

20th June 2024 (10 Topics)
Context
Recent research has examined the aftermath of methane release resulting from explosions damaging the Nord Stream pipelines in September 2022. An estimated 10,000 to 50,000 tonnes of methane dissolved in the surrounding seawater post-explosion.
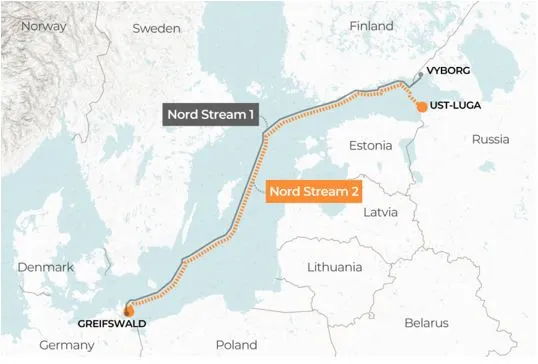
About Nord Stream Pipeline
- Nord Stream 1 (NS1) and Nord Stream 2 (NS2), constructed by Russia's Gazprom, span 1,200 km across the Baltic Sea, each consisting of two large pipes.
- They were designed to transport 110 billion cubic meters of natural gas annually from Russia to Germany.
- 2022 Explosions: In September 2022, explosions damaged both NS1 and NS2 at multiple points in Swedish and Danish waters, rendering them non-operational. This incident raised significant environmental concerns due to the release of methane.
Key-highlights of the Study
- The methane release from the Nord Stream explosions is among the largest documented from such events, underscoring its environmental significance.
- During the incident, methane emissions from the breaches reached 79 tonnes per hour into the atmosphere, totaling approximately 40,000 tonnes over seven days.
- Methane concentrations in seawater ranging from 10,000 to 55,000 metric tonnes. This poses potential risks to microbial ecosystems and could influence the growth of methane-consuming bacteria.
Fact Box: About Methane and its Emission
|
More Articles


