21st March 2024 (9 Topics)
Context
Recent findings from the 'Income and Wealth Inequality in India' report highlight the substantial increase in the income share of the wealthiest 1% of Indians, exceeding levels observed during British colonial rule.
Key-highlights of the Report
- Report Title: Income and wealth inequality in India
- In 2022, 22.6% of the national income went to the top 1% of Indians.
- In 1951, their share in the income was only 11.5% and even lower in the 1980s — just before India opened-up its economy — at 6%.
- The share of the top 10% of Indians too had increased — from 36.7% of national income in 1951 to 57.7% in 2022.
- The bottom 50% of Indians earned only 15% of the national income in 2022, compared with 20.6% in 1951.
- The middle 40% of Indians also recorded a sharp fall in their share of income from 42.8% to 27.3% in the period.
- 10,000 richest Indians — the top 0.001% of the income pyramid — earned 2.1% of the national income. The top 0.01% and top 0.1% earned 4.3% and 9.6% of the national income respectively.
1: Dimension- Historical Trends in Income Distribution
- Evolution of Income Share: The top 1% of Indians witnessed a remarkable increase in their income share, rising from 11.5% in 1951 to 22.6% in 2022, and surpassing even colonial-era levels.
- Rise of the Top 10%: Similarly, the top 10% saw a significant surge in their income share, from 36.7% in 1951 to 57.7% in 2022.
- Decline of the Bottom 50% and Middle 40%: In contrast, the income share of the bottom 50% and middle 40% steadily declined over the years, exacerbating income inequality.
2: Dimension- Widening Income Disparity Post-Liberalization
- Impact of Liberalization: The income gap between the top 10% and the middle 40% widened significantly post-liberalization in the 1990s, leading to a sharp increase in income inequality.
- Steady Decline of Bottom 50%: Despite marginal increases in the 1980s, the income share of the bottom 50% has steadily fallen, exacerbating socioeconomic disparities.
- Historic Peak of Top 1%: In 2022, the top 1% reached a historic peak in their income share, surpassing levels seen during British colonial rule, highlighting the rapid increase in income inequality.
3: Dimension- Comparative Analysis with Global Economies
- India's Position: Despite slower income growth compared to other economies like China and Vietnam, India's top 1%'s share of national income exceeds that of many advanced countries, including the United States, China, France, the United Kingdom, and Brazil.
- Global Trends: Globally, income inequality has been on the rise, with the wealthiest individuals accruing a disproportionate share of national income. Reports from the World Inequality Lab indicate that income inequality has increased in many countries, including India, since the 1980s.
- Policy Implications: The widening income gap underscores the urgent need for policies aimed at promoting equitable economic growth and addressing socioeconomic disparities. According to experts at the International Monetary Fund, addressing income inequality is crucial for sustainable and inclusive economic development.
4: Dimension- Implications and Analysis
- Urgent Need for Policy Intervention: The widening income gap underscores the urgent need for policies aimed at promoting equitable economic growth and addressing socioeconomic disparities.
- Social Cohesion and Development: Failure to address income inequality could have far-reaching implications for India's social cohesion and long-term development prospects.
- Long-term Development Prospects: Addressing income inequality is imperative for India's sustainable and inclusive development. According to the United Nations Development Programme, reducing income inequality is crucial for achieving sustainable development goals and ensuring that economic growth benefits all segments of society.
|
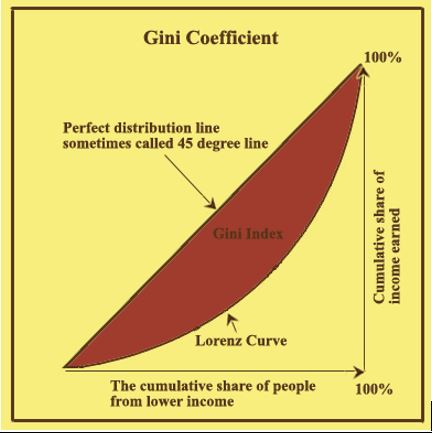
Fact Box: Gini Coefficient The Gini index, or Gini coefficient, measures income distribution across a population. Developed by Italian statistician Corrado Gini in 1912, it often serves as a gauge of economic inequality. |
Mains Practice Question
Q Evaluate the effectiveness of existing policy measures in mitigating income inequality in India.
More Articles