

10th May 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
The Institute of Wood Science and Technology (IWST), has conducted an analysis of plantations in five states — Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Kerala, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana.
- It has found that the loss to timber plant grower is because of the unnecessary pruning of the timber trees.
About
What is Pruning?
- Pruning is the practice of removing a specific part of a tree or shrub drying or dying due to pests, diseases and lack of sunlight.
- Several tree species self-prune; it is a part of their biological process.
- Fruit farmers also prune trees, such as mango, pomegranate, moringa and mulberry after every harvest, based on recommendation from horticultural scientists.
- But here, apart from maximising yield, the practice is also for convenience.
- Pruning limits the height of the branches and ensures easy access to leaves, flowers and fruits. The removed limbs, if healthy, can then be replanted.
- Similarly, trees in public parks and gardens are pruned to control their shape and structural integrity, thereby increasing their aesthetic value.
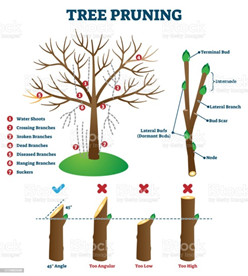
Effects of pruning:
- The bark is the trees’ first line of defence; it protects the inner layers of the stem — sapwood, which forms the peripheral part of the trunk just beneath the bark and heartwood, the central core.
- But when branches are pruned, the bark gets wounded and dries and the cut ends expose the inner tissues.
- Bio-deteriorating organisms such as wood-decaying fungi (namely Allophoma tropica, Ganoderma applanatum and Xylaria berteroi) and insects like wood borers tend to feed on the dried bark and infest the cut ends of the stem.
- Soon, they attack the inner layers and cause decay. This makes the tree weak; leaves grow small and fruits drop prematurely.
- Pruning-induced wounds also hinder the natural growth of branches, leading them to bunch profusely at certain points.
- This disrupts the tree’s balance and makes it vulnerable to heavy winds.
- Pruned trees often need support from wooden planks to stay upright, but these too attract termites when they dry. In many instances, such trees die quickly.
- Pruning has also restricted pollinating insects from accessing nutrient and nesting resources, affecting their foraging and nesting behaviour and phenology and reproduction.
- This will have an adverse effect on cross-pollinating species like sandalwood and teak.
More Articles


