

4th March 2022 (6 Topics)
Context
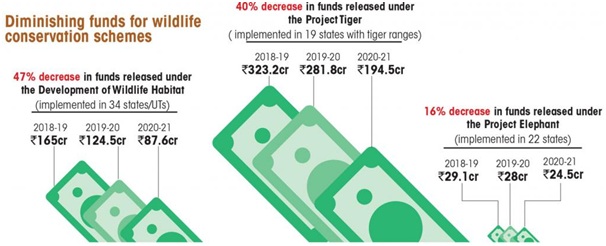
The Union government has cut the funds released under three flagship wildlife schemes even though poaching remains rampant.
About
What is wildlife crime?
- According to International Consortium on Combating Wildlife Crime (ICCWC), wildlife crime refers to acts committed contrary to national laws and regulations intended to protect natural resources and to administer their management and use.
- This includes the illicit exploitation of natural resources, such as poaching of animals and unauthorized logging of trees.
- It may also include subsequent acts, such as the processing of fauna and flora into products, their transportation, sale and possession.
- Wildlife offenders can be divided into two groups –
- The poachers or hunters who kill or capture wild animals or collect wild plants
- Persons trading, buying hunted and/or captured animals or its body parts or derivatives or collected plants or its parts or derivatives, for own consumption or for sale.
- Major wildlife crime in India includes poaching of tigers, rhinos and the sale of Star tortoises.
Reasons for upsurge of Illegal Wildlife Trade in India
- Illegal wildlife trade is driven mainly by the huge profits earned by the traders.
- Low risk and low penalties make the trade highly lucrative.
- Unlike other conventional crimes, no stigma is attached to the offenders who commit wildlife crimes.
- Wealthy markets in Asia, Europe, USA and the Middle East are the force driving the illegal trade of wildlife.
- Craze for ornaments made of animal body parts (ivory, tiger teeth/bones), use of animal body parts or plants in traditional medicines, keeping the skins or horns or antlers as status symbols, cultural beliefs or even superstitious beliefs are other factors driving the illegal trade in wildlife and their parts & products.
|
About Wildlife Crime Control Bureau:
|
More Articles


