

|
Overview
|
Context
Experts from the ‘Wetlands International’ suggested that wetland conservation should feature as an independent topic of discussion in the negotiations at the upcoming biodiversity and climate change conferences for effective carbon sequestration, mainly in CoP15, and CoP27.
Background
The issue of ‘wetland conservation’ is often avoided or ignored at international level.
- Global Biodiversity Framework, 2002 failed to mention ‘wetlands’ in text.
- Focus area for negotiations in COP15 would include achieving global biodiversity targets. However, it also missed out on wetland conservation on land and sea.
Analysis
What are the Wetlands?
- Wetland refers to almost any habitat where water is key to the environment and its wildlife.
- Examples: swamps, marshes, billabongs, lakes, salt marshes, mudflats, mangroves, coral reefs, fens, peat bogs, or bodies of water - whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary.
- Water within these areas can be static or flowing; fresh, brackish or saline; and can include inland rivers and coastal or marine water to a depth of six metres at low tide.
- There are even underground wetlands.
- Anywhere from estuaries, lakes and rivers to underground aquifers, mangroves, coral reefs and rice paddies count.
|
The Indian definition
“area of marsh, fen, Peat land or water; whether natural or artificial, permanent or temporary, with water that is static or flowing, fresh, brackish or salt, including areas of marine water the depth of which at low tide does not exceed six meters, but does not include river channels, paddy fields, human-made water bodies/ tanks specifically constructed for drinking water purposes and structures specifically constructed for aquaculture, salt production, recreation and irrigation.” |
Distribution of wetland in India
- Globally, wetlands cover 6.4 per cent of the geographical area of the world.
- In India, wetlands are spread over 1,52,600 square kilometres (sq km) which is 4.63 per cent of the total geographical area of the country.
- Of the 1,52,600 sq km,
- inland-natural wetlands- 4%
- coastal-natural wetlands- 3%
- Rivers/streams occupy- 52,600 sq km
- reservoirs/barrages- 24,800 sq km
- inter-tidal mudflats- 24,100 sq km
- tanks/ponds- 13,100 sq km
- lake/ponds- 7300 sq km
- India has 19 types of wetlands.
- State-wise distribution: Gujarat is at the top with 34,700 sq km (17.56 percent of total geographical area of the state), or 22.7 percent of total wetlands areas of the country thanks to a long coastline.
- It is followed by Andhra Pradesh (14,500 sq km), Uttar Pradesh (12,400 sq km) and West Bengal (11,100 sq km).
Why wetlands are valuable for the environment?
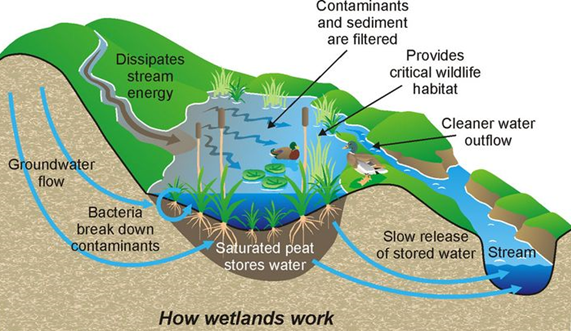
- Balancing ecosystem: Wetlands provide a wide range of important resources and ecosystem benefits such as food, water, fibre, groundwater recharging, water purification, flood moderation, erosion control and climate regulation. They are also one of the major supplies of freshwater.
- Biodiversity hotspot: The wetlands support rich biodiversity and help stabilise water supplies, cleanse polluted waters, protect shorelines, and recharge groundwater aquifers.
- 200 new species are found in freshwater wetlands and are responsible for sequestering almost one third of the global soil carbon.
- Food basket: Wetlands play an integral role in the ecology of the watershed. The combination of shallow water, high levels of nutrients and primary productivity are ideal for the development of organisms that form the base of the food web and feed many species of fish, amphibians, shellfish and insects.
- A safe habitat: They are multifunctional habitats—they nurture a great diversity of life. They are also important as feeding and breeding grounds for migratory birds.
- Climate protection: Wetlands store carbon within their plant communities and soil instead of releasing it to the atmosphere as carbon dioxide. Thus wetlands help to moderate global climate conditions.
- Flood protection: Wetlands function as natural sponges that trap and slowly release surface water, rain, snowmelt, groundwater and floodwaters, which lowers flood heights and reduces erosion.
What is the need for wetland conservation?
The wetlands account for just six per cent of the plant but are home to 40 per cent of world’s plant and animals.
- Disappearing at a fast rate: It is estimated that wetlands are vanishing three times faster than forests and their rate of disappearance is increasing. For instance, 87% of wetlands have been lost since the 1700s and 35% have disappeared since the 1970s.
- Exploitative developmental activities: Wetlands in India are under threat due to urbanization and land-use changes, municipal and industrial pollution and global climate change, which is an important determinant of loss and change in wetland ecosystems.
- Factors causing threat in the long run: Various factors such as infilling for agriculture and construction, pollution, overexploitation of resources, invasive species and climate change threaten their existence.
- Lack of protection & recognition: In India, forests have been historically protected since colonial times, while wetlands have been ignored from long. Over the years people who were traditionally involved in managing wetland share no more there. Even in the way, wetland systems were considered by the government authorities has changed. All this together has impacted the wetlands and their future.
Conclusion
Wetlands not only support high concentrations of biodiversity, but also offer a wide range of important resources and ecological functions such as food, water, fibre, groundwater recharge, water purification, flood moderation, storm protection, erosion control, carbon storage and climate regulation. Wetlands may comprise a minor portion of the planet, but are crucial parts of the ecosystem and are under tremendous pressure. Hence, their conservation is the need of the hour.
|
PRACTICE QUESTION Q1. Discuss the importance and role played by Wetlands in the Ecological conservation of Earth. Q2. What are the threats causing depletion of wetlands? Enumerate measures to conserve wetland ecosystems. |


