10th August 2023 (6 Topics)
Context
The recent increase in coal consumption, despite the increase in solar and wind power, suggests that reliable and low-carbon electricity resources are critical to ensure the deep decarbonisation of power generation, along with grid stability and energy security.
Small modular reactors – a type of nuclear reactor – can be helpful to India in this regard.
About
Sources of Energy Production:
- India’s Energy sector is one of the most diversified in the world. Sources of power generation range from conventional sources such as coal, lignite, natural gas, oil, hydro and nuclear power, to viable non-conventional sources such as wind, solar, agricultural and domestic waste.
- India was ranked fourth in wind power, fifth in solar power and fourth in renewable power installed capacity, as of 2020.
- Near-universal household access to electricity was achieved in 2019, meaning that over 900 million citizens have gained an electrical connection in less than two decades.
- But, the per capita electricity consumption in India is only one-third of the global average, even though the demand for energy has doubled.
- So, to catch up with the increasing demand for energy, there is a need to make arrangements for a secure and sustainable form of self-reliance in the energy sector.
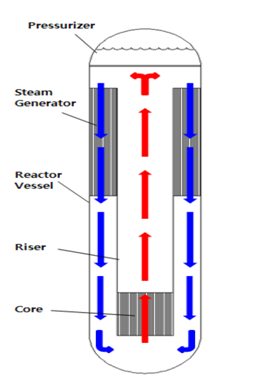
What are Small Modular Nuclear reactors (SMRs)?
- Small modular reactors (SMRs) are advanced nuclear reactors that have a power capacity of up to 300 MW (e) per unit, which is about one-third of the generating capacity of traditional nuclear power reactors.
- SMRs, which can produce a large amount of low-carbon electricity using:
- Small– physically a fraction of the size of a conventional nuclear power reactor.
- Modular – making it possible for systems and components to be factory-assembled and transported as a unit to a location for installation.
- Reactors – harnessing nuclear fission to generate heat to produce energy.
Conventional Nuclear power plants vs. Small modular reactors:
- Nuclear Power Plants (NPPs) are efficient users of land and their grid integration costs are lower than those associated with variable renewable energy (VRE) sources because NPPs generate power 24x7 in all kinds of weather.
- As an alternative, several countries are developing small modular reactors (SMRs) – nuclear reactors with a maximum capacity of 300 MW – to complement conventional NPPs.
- SMRs can be installed in decommissioned thermal power plant sites by repurposing existing infrastructure, thus sparing countries from having to acquire more land and/or displace people beyond the existing site boundary.
- SMRs can be safely installed and operated at several brownfield sites that may not meet the more stringent zoning requirements for conventional NPPs.
|
Many SMR projects that have already been ordered by European countries till 2035. |
Need for SMRs:
- According to the International Energy Agency, the demand for critical minerals like lithium, nickel, cobalt, and rare earth elements, required for clean-energy production technologies, is likely to increase by up to 3.5x by 2030.
- This jump poses several global challenges, including the large capital investments to develop new mines and processing facilities.
- The environmental and social impacts of developing several new mines and plants in China, Indonesia, Africa, and South America within a short time span, coupled with the fact that the top three mineral-producing and -processing nations control 50-100% of the current global extraction and processing capacities, pose geopolitical and other risks.
Advantages of SMRs:
- SMRs are designed with a smaller core damage frequency (the likelihood that an accident will damage the nuclear fuel) and source term (a measure of radioactive contamination) compared to conventional NPPs.
- They also include enhanced seismic isolation for more safety.
- SMR designs are also simpler than those of conventional NPPs and include several passive safety features, resulting in a lower potential for the uncontrolled release of radioactive materials into the environment.
How nuclear reactors can lead to sustainable energy generation?
- Accelerating the deployment of SMRs under appropriate international safeguards, by implementing a coal-to-nuclear transition at existing thermal power-plant sites, will take India closer to net-zero and improve energy security because uranium resources are not as concentrated as reserves of critical minerals.
- Most land-based SMR designs require low-enriched uranium, which can be supplied by all countries that possess uranium mines and facilities for such enrichment if the recipient facility is operating according to international standards.
- Further, serial manufacture of SMRs can reduce costs by simplifying plant design to facilitate more efficient regulatory approvals and experiential learning with serial manufacturing.
What are the Initiatives to Achieve Self-reliance in the Energy Sector?
- Gas Based Economy
- Blending of Ethanol in Petrol
- Prime Minister UjjwalaYojna
- Renewable Energy Initiatives
- National Hydrogen Mission
Way forward:
- The aspects like investment, infrastructure development, private-public partnership, green financing, policy framework need to be strengthened both at the national level and regional level to cater to inclusiveness in the development process.
- Green energy has tremendous potential in contributing to income, employment, and entrepreneurship and undoubtedly fosters sustainable development.
- In addition to job and income generation, it opens up opportunities/avenues for investment and markets for new products and services. So, India should focus on achieving green energy and self-reliance in the Energy Sector together.