

A group of global philanthropic foundations, including UBS Optimus Foundation, British Asian Trust, Michael & Susan Dell Foundation, and Tata Trust have announced a Development Impact Bond (DIB) worth $11 million.
Context
A group of global philanthropic foundations, including UBS Optimus Foundation, British Asian Trust, Michael & Susan Dell Foundation, and Tata Trust have announced a Development Impact Bond (DIB) worth $11 million.
About
- It is an innovative education financing model based on measurable outcome rather than the present input model of social financing that does not bother about result.
- To be known as Quality Education India, it is expected to improve education outcome of 300,000 students in Delhi and Gujarat.
- It is the largest education DIB in the world.
Development Impact Bonds (DIBs)
- They are a performance-based investment instrument intended to finance development programmes in low resource countries, which are built off the model of social impact bond (SIB) model.
- The first social impact bond was originated in UK in 2010, supported by the Rockefeller Foundation, structured to reduce recidivism among inmates from Peterborough Prison.
- DIB is not a money market instrument.
How it works?
- Investors identify a problem and then ‘risk investor’ or a group puts money upfront to roll out the programme.
- If the programme becomes a success, the “outcome funders” pay back the risk investors the funds invested plus a certain percentage of incentives.
- If the target is not achieved, the risk investor is not paid.
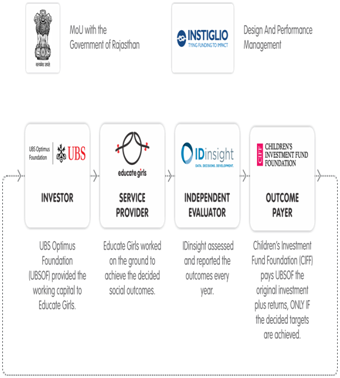
- The innovative results-based financing model works through the collaboration of three key stakeholders – a primary investor, the service provider, and the outcome payer.
- Primary investor: One who funds the social impact project expecting a return at the end.
- Second key stakeholder: The service provider that executes the projects on the ground, to attain results by funds procured from the primary investor.
- Outcome payer: One who pays the primary investor the full investment plus returns on successful attainment of the bond’s targets.
- An independent evaluator verifies the service provider’s achievement.
DIB in India:
- In 2015, an innovative financing experiment was started in Rajasthan, known to be the Educate Girls Development Impact Bond (DIB).
- It aimes to provide a targeted intervention to 9,000 out-of-school girls in Bhilwara district where one in 10 girls aged between 11 and 14 were kept out of school.
- By July 2018, the programme had achieved 116% of its enrolment target and 160% of its learning target.
- Student enrolment was defined by the percentage of out-of-school girls (between the ages of seven and 14) enrolled in school by the end of the third year.
- Students’ learning was measured using the ASER test.
Other such DIBs in India:
- Britain's Prince Charles had launched a 10-million-dollar Development Impact Bond (DIB) to help improve education for over 200,000 children in India in February 2018.
- The Utkrisht Impact Bond is the world’s first maternal and newborn health impact bond. It was developed by partners including USAID and others.
Benefits:
- Impact bonds are an innovative way to finance development.
- They are 100% focused on outcomes and have the potential to leverage private investor capital to address some of the world’s greatest challenges.
Significance
- This landmark financial instrument applies an entrepreneurial approach to philanthropy and is likely to change the lives of millions of children and women in India by driving up standards.
- If the potential of this type of funding is unleashed, it could improve the lives of generations to come.


