The Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR) released the Glacial Lake Atlas of Ganga Basin.
Context
The Department of Water Resources, River Development, and Ganga Rejuvenation (DoWR, RD & GR) released the Glacial Lake Atlas of Ganga Basin.
- The NHP –Bhuvan portal was also launched.
About
About the Glacial Lake Atlas
- The present glacial lake atlas is based on the inventoried glacial lakes in part of Ganga River basin from its origin to foothills of Himalayas covering a catchment area of 2,47,109 sq. km.
- The study portion of Ganga River basin covers part of India and transboundary region.
- The Ganga River Basin Atlas is brought out under the National Hydrology Project (NHP).
- The atlas is prepared with the efforts of the National Remote Sensing Centre (NRSC), ISRO under the National Hydrology Project (NHP).
|
National Hydrogen Project (NHP)
|
|
NHP-Bhuvan Portal
|
About Ganga Basin
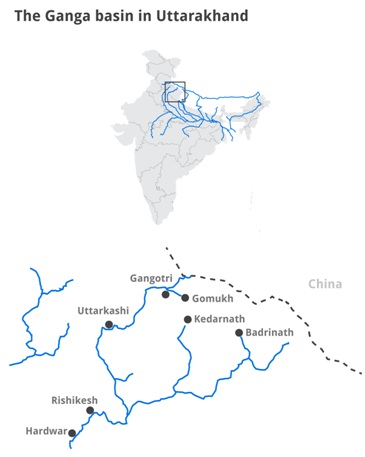
- The Ganges River originates in the Himalaya Mountains at Gomukh, the terminus of the Gongotri Glacier.
- When the ice of this glacier melts, it forms the clear waters of the Bhagirathi River.
- As the Bhagirathi River flows down the Himalayas, it joins the Alaknanda River, officially forming the Ganges River.
- The Ganges River Basin is sometimes considered part of a larger river basin consisting of the nearby Brahmaputra and Meghna rivers.
- Known as the Ganges-Brahmaputra-Meghna (GBM) River Basin, it is one of the largest river systems in the world.
|
River Basin
|
Utilization of the Atlas
- The atlas provides a comprehensive and systematic glacial lake database for Ganga River basin with size > 0.25 ha.
- The atlas also provides authentic database for regular or periodic monitoring changes in spatial extent (expansion/shrinkage), and formation of new lakes.
- The atlas can also be used in conjunction with glacier information for their retreat and climate impact studies.
- Central and State Disaster Management Authorities can make use of the atlas for disaster mitigation planning and related program.
Glacial Lakes and Glacial lake outburst flood (GLOF)
|