Magnetic north and true north (Geographical North Pole) are going to synch for the first time in 360 years.
Issue
Context
Magnetic north and true north (Geographical North Pole) are going to synch for the first time in 360 years.
BACKGROUND
What is the difference between magnetic and geographic poles?
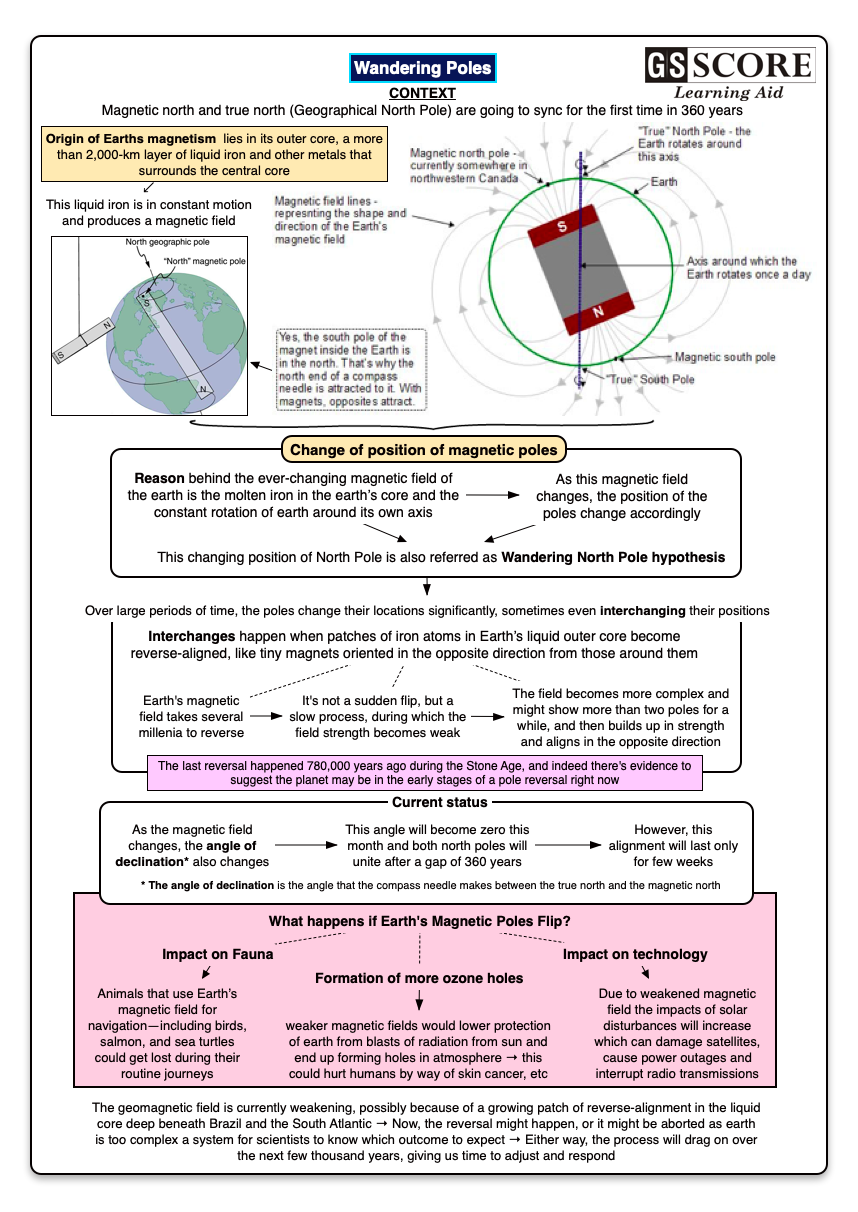
The Earth has two pairs of north and south poles.
- The geographic poles: They are defined by the axis around which the planet rotates, and are fixed.
- Magnetic poles: The Earth behaves like a giant bar magnet and this behaviour defines its magnetic north and south poles, which are not static.
Origin of Earths magnetism:
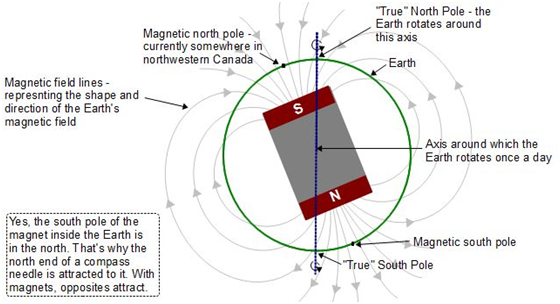
- The origin of Earth’s magnetism lies in its outer core, a more than 2,000-km layer of liquid iron and some other metals like nickel that surrounds the central core, or the innermost part.
