

Context
Union Budget for 2022-23 has increased the allocation to Ministry of Home Affairs. Lion’s share of this allocation has been given to police.
Background
- The allocation of funds to police in Union Budget 2022-23 has increased but this news does not bring cheers for those rooting for reforms in India’s police forces.
- It is important to note that out of total amount of money allotted to the police force (Rs. 1.03 lakh crore), only a small fraction is available for utilization as capital expenditure (Rs. 9,715 crore).
Analysis
Need for Police Reforms in India:
- Indian Police Act, 1961 was enacted in the Background of the Revolt of 1857.
- The Colonial government therefore enacted an Act which was designed in such a way that police would ‘rule’ the people and not ‘serve’ them.
- The principle of police in India hence during colonial times was not Peelian, but based on Irish Constabulary.
Peelian Principles- Thess are the principles that summarize the ideas that Sir Robert Peel developed to define an ethical police force. - After India’s Independence, need was felt time and again to reform and restructure the police system in India. The same though has happened only to a limited extend.
- Reforms in police would better the law and order in India and this will result in improved socio-economic conditions of the country.
Why police reforms have had limited success in India?
- Law and Order is a state subject and hence enforcing police reforms from Centre is difficult.
- As section of those in power, in both politics and civil services, benefit from the colonial system of policing.
- Inertia shown by the stakeholders required to manifest willingness to change that would lead to modernization of police in India.
Issues plaguing the police establishment in India
- Funds allotted to police forces all over India are only 3% of the combined expenditure of Centre and all the states in India.
- Recruitments in the police departments all over the country is awfully law leading to vacancies of around 24% throughout the country. This adversely impacts police-public ratio.
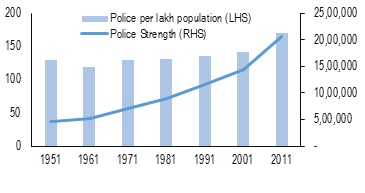
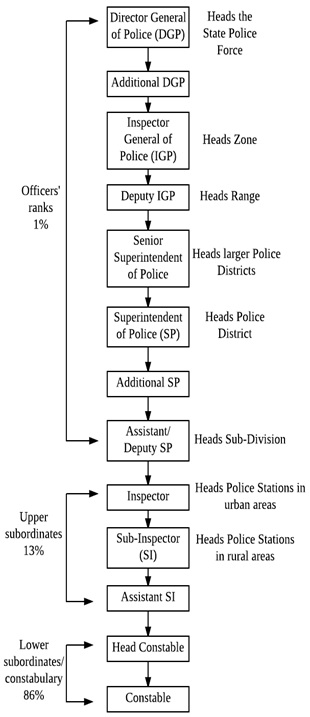
- It is also important to note that the proportion of personnel working in the police departments are largely concentrated at the subordinate or constabulary level.
- This not only burdens the officials at higher ranks but also leads to concentration of power in the hands of few leading to lack of accountability.
- Corruption has impacted the working of police department and led to deterioration of its functioning.
Efforts made for the purpose of modernizing police force in India-
- First effort to modernize the police force in India was done by the state of Kerala when in the 1959 it established the Police Commission to reform its police force.
- At the national level the earliest initiative to bring reforms was done when the Central Government instituted the National Police Commission in the 1977.
- Nation Police Commission recommended Amendment of Code of Criminal Procedure, 1973 and revision of syllabus for IPS probationers. Very little though was done to implement its recommendation.
- The Padmanabhaiah Committee on police reforms that was set in the year 2000 looked into police reforms in a comprehensive manner. It recommended modern methods for not only recruiting the police personnel but also their training, patrolling, posting and transfers.
- Padmanabhaiah Committee also recommended modernization of police forces and police stations all over India.
- Malimath Committee set up in the year 2000 was invested with the work of revamping the whole of criminal justice system in India. It paid special attention on technologically modernizing and paying special attention on improving the investigating abilities of the police forces in India.
- New Model Police Act was drafted by the Union Government in 2006 and the same was forwarded to the state governments to be implemented. As of now only 16 states have implemented it in limited way.
Following are the salient features of New Model Police Act-
-
- Effort was made through New Model Police Act to make policing in India a professional service that would strengthen country’s democratic society.
- Police to be governed by impartiality and human rights.
- Special attention for the protection of weaker sections including minorities.
- Functional autonomy to be provided by creation of State Police Board, Merit based selection, merit based selection and appointment of DGP.
- Professionalism in police departments has be encouraged by dedicating staff for crime investigation.
- Accountability from police personnel has to be demanded through their conduct.
- Police personnel should be provided better service conditions.
Supreme Court’s view on Praskash Singh v/s Union of India
- While considering a PIL filed by an eminent former police officer named Prakash Singh, the Supreme Court observed that reforms in the police force have to be undertaken at the earliest and recommended some steps to be undertaken for the same-
- Establishment of State Security Commission which would be headed by the Chief Minister or Home Minister of the state and will consist of leader of Opposition in State Assembly, retired Judge of High Court and few non-political independent individuals as its members. This would check the misuse of police forces in India.
- Police Establishment Board to be set up consisting of DGP and four senior police officers. This board would decide on transfer/posting of officers’ upto the rank of Dy. SP rank.
- A Police Complaint Authority to be formed and to be headed by retired High Court Judge. This body would decide the fate of police officers who have been alleged to have committed misconduct on duty.
- Merit based process for selection of DGP to take place.
- It is disheartening to know that the monitoring committee appointed by the Supreme Court reported that the states had shown total indifference to it’s recommendation and only few measure were adopted to bring reforms in the police force.
Allocation to the police force in Union Budget 2022-23
- The Union Territory of Jammu & Kashmir has been allotted Rs. 4,800 for reshaping of its law and order machinery.
- The Union Territory of Ladakh has been allotted Rs. 3,768 for the purpose building its police infrastructure.
- The Central Armed Police Forces have been allotted Rs. 2,744 crore for infrastructure development.
- The Central Armed Police Forces have been mandated to take up border infrastructure management more effectively and for that purpose allocations have been made to erect barbed wires on fences, install flood lightings, construct roads and construct observation post towers along the border and install hi-tech surveillance.
What next for police reforms? (Way forward)
People of India should make police reforms important a political issue. Thus for the purpose of winning elections, political parties will have take-up this issue seriously. It is essential that community leaders, NGOs etc. let people know as to what will be the benefits of good policing and why democratically pressure has to be exerted on law makers to make it happen.


