17th November 2022 (7 Topics)
Context
IMD forecasts the formation of a low-pressure area over the southeast Bay of Bengal, thereby increasing the rainfall in the coastal districts of Tamil Nadu.
Details
Details:
- The formation of a low-pressure area over the Southeast Bay of Bengal and the adjoining Andaman Sea is expected to intensify into a depression over central parts of the South Bay of Bengal.
- Prevailing upper air circulation would influence the formation of the fresh system.
- Weather models have indicated rain in the coastal parts of Tamil Nadu.
What is the pressure system?
- A pressure system is an area of the Earth’s atmosphere that has a particularly high or low pressure compared to the surrounding
- Types of pressure systems are:
- Low-Pressure System
- High-Pressure System
What is a low-pressure system?
- A low-pressure area is a region where the atmospheric pressure at sea level is below that of surrounding locations. Low-pressure systems form under areas of wind divergence that occur in upper levels of the troposphere.
- A low-pressure system is formed due to localized heating caused by greater sunshine over deserts and other landmasses.
- Since the warm air in localized areas is less dense than the surroundings, the warm air rises, lowering the atmospheric pressure.
- Large-scale thermal lows over continents help create pressure gradients that drive monsoon circulations.
- Due to Earth’s spin and the Coriolis effect, winds of a low-pressure system swirl counterclockwise. This type of flow is known as cyclonic flow.
- Around the world, the low-pressure systems are most frequently located over the Tibetan Plateau and the lee of the Rocky Mountains. In Europe, the recurring low-pressure weather system is known as depressions.
High-Pressure System
- High-pressure systems are normally associated with light winds at the surface and subsidence at the lower portion of the troposphere.
- Subsidence dries out an air mass by adiabatic or compressional heating. Hence, high pressure usually results in clear skies.
- Since no clouds are present to obstruct the incoming shortwave solar radiation, the temperature rises during the day.
- At night, due to the absence of clouds, the outgoing longwave radiation is not absorbed and results in cooler low temperatures in all seasons
- A high-pressure system swirls in the opposite direction from a low-pressure system. This type of flow is known as anticyclonic flow.
- In high mountainous areas, rice takes more time to cook because low pressure reduces the boiling point of water.
|
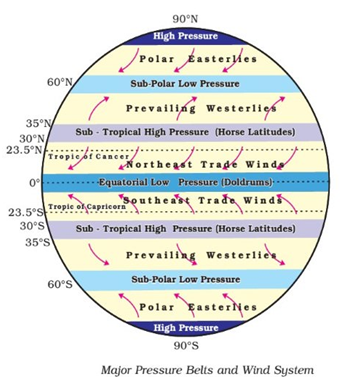
The seven pressure belts are: 1. Equatorial Low-Pressure Belts 2. Subtropical High-Pressure Belts (two) 3. Circum-Polar Low-Pressure Belts (two) 4. Polar High-Pressure Areas (two) |
Vertical Variation of Pressure
- In the lower atmosphere, the pressure decreases rapidly with height.
- In general, the atmospheric pressure decreases on average at the rate of about 34 millibars every 300 meters of height.
- The vertical pressure gradient force is much larger than that of the horizontal pressure gradient. But it is generally balanced by a nearly equal but opposite gravitational force. Hence, we do not experience strong upward winds.
- Due to gravity, the air at the surface is denser and hence has higher pressure. Since air pressure is proportional to density as well as temperature, it follows that a change in either temperature or density will cause a corresponding change in pressure.
- The pressure decreases with height. At any elevation, it varies from place to place and its variation is the primary cause of air motion, i.e., wind which moves from high-pressure areas to low-pressure areas.
- A rising pressure indicates fine, settled weather, while a falling pressure indicates unstable and cloudy weather.
Horizontal Distribution of Pressure
|
An isobar is a line connecting points that have equal values of pressure. Isobars are analogous to the contour lines on a relief map. |
- The distribution of atmospheric pressure over the globe is known as the horizontal distribution of pressure.
- It is shown on maps with the help of
- The spacing of isobars expresses the rate and direction of change in air pressure.
- This change in air pressure is referred to as the pressure gradient.
- The pressure gradient is the ratio between the pressure difference and the actual horizontal distance between two points.
- Close spacing of isobars expresses a steep pressure gradient while wide spacing indicates a gentle pressure gradient.
- The horizontal distribution of atmospheric pressure is not uniform in the world. It varies from time to time at a given place; it varies from place to place over short distances.
- The factors responsible for variation in the horizontal distribution of pressure are as follows:
- Air temperature
- The earth’s rotation
- Presence of water vapor
|
SHORT NEWS |
|
|
Economy IFSCA signs MoU with RBI in the field of regulation, supervision of regulated entities
|
|
|
Environment India Ranks 8th in Climate Change Performance Index
|
|
|
Environment 2022 Summit of the Leadership Group for Industry Transition (LeadIT)
|
|
More Articles