- This liquid iron is in constant motion due to Earth’s rotation and various other reasons, and this motion produces a magnetic field.
- The movement of liquid iron and other metals in the outer core of the Earth is known to influence the magnetic field, but this movement is chaotic and turbulent.
- Therefore the Earth’s magnetic behaviour is far more complex than that of a simple bar magnet.
Why magnetic poles often change their position?
- The magnetic poles shift according to the magnetic field of the earth. The presence of the molten iron in the earth’s core and the constant rotation of earth around its own axis are the reasons behind the ever-changing magnetic field of the earth.
- The changing position of North Pole is also referred as Wandering North Pole hypothesis.
- So generally there is the gap between true North Pole and the magnetic north pole of the earth.
- Its north poles and south poles move around sometimes erratically. Over large periods of time, they change their locations significantly, sometimes even interchanging their positions.
How Magnetic poles interchange their positions?
- The geologic record shows that hundreds of pole reversals have occurred throughout Earth's history; they happen when patches of iron atoms in Earth’s liquid outer core become reverse-aligned, like tiny magnets oriented in the opposite direction from those around them.
- Earth's magnetic field takes between 1,000 and 10,000 years to reverse, and in the process, it greatly diminishes before it re-aligns. It's not a sudden flip, but a slow process, during which the field strength becomes weak. The field becomes more complex and might show more than two poles for a while, and then builds up in strength and align in the opposite direction.
- When the reversed patches grow to the point that they dominate the rest of the core, Earth's overall magnetic field flips. The last reversal happened 780,000 years ago during the Stone Age, and indeed there's evidence to suggest the planet may be in the early stages of a pole reversal right now.
What happens if Earth's Magnetic Poles Flip?
- Formation of more ozone holes: A strong magnetic field helps protect Earth from blasts of radiation from the sun. Due to weak magnetic field the charged particles bombarding Earth's atmosphere during solar storms would punch holes in Earth's atmosphere, and this could hurt humans. These 'holes' would not be permanent, but might be present on one- to 10-year timescales and could be the cause of skin cancer.
- Impact on Fauna: Animals that use Earth’s magnetic field for navigation—including birds, salmon, and sea turtles could get lost during their routine journeys.
- Impact on technology: Due to weakened magnetic field the impacts of solar disturbances will increase which can damage satellites, cause power outages and interrupt radio transmissions.
- Some scientist believe that there is a relation between reversal of magnetic field and species extinction but some believe that there is no such relation.
What is the current position of magnetic poles?
- Currently, the magnetic north pole is located somewhere over northern Canada as discovered in 1831 by Sir James Clark Ross.
- The magnetic South Pole is near McMurdo Sound, at the sea edge of the Antarctic continent.
- Since then the magnetic north pole has been moving across the Canadian Arctic towards Russia, and has moved hundreds of miles over the last several decades.
The magnetic compass points towards which pole and what are the related concepts?
- A compass needle generally points at the earth’s magnetic north pole.
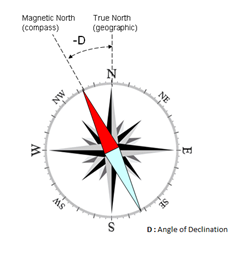
- As the magnetic field changes so that angle of declination also changes. The angle of declination is the angle that the compass needle makes between the true north and the magnetic north.
- The angle of declination will become zero this month. And both north poles will unite after a gap of 360 years. This alignment will last only for few weeks.
- Over the past few hundred years the declination has been negative as all compass needles have pointed west of the true north.
- Now after few weeks scientists are speculating that the declination will become positive and the compass needles will point east of the true north.
Conclusion:
The geomagnetic field is currently weakening, possibly because of a growing patch of reverse-alignment in the liquid core deep beneath Brazil and the South Atlantic. The reversal might happen, or it might be aborted — Earth is too complex a system for scientists to know which outcome to expect. Either way, the process will drag on over the next few thousand years, giving us time to adjust to the changes.
Learning Aid
Practice Question:
What is the difference between magnetic and geographic poles and also discuss why magnetic poles often change their position?