19th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
According to a new study, a seasonal imbalance of the ratio of solar energy absorbed by Mars and heat released by the planet into space may be fuelling dust storms in the red planet.
Background
Key findings:
- The ratio, known as energy budget, goes out of balance in the spring and summer seasons of red planet’s southern hemisphere.
- The resultant dust storms cover areas as large as continents on Earth and last for weeks.
- According to NASA, the storms are so intense that they’ve been captured by Earth’s telescopes.
- Energy excess (when the planet absorbs more energy than it emits) can be one of the drivers of Mars’ dust storms.
How is it important for us?
- Earth has an energy budget, too. Therefore, Mars’ energy budget might provide clues about the role Earth’s energy budget plays in developing severe storms, including hurricanes.
- The researchers calculated that the global average emitted power is around 111.7 watts per square metre on Mars.
- But this varied during seasons.
- The energy excess in ‘northern autumn’, a southern hemisphere season, is roughly 15.3 per cent of the emitted energy.
- This imbalance could affect the seasonal change of surface temperature on Mars.
- The researchers found a correlation between dust storms and emitted energy by comparing emitted energy in dust storm years and non-dust storm years on Mars.
- Dust storms lift clouds of dust from the surface to the atmosphere, thereby changing the incoming solar energy and outgoing thermal energy.
- For the energy imbalance at longer time scales (more than one Earth year), Earth has a small energy imbalance (lesser than 0.1 per cent of the emitted thermal energy).
- Such an energy imbalance plays a critical role in global warming and climate change on Earth.
Energy Budget:
- The radiant energy budget of a planet is essential to understanding its surface and atmospheric processes.
- Mars has strong seasonal and diurnal variations of emitted power.
- The strong seasonal variations further suggest an energy imbalance at the time scale of Mars’ seasons (e.g., ∼3% of the emitted power in the Northern autumn for the Southern Hemisphere), which could play an important role in generating dust storms on Mars.
|
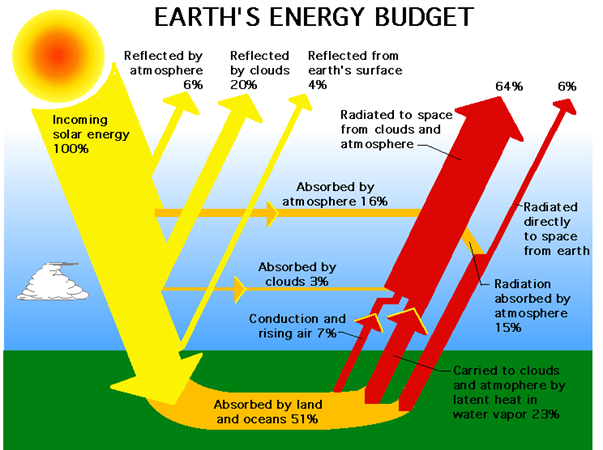
Earth’s heat budget:
Ways of heating & cooling of earth’s atmosphere:
|
More Articles