

1st December 2022 (5 Topics)
Context
Recently, Mauna Loa, the world’s largest active volcano, erupted after 38 years.
Background:
- Mauna Loa is among Earth's most active volcanoes, having erupted 33 times.
- It last erupted in 1984 which led to destruction on the Island.
- It has produced large, voluminous flows of basalt that have reached the ocean eight times since
- It last erupted in 1984, when a lava flow came within 7.2 km (4.5 mi) of Hilo, the largest population center on the island.
- Mauna Loa is certain to erupt again, and with such a propensity to produce large flows, we carefully monitor the volcano for signs of unrest.
About
About Mauna Loa:
- It is the World’s largest active Volcano in the Island of Hawaii in the U.S. state of Hawaii in the Pacific Ocean.
- The volcano makes up 51% of the Hawaii Island landmass.
- It is an active shield volcano with relatively gentle slopes.
- Lava eruptions from Mauna Loa are silica-poor and very fluid, and they tend to be non-explosive.
|
How big is Mauna Loa?
|
Significance:
- Its eruption remains important as the volcano covers a large area of the island.
- It gives the opportunity to the current scientist to study the volcanic phenomenon.
Type:
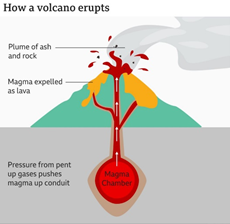
- Shield Volcano: A shield volcano is a broad volcano with sloping sides that is formed mainly out of runny lava that flows out of its central summit vent.
- Examples of Shield Volcanoes: are Mauna Loa on the Island of Hawaii, Wolf volcano on the Galapagos Islands, and Nyamuragira in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
- Examples of Shield Volcanoes: are Mauna Loa on the Island of Hawaii, Wolf volcano on the Galapagos Islands, and Nyamuragira in the Democratic Republic of Congo.
Why the volcano is ‘very fluid’?
- Basaltic magma is high in temperature, very low on silica, and with low gas content.
- Basic lava, which is non-acidic and very runny.
- Gentle sides as the lava flow for long distances before it solidifies.
- No layers, as the volcano just consists of lava.


