

Context
A groundbreaking IVF procedure has been successfully performed in the United Kingdom, resulting in the birth of the first baby with genetic material from three persons, with the help of Mitochondrial donation treatment (MDT).
What is Mitochondrial Donation Treatment (MDT)?
|
Mitochondrial diseases affect 1 in 5,000 people globally and can cause severe health problems, including muscle weakness, organ failure, and neurological disorders. |
- Mitochondrial donation treatment (MDT) is a medical procedure aimed at preventing inherited diseases caused by mutations in the mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA).
- The treatment involves replacing the faulty mitochondria in a woman's egg or embryo with healthy mitochondria from a donor.
- Inherited mutations in mtDNA can cause mitochondrial disease, which is incurable and can lead to severe health problems.
|
Mitochondria are the powerhouse of the cell and are responsible for producing energy. They have their own DNA, separate from the nuclear DNA that determines an individual's physical traits. |
How defects occur in Mitochondria?
- Mitochondria are basically the powerhouses of the cells. They generate energy, and thus are also responsible for cell function in the human body.
- They have their own DNA, which is separate from the DNA in the cell's nucleus, and mutations in mitochondrial DNA can lead to a range of serious health conditions.
- Certain defects might occur impacting the way the mitochondria produces energy for the cells (especially in the ‘energy-hungry’ tissues of the brain, nerves, muscles, kidneys, heart, liver), and thereby impacting cell function.
- The diseases that arise out of such mitochondrial mutations are called mitochondrial diseases.
|
- Impact: When the mitochondria are impaired and do not produce sufficient energy, it affects how organs function, leading to a broad assortment of symptoms across the body, including brain damage, organ failure and muscle wastage.
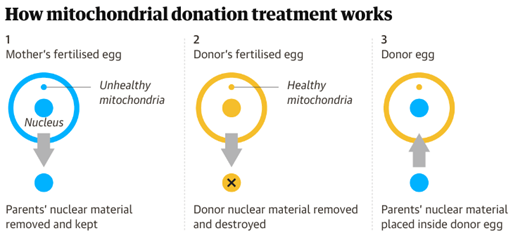
How Does MDT Work?
- MDT involves the use of in vitro fertilization (IVF) to create an embryo with genetic material from three people: the mother, the father, and the mitochondrial donor. The process can be done in two ways:
|
The genetic material from the donated egg comprises less than 1 percent of the child’s genetics |
- Pronuclear transfer: This involves transferring the nucleus of the mother's fertilized egg or embryo into the cytoplasm of a donor egg or embryo with healthy mitochondria. The resulting embryo has nuclear DNA from the mother and father and healthy mtDNA from the donor.
- Maternal spindle transfer: This involves transferring the nucleus of the mother's egg into a donor egg with healthy mitochondria before fertilization. The resulting embryo has nuclear DNA from the mother and father and healthy mtDNA from the donor.
What is the legal Status of MDT?
- The United Kingdom was the first country to legalize MDT in 2015.
- The law allows the procedure to be used in cases where there is a high risk of transmitting a severe mitochondrial disease. The first baby born using MDT in the UK was in 2016.
- Since then, a few other countries, including the United States, have also approved the use of MDT under strict regulations.
|
Status in India
|
What are the potential Benefits of MDT?
- MDT could prevent the transmission of mitochondrial disease to future generations and potentially eradicate it altogether.
- It could also provide families with a much-needed option to have a healthy child without passing on a debilitating genetic condition.
Ethical Concerns with MDT
- Questionable consequences of designer babies: One of the main ethical concerns with MDT is the creation of genetically modified babies. The procedure involves altering the genetic material of an embryo, which raises ethical questions about the creation of designer babies and the potential for unintended consequences.
- Exploitation of vulnerable: Another concern is that MDT could lead to the exploitation of vulnerable women who donate their eggs. It is essential to ensure that MDT is regulated and used only for medical purposes.


