

19th April 2025 (11 Topics)
Context
Recently, reports have suggested that the United States may be willing to recognise Russia’s control over Crimea as part of a broader peace deal with Ukraine. This potential shift is happening amid efforts by US President Donald Trump to negotiate a ceasefire between Russia and Ukraine, which remains one of the most severe armed conflicts in Europe since World War II.
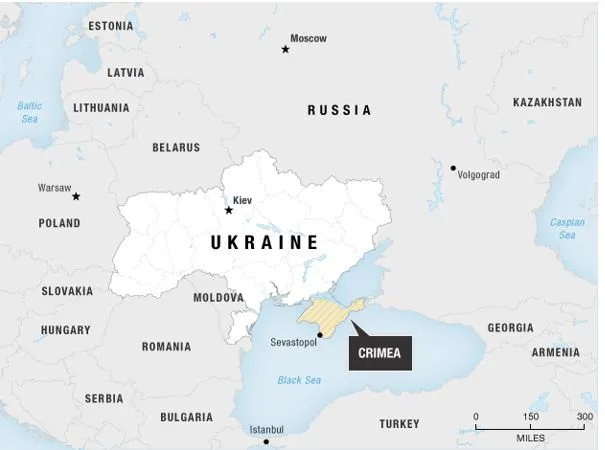
What is Crimea and why is it controversial?
- Crimea is a peninsula that juts into the Black Sea, located in southern Ukraine, and is connected to mainland Ukraine by a narrow strip of land. To the east, it is separated from Russia by the Kerch Strait.
- Area and Capital: Crimea spans 27,000 sq. km (roughly the size of Belgium). Its capital is Simferopol.
- Strategic Bridge: Russia constructed the Kerch Bridge linking Crimea with mainland Russia, but this has sustained war-related damage during the conflict.
- Background:
- Russian Empire Era: Crimea was absorbed into the Russian Empire by Catherine the Great in the 18th century. The naval base at Sevastopol was soon established.
- Crimean War (1853–1856): The war was fought between Russia and the Ottoman Empire (aided by Britain and France); it reshaped European geopolitics and is seen as a precursor to World War I.
- Soviet Period: Crimea became part of the Soviet Union in 1921. In 1954, Nikita Khrushchev (then Soviet Premier and a Ukrainian) transferred Crimea to Soviet Ukraine.
- Post-Soviet Disputes: After the USSR’s collapse in 1991, disputes grew between Russia and Ukraine over Crimea’s status.
- Russian Annexation in 2014: In 2014, after the fall of Ukraine’s pro-Russia President Viktor Yanukovych, Russia invaded Crimea and held a controversial referendum, claiming overwhelming support for joining Russia.
- The annexation was rejected by the United Nations General Assembly, the US, and the EU.
- Sanctions were imposed on Russia.
- The Kremlin maintains that the issue is settled, despite limited international recognition.
- Agriculture and Industry:
- The region is important for crops like wheat, corn, and sunflowers.
- The Kerch region in eastern Crimea has iron ore mining.
- Two grain storage terminals exist — one in Kerch and one in Sevastopol.
What’s Happening Now?
- Amid the ongoing war, which began in February 2022, there is growing diplomatic pressure to find a peace solution.
- The United States has been trying to push for a negotiated ceasefire.
- But the peace talks are progressing slowly, and US officials have expressed frustration, suggesting that Washington may withdraw from mediation if there is no breakthrough soon.
Why this matters?
- International Law at Stake: Recognising Crimea as Russian could legitimise forceful territorial expansion, weakening the global rules-based order.
- US Policy Shift: This move would represent a major shift in US foreign policy and could divide Western allies, many of whom oppose any concession to Russia.
- Geopolitical Precedent: If accepted, this deal may set a dangerous precedent for other countries with territorial ambitions — such as China in the South China Sea or Taiwan.
- Ukraine’s Sovereignty: The proposed compromise undermines Ukraine’s national sovereignty and long-standing aspirations to integrate with NATO and the EU.
More Articles


