

Context
At least eight people have been killed in wildfires that have ripped through southern Turkey, ravaging coastal resorts and forcing tourists to flee.
Background
- Forest fire is a major cause of injury and loss to forests, with the population increase, the frequency and subsequent damage due to forest fire is increasing day by day.
- Major forest fires recently witnessed were- Australia Bush Fire, Uttarakhand forest fire, Russian wildfires etc.
- Climate change, anthropogenic activities are seen as major cause of wildfires with increased frequency in recent past.
Analysis
Types of Forest Fire
- Surface fires: Surface fire is the most common forest fires that burn undergrowth and dead material along the floor of the forest. It is the type of fire that burns surface litter, other loose debris of the forest floor and small vegetation.
- Underground fires: The fires of low intensity, consuming the organic matter beneath and the surface litter of forest floor are sub-grouped as underground fire. In most of the dense forests a thick mantle of organic matter is found on top of the mineral soil. This fire spreads in by consuming such material.
- Ground fires: There is no clear distinction between underground and ground fires. The smoldering underground fire sometime changes into ground fire. This fire burns root and other material on or beneath the surface i.e. burns the herbaceous growth on forest floor together with the layer of organic matter in various stages of decay.
- Crown fires: Crown fire is the most unpredictable fires that burn the top of trees and spread rapidly by wind. In most of the cases these fires are invariably ignited by surface fires. Since it is over the heads of ground force it is uncontrollable until it again drops to the ground, and since it is usually fast moving, it poses grave danger to the fire fighters becoming trapped and burned.
Causes of Forest fire
More than ninety five percent forest fires are caused either by negligence or unknowingly by the human being. The rest of the fires are caused by natural reasons i.e. lightning, extreme rise in the temperature etc., which are very rare.
|
Natural Cause |
Anthropogenic Cause |
|
|
Deliberate |
Accidental |
|
|
Lighting |
Shifting Cultivation |
Collection of Non Timber Forest Produce |
|
Friction of rolling stones |
To flush growth of tendu leaves |
Burning farm residues |
|
Rubbing of dry bamboo clumps |
To have good growth of grass and fodder |
Driving away wild animals |
|
Volcanic explosion |
To settle score with forest department or personal rivalry |
Throwing burning bidi/cigarettes |
|
To clear path by villagers |
Camp fires by picnickers |
|
|
To encroach upon the forest land |
Sparks from vehicle —exhaust |
|
|
For concealing illicit felling |
Sparks from transformers |
|
|
Tribal traditions/ customs |
Uncontrolled prescribed burning |
|
|
Resin tapping |
||
|
Making charcoal in forests |
||
|
Extracting wine in forest |
||
|
Sparks from cooking near the forest |
||
|
Heating coal tar for road construction in forest |
||
Damage caused by Forest Fire
- Loss of valuable timber resources
- Forest fires cause indispensable loss to timber and deteriorate its quality. Valuable timber species like teak, sal, chir, deodar, sheesam, rosewood etc. are adversely affected by fire
- Impact of forest fire on eco- system
- The most damaging impact of forest fire on ecosystem is very evident in the Himalayas, where hills existing between the heights of 1000 to 1800 meters are dominated by pine forests and seem to be more fire prone.
- The uncontrolled fires in such areas help in spreading pine forest at the cost of indigenous oak forest, which is very serious threat to the ecological balance in the Himalayan region.
- Degradation of water catchments areas resulting into loss of water
- After forest fire, soil moisture is decreased and litter decomposition becomes almost negligible, which creates a possibility of forest fire in future.
- Loss of wildlife habitat and depletion of wildlife
- Forests are the habitat of many wild animals, when fire becomes uncontrolled, the problem of survival of animals and their habitat arises.
- The forest fires in Sankhuwasabha and Ilam in Nepal claimed red pandas, leopards as well as monkeys, deer, bear and other species.
- Global warming
- The immediate effect of vegetation burning is the production and release of gases including carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, non-methane hydrocarbons, nitric oxide, methyl chloride and various other gases, which are released and returned to the atmosphere.
- Soil erosion
- The scientific studies indicate that erosion of the soil from the forest land depends on many factors i.e. the soil porosity, its mineral composition, the texture, the gradient of the land and length etc.
- All these factors decide the ease with which the individual soil particles are detached
|
National Action Plan on Forest Fires, 2018
|
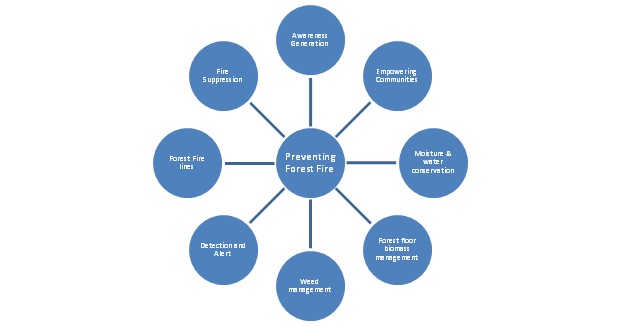
Conclusion
It is critical to monitor and understand such fires using satellite data so that we can successfully manage them in a warmer world.
Understanding both the immediate and long-term effects of fire requires long-term global datasets that follow fires from their detection and that accurately map the scale of the burned area.


