

24th May 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
Researchers from the National Institute of Health Doutor Ricardo Jorge (INSA), Lisbon, Portugal have shared the draft genome sequence of the monkeypox virus that is rapidly spreading in many European countries.
About
Draft Genome Sequencing:
- The released draft genome sequence covers about 92% of the reference sequence.
- Researchers from Belgium were able to reconstruct 98.9% of the genome.
- The phylogenetic analysis of the draft genome indicates that the 2022 virus belongs to the West African clade and is most closely related to viruses associated with the exportation of monkeypox virus from Nigeria to several countries in 2018 and 2019, namely the United Kingdom, Israel and Singapore.
Monkey Pox:
- Monkeypox virus is an orthopoxvirus that causes a disease with symptoms similar, but less severe, to smallpox.
- While smallpox was eradicated in 1980, monkeypox continues to occur in countries of Central and West Africa.
- Two distinct clade are identified: the West African clade and the Congo Basin clade, also known as the Central African clade.
- Monkeypox is a zoonosis- a disease that is transmitted from animals to humans.
- Cases are often found close to tropical rainforests where there are animals that carry the virus.
- Evidence of monkeypox virus infection has been found in animals including squirrels, Gambian poached rats, dormice, different species of monkeys and others.
- Detection of viral DNA by polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is the preferred laboratory test for monkeypox.
- The best diagnostic specimens are directly from the rash – skin, fluid or crusts, or biopsy where feasible.
- Antigen and antibody detection methods may not be useful as they do not distinguish between orthopoxviruses.
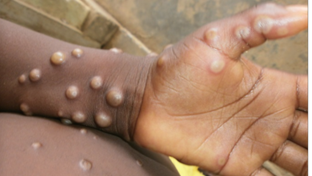
- Symptoms: Monkeypox presents with fever, an extensive characteristic rash and usually swollen lymph nodes.
- It is important to distinguish monkeypox from other illnesses such as chickenpox, measles, bacterial skin infections, scabies, syphilis and medication-associated allergies.
- According to the WHO, the proportion of patients who die has varied between 0 and 11% in documented cases, and has been higher among young children.
More Articles


