

Context
The latest Miller Centre for Social Entrepreneurship (MCSE) report highlighted that Myanmar is one of the least developed countries with the lowest electrification rate in Asia.
Energy needs of Myanmar:
- In 2022, “80 per cent of the rural people had no access to grid electricity”.
- Around 26 per cent of the population in the country lives in poverty.
- Most people living in rural areas use candles, kerosene, batteries, and generators due to the inaccessibility of grid electricity. The poverty rate in rural areas is twice that of urban areas.
- Power generation in Myanmar is dominated by gas (57 per cent) and hydroelectric power (39 per cent).
- The economic growth in such areas has been dampened due to the twin challenges of affordable and reliable electricity.
|
The country’s per capita annual power consumption was 389 kilowatts per hour (kWh) in 2019-20. |
Renewables in Myanmar: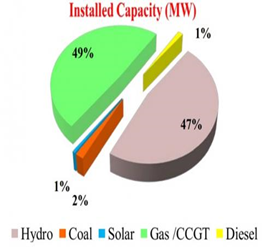
- Myanmar has enormous solar energy potential, specifically in its dry zones.
- The estimated potential for wind energy is 33.83 GW; for solar energy, it is 26.96 GW. Effective tapping of these resources can reduce the carbon footprint of the country, as well as lower its dependency on fossil fuels.
- Myanmar has more than 100 GW of hydropower installed capacity potential, according to estimates.
- Around 92 large hydropower potential projects have been identified with a combined installed capacity of 46 GW.
- The four main large rivers flowing across the country, namely, Ayeyarwady, Thanlwin, Chindwin, and Sittaung, house around 200 large dams built for hydroelectricity.
How can India help Myanmar?
- Strengthening the India-Myanmar electricity grid connection and accessing the large Indian power market can provide Myanmar access to a reliable supply of electricity.
- This will allow the country to employ resources and kick-start the process of larger South Asia-ASEAN power Grid integration.
- About 3-5 MW of power is currently being supplied to Tamu (Myanmar) from Moreh (Manipur, India) through an 11 kV line between the two countries.
India-Myanmar relations:
- India’s gateway to South-East Asia: India and Myanmar share a long 1,643 km geographical land border and maritime boundary in the Bay of Bengal. Myanmar shares borders with 4 Indian states – Mizoram, Manipur, Nagaland and Arunachal Pradesh in Northeast India.
- Infrastructural Projects: India is building the Kaladan Multi-Modal Transit Transport, a road-river-port cargo transport project, to link Kolkata to Sittwe in Myanmar and then from Myanmar’s Kaladan river to India’s north-east.
- India, Myanmar, and Thailand are building the Asian Trilateral Highway, which will connect India to ASEAN.
- Defence: India-Myanmar Bilateral Army Exercise (IMBAX) is aimed at building and promoting closer relations with armies. Myanmar is a key partner in the fight to end insurgency in India's northeast.
Challenges:
- Internal Security: Indo-Myanmar border is porous and lightly policed which is exploited by terrorist outfits and insurgent groups from North Eastern part of India.
- Bilateral trade between India and Myanmar still falls short of expectations.
- China has asserted itself through its soft power as well as through its trade and economic relations with Myanmar by taking up large infrastructure projects.
- India has found it difficult to counter Chinese influence in Myanmar.
- Lack of basic infrastructure and low trading volume at the Indian border.
- The India Intelligence Agency stated that the smuggling of light arms, drugs and counterfeit currencies have been spotted along the border.


