

|
Overview
|
Context
The National Human Rights Commission (NHRC) had issued an advisory to the Centre and State Governments on preventing, minimising and mitigating the impacts of environmental pollution and degradation on human rights.
Background
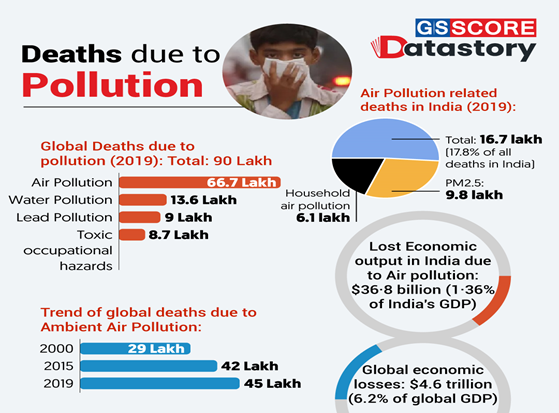
- A latest Lancet Commission report on Pollution and Health has highlighted the impact of increasing pollution on human health in India.
- Air pollution was responsible for 16.7 lakh deaths in India in 2019, or 17.8% of all deaths in the country that year.
- This is the largest number of air-pollution-related deaths of any country.
- 9.8 lakh were caused by PM2.5 pollution, and another 6.1 lakh by household air pollution.
- Pollution sources associated with extreme poverty (such as indoor air pollution and water pollution): This number has reduced; but, this reduction is offset by increased deaths attributable to industrial pollution (such as ambient air pollution and chemical pollution).
- Worst affected places: Air pollution is most severe in the Indo-Gangetic Plain. This area contains New Delhi and many of the most polluted cities.
- Causes: Burning of biomass in households was the single largest cause of air pollution deaths in India, followed by coal combustion and crop burning.
- Lead: 27.5 crore children are estimated to have blood lead concentrations that exceed 5 µg/dL.
- Economic losses due to modern forms of pollution have increased as a proportion of GDP between 2000 and 2019 in India. It amounts to 1 percent of GDP.
Analysis
Air pollution
Air pollution can be defined as the presence of one or more contaminants such as dust, fumes, gas, mist, smoke or vapour in the outdoor atmosphere which is injurious to human, plant and animal life. Pollution can be man-made or natural. Man-made pollution can be described at 3 levels:
- Personal Pollution:It is caused by an individual and is restricted to small area. Example: tobacco smoke, kitchen smoke.
- Occupational Pollution:It is due to an occupation which affects all the workers and some area around them. Example: gem cutting, stone crushing; textile mill. These generally lead to occupational diseases or hazards.
- Community Pollution:It affects the whole community or area around the source of pollution. Example: Thermal power plant, automobiles.
|
Right to a clean environment
|
|
National Human Rights Commission (NHRC)
|
Causes of Air Pollution
- Growing population: The pressure and haphazard growth of the population is deteriorating the environment.
- Industrialisation:There has been highly haphazard and unplanned development of industries. Studies have revealed that only about 20% of the industrial units are set up in the approved industrial areas whereas the rest of them are in residential and commercial areas.
- Vehicular Pollution:There has been a huge rise in the vehicular population, despite the metro railways, aggravating traffic congestion and increasing air and noise pollution.
- Fossil-fuel dependence:There has been too much dependence on fossil fuels like coal-fired power plants, improper use of energy in buildings and the excessive use of biomass for cooking and heating, etc.
- Burning of Crop Stubble: Burning of crop residue by farmers in Northern states of Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh is considered as the prime reason for a spike in air pollution during the winter months in Delhi NCR.
|
National Clean Air Programme
|
|
WHO’s limits for air pollution The World Health Organization has cut its recommended limits for air pollution, for the first time since 2005. The new recommendations target pollutants including particulate matter and nitrogen dioxide, both of which are found in fossil fuel emissions.
|
Government initiatives to safeguard the environment
- Graded Response Action Plan: Delhi launched a ‘Graded Response Action Plan’ under directions from the Supreme Court.
- NCAP: Launched in 2019, the National Clean Air Programme (NCAP) aimed at a long-term, time-bound, national-level strategy to tackle the air pollution problem across the country in a comprehensive manner with targets to achieve a 20 percent to 30 percent reduction in particulate matter concentrations by 2024, keeping 2017 as the base year.
- Green Skill Development program: Launched in 2017 by the Ministry of Environment, Forest, and Climate Change under PM NarendraModi, the Green Skill Development program aims to introduce innovative skills among the youth working in the environment and forest sector.
- Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act (CAMPA): One of the most robust legal acts aiming to hold those, who exploit natural resources and forests for the development of industries, responsible. The Compensatory Afforestation Fund Act was introduced in 2016.
- Nagar Van Scheme: Nagar Van Scheme was launched on the occasion of World Environment Day in 2020 (5th June). It aims to develop 200 Urban Forests across the country in the next five years.
- National Ambient Air Quality Standards: envisaging 12 pollutants have been notified under EPA, 1986 and 115 emission/effluent standards for 104 different sectors of industries, besides 32 general standards for ambient air have also been notified.
- Biofuels: With reference to Vehicular pollution the steps taken include introduction of cleaner / alternate fuels like gaseous fuel (CNG, LPG etc.), ethanol blending, universalization of BS-IV.
- Thrust to public transports: ongoing promotion of public transport network of metro, buses, e-rickshaws and promotion of carpooling, streamlining granting of Pollution Under Control Certificate, lane discipline, vehicle maintenance etc.
- National Air Quality index (AQI): was launched by the Prime Minister in April, 2015 starting with 14 cities and now extended to 34 cities.
Conclusion
India has a one of the world’s best statutory and policy framework for environment protection. The problem lies in its effective implementation.The solution lies in better coordination among various agencies, robust implementation of the programs. Thrust to renewable energy, massive afforestation, hybrid vehicles, and public transportation is the need of the hour.
|
Q1. The right to clean, healthy and sustainable environment isa basic human right. Elucidate. Q2. “Despite having one of the world’s best statutory and policy framework for environment protection, India is facing a serious problem of pollution.” Discuss why India is unable to curb the rising pollution? Suggest measures to minimise and mitigate the problem of environmental pollution. |


