Context
The flocks of birds are dwindling in numbers as they navigate through regions that are becoming ‘increasingly uninhabitable’ for them. Nearly half of all migratory species are in decline.
1: Dimension-Factors responsible for decline
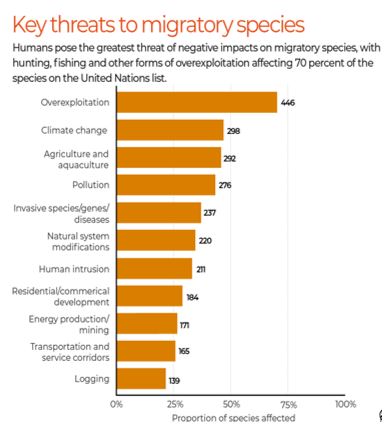
- Loss of natural habitat and overexploitation: These species face shifting landscapes due to urbanisation, farming and climate change among several other challenges.
- Habitat loss happens when land becomes urbanised, transformed for human use or degraded through pollution. Farming is a primary driver of this sort of fragmentation.
- Migratory birds have experienced significant declines across certain regions, particularly those using the Afro-Palearctic migratory route. These birds typically travel southwards across Africa from Europe and Asia.
- Agricultural and industrial activity also release dangerous chemicals into habitats.
2: Dimension-Role of climate change in affecting migratory species
- Decline: Climate change is the second most significant factor contributing to the decline of migratory species.
- Changes to natural landscape: The changes in temperature, precipitation and weather patterns can affect the suitability of breeding and stopover sites along migration routes.
- Direct mortality of species or less breeding: Species may no longer be able to follow their usual migratory patterns.
3: Dimension-Impact of this decline on human and environment
- Ecological, economic and cultural importance: They help keep ecosystems from degradation and collapse. This can especially support carbon sequestration, the removal of carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, which mitigates climate change. This occurs through thicker vegetation or healthier coral reefs, for instance.
- Strong coastal ecosystems: They can also hold back floods and storm surges.
- Other “ecosystem services”: Pollination, seed dispersal, and pest-control.
|
DATA BOX IUCN Report
Migratory Flyways
|
|
Mains Practice Question Q: Migratory species globally are facing critical challenges, with nearly half in decline. Analyse the impact of climate change as an “amplifier” of other such threats as overexploitation and habitat loss along the Central Asian Flyway, citing specific examples. |