay the foundation for future extraction and utilization.
- International Collaborations:
- Initiative: Collaborations with lithium-rich countries for joint ventures in exploration and extraction.
- Example: Agreements with countries like Bolivia and Australia involve joint efforts to explore and develop lithium resources.
- Research and Development Support:
- Initiative: Funding for research and development in lithium-related technologies.
- Example: Support for research projects focused on improving lithium-ion battery technologies, exploring new extraction methods, and enhancing recycling processes.
- Incentives for Battery Manufacturing:
- Objective: To boost domestic manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries.
- Example: Incentives, subsidies, and policy support for setting up battery manufacturing units, which contribute to the growth of the lithium ecosystem.
- Policy Framework for Mineral Exploration:
- Objective: Streamlining regulatory processes for mineral exploration, including lithium.
- Example: Ongoing efforts to create a favorable policy framework that encourages responsible exploration and extraction of lithium resources.
- Sustainable Resource Management:
- Initiative: Incorporating lithium and other critical minerals into strategic resource planning.
- Example: Considering the importance of lithium in the context of national resource security and developing strategies for sustainable resource management.
IX. Indian Agreements for Lithium:
India has signed several agreements with different countries to secure its supplies of lithium. Here are some of the recent agreements:
- India-Argentina: In 2023, the Mines Ministry, through Khanij Bidesh India Limited (KABIL), signed an agreement with Argentina’s State-owned CAMYEN. CAMYEN, which stands for Catamarca Minera Y Energetica Sociedad Del Estado, is based out of the Catamarca province in the Latin American nation.
- India-Argentina: In 2022, India signed a memorandum of understanding with Argentina to jointly explore and develop lithium resources. The agreement was signed between Khanij Bidesh India Limited (KABIL) and the state-owned enterprise of Catamarca Province, Argentina. KABIL will start the exploration and development of five lithium brine blocks, covering an area of about 15,703 hectares, located in the Catamarca province of Argentina.
- India-Bolivia: In the same year, India signed a deal with Bolivia to import lithium carbonate. Bolivia has the world’s largest reserves of lithium, and the country is willing to sign a Preferential Trade Agreement (PTA) with India for select goods.
- India-Australia: In 2021, India signed a memorandum of understanding with Australia to collaborate on critical minerals, including lithium. The agreement aims to strengthen the supply chains for critical minerals and reduce the dependence on China.
- India-Chile: In 2018, India signed an agreement with Chile to acquire lithium. The agreement was signed between the Indian state-owned companies, National Aluminum Company (NALCO) and Hindustan Copper Limited (HCL), and the Chilean state-owned copper mining company, Codelco.
|
Case Studies: 1. The Tata Power and Australia Partnership: Tata Power, one of India's major energy players, has entered into a partnership with Australian mining firm Neometals to explore lithium recycling opportunities. This collaboration showcases India's commitment to innovative solutions and sustainable lithium practices. 2. India's Lithium Exploration in Rajasthan: Ongoing exploration activities in Rajasthan exemplify India's efforts to tap into its domestic lithium potential. Pilot projects and collaborations with global mining companies signify a concerted push towards self-reliance in lithium resources. |
X. Way Forward: Navigating Challenges for a Sustainable Lithium Ecosystem
- Investments in Research and Development: The Indian government's emphasis on research and development in lithium technologies is pivotal. Investments in innovation, including advancements in lithium-ion battery technologies, are essential for overcoming challenges and fostering a sustainable lithium ecosystem.
- Policy Frameworks for Lithium Integration: Strategic policy frameworks that incentivize lithium exploration, extraction, and manufacturing are critical. The Indian government's commitment to creating an enabling environment for the lithium sector is evident in policy initiatives aimed at promoting sustainable practices.
XI. Conclusion
- Lithium is a critical metal that is essential for the production of lithium-ion batteries, which are essential for the storage of renewable energy.
- The geographical distribution of lithium is concentrated in a few countries, including Bolivia, Argentina, and Chile.
- India has recently discovered lithium deposits in Jammu & Kashmir and has signed agreements with several countries to secure its supplies of lithium.
- The shift from an oil-based economy to a lithium-based economy is expected to have significant economic and environmental benefits for India, but there are several challenges that need to be addressed, including the lack of domestic reserves and the environmental impact of lithium mining.
- The Indian government has taken several initiatives to promote the development of a domestic lithium-ion battery industry, which is expected to create jobs and reduce India’s dependence on imports.