

Context
After a gap of more than a year and a half, educational institutes across India are beginning to open their doors to students once again. Learners are gradually returning to conventional modes of classroom teaching, and are being able to access physical libraries and academic resources.
However, the online trend of education is every indication that this trend is now irreversible. This brief attempts to analyze the rise of platform economy during the pandemic.
Background
- After a gap of more than a year and a half, educational institutes across India are beginning to open their doors to students once again.
- Learners are gradually returning to conventional modes of classroom teaching, and are being able to access physical libraries and academic resources.
Analysis
The new trend set by COVID Pandemic
- The COVID pandemic has jump-started a hitherto sluggish trend (both globally and in India)—“the use of digital platforms to access learning materials”.
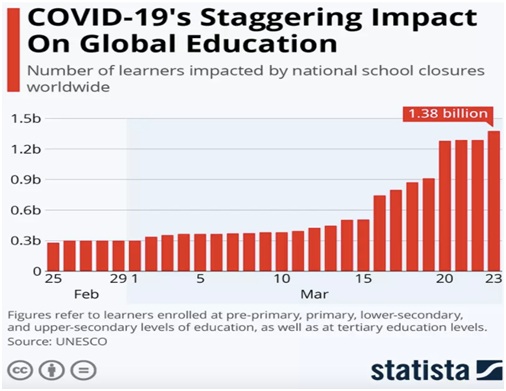
- However, during the pandemic, 6 billion childrenglobally were affected by school closures.
- As a new studypoints out, India’s online education market for classes 1-12 is poised to grow more than six-fold to become a US $1.7-billion market by 2030, while higher education is likely to grow almost four-fold to become a US $1.8-billion market in the same period.
|
Benefits of online learning
|
Type of educational platforms imparting education online (Open and Closed)
- The rise of a platform economy in India has been a key driver of the surge in online learning.
|
Platform A platform can be understood as a business model that creates value by facilitating exchanges between two or more interdependent groups, usually producers and consumers. In the sphere of online education, a digital platform translates into a network that brings together educational publishers and content providers on the one hand, and learners on the other, facilitating transactions between them such that the value of the platform grows with the volume of transactions, publishers, and learners on it. |
Open educational platforms
- Open educational platforms refer to those whose contents are freely available, and on which publishers or research institutions can place their academic products on the basis of their proven credentials as content providers.
Closed educational platforms
- Closed educational platforms are commercially driven.
- In such platforms, access to content is restricted by paywalls; a commercial publisher or ed-tech firm could be the platform owner; and multiple publishers might enter into an arrangement with the platform to make their contents commercially available.
|
Spectacular growth witnessed by Closed platform during COVID
|
Government initiative for e-learning
- SWAYAM: SWAYAM is a programme designed to achieve the three cardinal principles of Education Policy viz., access, equity and quality. It is the government’s national platform for massive open online courses (MOOCS). SWAYAM seeks to bridge the digital divide for students who have hitherto remained untouched by the digital revolution and have not been able to join the mainstream of the knowledge economy.
- National Digital Library of India: The National Digital Library of India (NDLI)—an open platform offering free access to over 55 million educational resources.
- Diksha: This is an initiative of the National Council of Educational Research and Training (NCERT), Ministry of Education, Government of India. DIKSHA can be accessed at diksha.gov.in by the learners and teachers across the country. It currently supports various courses of NCERT, CBSE and SCERTs across India.
- Free and Open Source Software for Education (FOSSEE): FOSSEE is a project promoting the use of open source software in educational institutions.
- Other initiatives include:
- e-ShodhSindhu
- e-PG Pathshala
- Swayam Prabha
- National Programme on Technology Enhanced Learning
|
Constitutional provisions regarding ‘education’ Till 1976, education was sole responsibility of state but constitutional amendment made it ‘concurrent subject’. Fundamental Rights
|
What are the challenges of online learning?
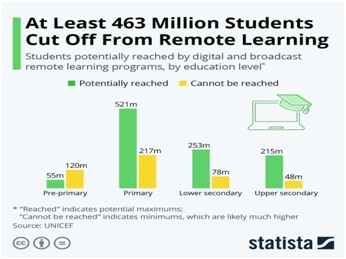
- Lack of internet access: Some students without reliable internet access and/or technology struggle to participate in digital learning; this gap is seen across countries and between income brackets within countries.
- Good, but only as a supplementary option: Online education is still not considered permanent alternatives to classrooms. The sector can at best make a useful supplementary learning system.
- Other issues:
- Uncertainty over accreditation and quality control also remain unresolved.
- Issue for poor households
- Unstable electricity
- Lack of awareness on cyber security and other technical glitches
- Lack of cultural experience
Concluding thoughts
COVID-19 pandemic and consecutive lockdowns have caused a lot of disturbance in the education sector. People started leaning towards the digital platforms of learning. But unfortunately, the coverage is still not uniform throughout the country due to various challenges.
However, in the upcoming future, online education is going to be a part of every person’s life and the country needs to be prepared for the changes. It needs to be considered as a need and not an option.


