Scientists from Agharkar Research Institute (ARI), Pune, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology have developed a biofortified durum wheat variety MACS 4028, which shows high protein content.
Context
Scientists from Agharkar Research Institute (ARI), Pune, an autonomous institute under the Department of Science & Technology have developed a biofortified durum wheat variety MACS 4028, which shows high protein content.
About
- MACS 4028 is a semi-dwarf variety, which matures in 102 days and has shown the superior and stable yielding ability of 19.3 quintals per hectare.
- It is resistant to stem rust, leaf rust, foliar aphids, root aphids, and brown wheat mite.
- The wheat variety has shown:
- high protein content of about 14.7%
- better nutritional quality having zinc 40.3 ppm, and iron content of 40.3ppm and 46.1ppm respectively
- good milling quality and overall acceptability
- The MACS 4028 variety is also included by the Krishi Vigyan Kendra (KVK) programme for United Nations Children's Fund (UNICEF) to alleviate malnutrition in a sustainable way.
- It can boost the Vision 2022 “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat”, the National Nutrition Strategy. An endeavor to tackle the hidden hunger in the rural areas of India is being continued using traditional plant breeding approach to achieve “Kuposhan Mukt Bharat.”
- The wheat variety MACS 4028 has been notified by the Central Sub-Committee on Crop Standards, Notification and Release of Varieties for Agricultural Crops (CVRC) for timely sown, rainfed condition of Peninsular Zone, comprising Maharashtra and Karnataka.
- Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) has also tagged this variety under the Biofortified category during the year 2019.
What is Biofortification?
- Fortification is the practice of deliberately increasing the content of an essential micronutrient, i.e. vitamins and minerals (including trace elements) in a food, so as to improve the nutritional quality of the food supply and provide a public health benefit with minimal risk to health.
- Biofortification is the process by which the nutritional quality of food crops is improved through agronomic practices, conventional plant breeding, or modern biotechnology.
- Examples of biofortification projects include:
- iron-biofortification of rice, beans, sweet potato, cassava and legumes;
- zinc-biofortification of wheat, rice, beans, sweet potato and maize;
- provitamin A carotenoid-biofortification of sweet potato, maize and cassava; and
- amino acid and protein-biofortification of sourghum and cassava.
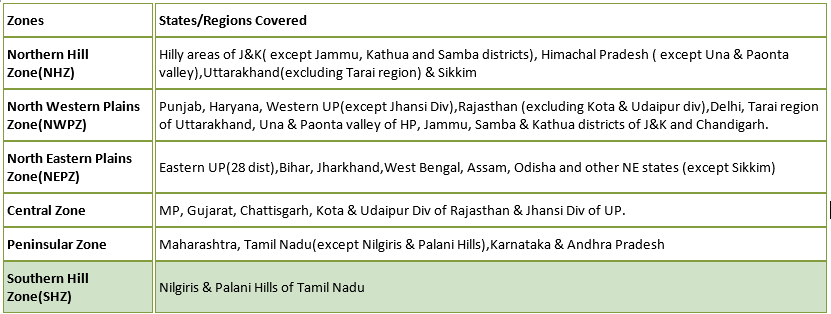
India & its wheat production:
- Wheat crop in India is grown under six diverse agro-climatic zones as follows:
- In the peninsular zone of India (Maharashtra and Karnataka states), wheat cultivation is majorly done under rainfed and limited irrigation conditions.
- Under such conditions, the crop experiences moisture stress. Hence, there is a high demand for drought-tolerant varieties.
- Efforts for the development of high yielding, early maturing varieties with good quality and disease resistance for rainfed conditions are carried out at Agharkar Research Institute, Pune under All India coordinated Wheat and Barley improvement programme, coordinated through Indian Institute of Wheat and Barley Research Karnal governed by the Indian Council of Agriculture Research.
- The MACS 4028 is an outcome of such intervention for the farmers.