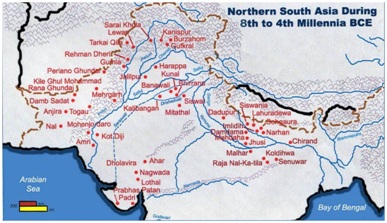
Context
Dholavira, the archaeological site of a Harappan-era city has received the UNESCO world heritage site tag. Dholavira became the fourth site from Gujarat and 40th site from India to make to the list. It is the first site of the Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC) in India to get recognition.
About
Important facts about Dholavira
- The Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC)city is located on a hillock near the present-day Dholavira village in the Kutch district.
- Dholavira is located on Khadir Island.
- The site was discovered in 1968 by archaeologist JagatPati Joshi and was excavated between 1990 and 2005 under the supervision of archaeologist Ravindra Singh Bisht.
- After Mohen-jo-Daro, Ganweriwala, and Harappa in Pakistan and Rakhigarhi in Haryana of India, Dholavira is the fifth largest metropolis of IVC.
- The ancient city was a commercial and manufacturing hub for about 1,500 years.
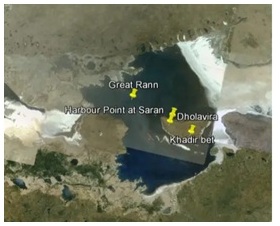
What are the distinct features of this ancient site?
- The site has a fortified citadel, a middle town, and a lower town.
- The walls of the city are made of sandstone or limestone instead of mud bricks like in many other Harappan sites.
- The city also has a cascading series of water reservoirs, outer fortification, and two multi-purpose grounds, one for festivities and another used as a marketplace.
- It also had nine gates with unique designs, and funerary architecture, which featured tumulus hemispherical structures like Buddhist Stupas.
- Like the graves at other IVC sites, no mortal remains of humans are discovered at Dholavira.
- Memorials that contain no bones or ashes but contain offerings of precious stones, etc. add a new dimension.
- People in Dholavira knew metallurgy.
- The traders of Dholavira used to source copper ore from Rajasthan, Oman, and UAE and export finished products.
- The beads specific to the Harappan workmanship have also been found in the royal graves of Mesopotamia that indicatesDholavira used to trade with the Mesopotamians.
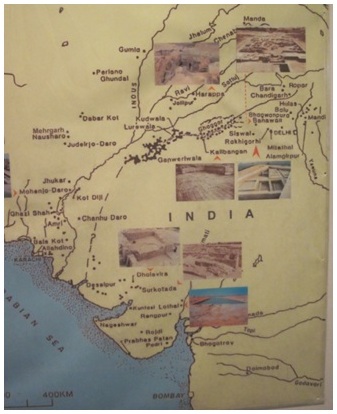
Other Harappan sites in Gujarat
- Lothal, in Saragwala village on the bank of Sabarmati
- Rangpur on the bank of Bhadar river in Surendranagar district
- Rojdi in Rajkot district
- Prabhas near Veraval in GirSomnath district
- Lakhabaval in Jamnagar
- Deshalpar in Bhujtaluka of Kutch
|
Indus Valley Civilisation (IVC)
|