

23rd November 2023 (11 Topics)
Context:
According to study published in Nature Communications, meteorological conditions have largely driven fluctuations in the size of the Antarctic ozone hole.
Minutes of the Study:
- The ozone hole over the Antarctic has not only grown larger but also thinner throughout most of the spring.
|
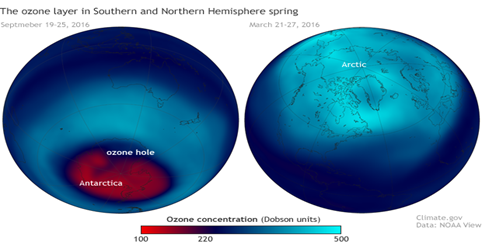
About Ozone Hole in Winters:
|
- Despite making a recovery in area and depth since the 2000s, the Antarctic ozone hole has been massive in the last four years
- There is much less ozone in the centre of the ozone hole compared to 19 years ago.
UNEP study on Ozone Hole:
- The ozone layer is on track to recover within four decades.
NASA Study on Ozone Hole:
- The hole averaged 23.1 million square kilometres, approximately the size of North America, making it the 16th largest over this period.
Changes in Antarctic Ozone Hole:
- Reduction in Ozone: The researchers saw a total reduction of 26 per cent at the core of the ozone hole from 2004 to 2022.
- Effectiveness of Montreal Protocol: The reduction is despite the 1987 Montreal Protocol on Substances that Deplete the Ozone Layer, which regulates the production and consumption of human-generated chemicals known to deplete the ozone.
- The Montreal Protocol on Ozone Depleting Substances quadrennial assessment report of 2022 confirmed the phase-out of nearly 99 per cent of banned ozone-depleting
Meteorological Conditions in Ozone Depletion:
- Ozone hole and Meteorological Conditions: According to UNEP, Meteorological conditions could have largely driven fluctuations in the size of the Antarctic ozone hole, from 2019 to 2021.
- Other factors: It is known that other factors such as springtime temperature and wind patterns, aerosols from wildfires and volcanic eruptions, as well as changes in the solar cycle ozone hole development could also be responsible.
- Polar vortex: The Antarctic ozone hole sits within the polar vortex, which is a circular pattern of wind in the stratosphere that forms during winter and is maintained until late spring.
- Within this vortex, the Antarctic air from the mesosphere (the atmospheric layer above the stratosphere) falls into the stratosphere.
- Ozone Chemistry: This intrusion of air brings natural chemicals (nitrogen dioxide) which impact ozone chemistry in October.
More Articles


