

Context
The 6th Minor Irrigation Census (MIC) report has been released recently.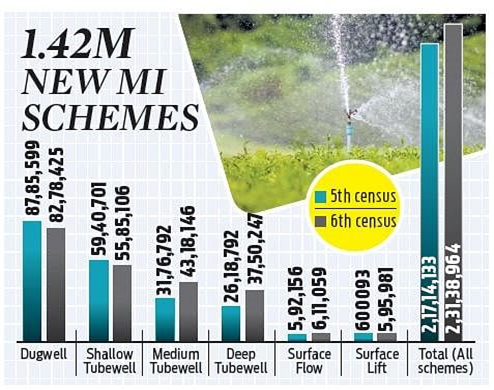
Highlights of the Report:
- As per the report, electricity is the primary power source for water extraction in private irrigation, surpassing diesel, wind, and solar pumps in majority of States in India.
- The report reflects irrigation trends for the year 2017-18.
- While the use of electricity showed a jump from powering only 56% of sources in 2011 to 70% in 2017.
- Out of all Micro Irrigation (MI) schemes, 21.93 million (94.8%) were for groundwater (GW) and 1.21 million (5.2%) for surface-water (SW)
- Dominant source of groundwater:
- While ‘dug-wells’ or ponds remain the dominant source of groundwater, their number has declined from 87 lakh to 82 lakh between the 5th and 6th editions.
- ‘Shallow’ tube wells have declined from 59 lakh to 55 lakh.
- However, ‘medium-sized’ wells grew from 31 lakh to 43 lakh and ‘deep’ wells rose from 26 lakh to 37 lakh.
- State-based data:
- Uttar Pradesh had the largest number of MI schemes in the country (17.2%) followed by Maharashtra (15.4%), Madhya Pradesh (9.9%) and Tamil Nadu (9.1%).
- Leading States in these schemes are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Madhya Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Telangana whereas Maharashtra, Karnataka, Telangana, Odisha and Jharkhand have the highest share in SW schemes.
- Causes for the increase of more powerful and deep-reaching tubewells:
- While excessive groundwater withdrawal has been a matter of long-standing concern, the report doesn’t discuss the causes for such increase.
- State governments announce schemes where farmers are incentivised or get access to loans to buy such tubewells, could be an explanation.
- However, the lower growth in electrification is also likely to be a result of greater emphasis on energy efficient water extraction.
Concerns:
- Electrification of groundwater withdrawal corresponds to a rise in the use of tubewells and borewells that are capable of extracting water at greater depths.
- There were 14 million schemes in the country, with Uttar Pradesh possessing the largest share, followed by Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh.


