

6th October 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
A New research supports the hypothesis that Alzheimer's disease is caused by a decline in levels of a protein called amyloid-beta.
About
Details of the Study:
- The research is focused on a protein called ‘amyloid-beta’. The protein normally carries out its functions in the brain in a form that is soluble, meaning dissolvable in water, but it sometimes hardens into clumps, known as ‘amyloid plaques’.
- The plaques are simply a consequence of the levels of soluble amyloid-beta in the brain decreasing.
- These levels decrease because the normal protein, under situations of biological, metabolic or infectious stress, transform into the abnormal amyloid plaques.
- In the Current study, it was also analysed that levels of amyloid-beta in a subset of patients with mutations that predict an overexpression of amyloid plaques in the brain, which is thought to make them more to develop Alzheimer’s disease.
Alzheimer as a disease:
- In Alzheimer’s disease the neurons stop functioning, lose connections with other neurons, and dies.
- Alzheimer’s disrupts processes vital to neurons and their networks, including communication, metabolism, and repair.
- Effects:
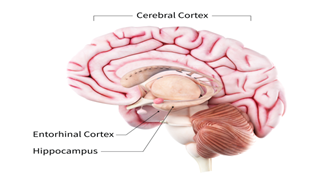
- Alzheimer’s disease typically destroys neurons and their connections in parts of the brain involved in memory, including the entorhinal cortex and hippocampus.
- Eventually, many other areas of the brain are damaged. Over time, a person with Alzheimer’s gradually loses his or her ability to live and function independently.
- Ultimately, the disease is fatal.
How they are responsible for Alzheimer
- The beta-amyloid protein involved in Alzheimer’s comes in several different molecular forms that collect between neurons.
- It is formed from the breakdown of a larger protein, called amyloid precursor protein. One form, beta-amyloid 42, is thought to be especially toxic.
- In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that collect between neurons and disrupt cell function.
Characteristics of Brain with Alzheimer
- Neurofibrillary tangles: Neurofibrillary tangles are abnormal accumulations of a protein called tau that collect inside neurons. Healthy neurons, in part, are supported internally by structures called microtubules, which help guide nutrients and molecules from the cell body to the axon and dendrites.
- Chronic inflammation: In Alzheimer’s, parts of brain cells fail to clear away waste, debris, and protein collections, including beta-amyloid plaques.
- Vascular contributions to Alzheimer’s disease: Vascular problems may lead to reduced blood flow and oxygen to the brain, as well as a breakdown of the blood-brain barrier, which usually protects the brain from harmful agents while allowing in glucose and other necessary factors.
- Loss of neuronal connections and cell death
More Articles


