

12th November 2022 (8 Topics)
Context
The project for the trial of the Twin Engine Deck Based Fighter (TEDBF), is expected to get approval from the Cabinet Committee on Security (CCS) by mid-2023.
About
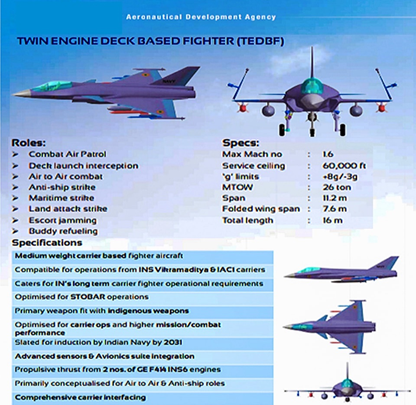
Twin-Engine Deck-Based Fighter (TEDBF):
- It will be the first twin-engine aircraft project in India that too for dedicated carrier-based operations.
- This fighter is getting developed for the Navy.
- It is viewed as the naval variant of the indigenous Tejas Jet.
- It will replace the existing fleet of Mikoyan MiG-29K carrier-based fighters
- The TEDBF is being designed and developed by the Aeronautical Development Agency (ADA).
- It will be manufactured by Hindustan Aeronautics Limited (HAL).
- The TEDBF is being designed based on lessons learned from the Naval LCA programme.
- Indigenous aircraft carrier INS Vikrant is gearing up for aviation trials.
Weapons:
- The aircraft will be equipped predominantly with domestic weapons.
Size and Capacity:
- It will have a maximum Mach number of 1.6, a service ceiling of 60,000 feet, a maximum takeoff weight of 26 tons, unfolded wing span of 11.2 meters, folded wing span of 7.2, and a length of 16.3 meters.
Induction:
- It will be inducted with the Navy by 2031-32.
|
About MiG-29K:
|
Indigenization efforts of the Indian Navy:
- Indian navy indigenization plan 2015-2030: In 2014 Navy promulgated the Indian Navy indigenization Plan (INIP) 2015-2030 to enable the indigenous development o equipment and system.
- So far, the Navy has indigenized around 3400 items under INIP, including over 2000 machinery and electrical spares, over 1000 aviation spares, and over 250 weapon spares.
- Naval Aviation Indigenization Roadmap 2019-22:
- The existing Naval Aviation Indigenization Roadmap (NAIR) 2019-22 is too under revision.
- All fast-moving aircraft mandatory spares and high-cost indigenous repairs are being included in the revised NAIR 2022-27.
- Indigenization Committees: Four in-house indigenization committees have been formed to handle the indigenization of spares with respect to naval aircraft.
- Naval Liaison Cells: In addition, the Naval Liaison Cells (NLCs) located at various places have been nominated as ‘indigenization cells.
- Collaboration with DRDO: The Navy is working with the Defense Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) and the industry to cut down developmental timelines.
- Naval Innovation and Indigenisation Organisation (NIIO): Launched in August 2020, it provides a flexible and accessible interface for academia and industry with the Indian Navy capability development apparatus.
|
Make I & Make II:
|
Related initiates:
- Corporatization of the ordnance factory Boards: To improve autonomy, accountability, and efficiency in ordnance suppliers.
- Increased the FDI limit from 49% to 74%: It will likely result in better access to modern technology.
- Defense India Start-up Challenge (DISC): DISC aims at supporting Startups/MSMEs (Micro Small and Medium Enterprises)/Innovators to create prototypes and/or commercialize products/solutions in the area of National Defence and Security.
- SRIJAN Portal: It is a one-stop shop online portal that provides access to the vendors to take up items that can be taken up for indigenization.
- Innovations for Defence Excellence (iDEX): iDEX aims to promote innovation and technology development in Defence and Aerospace.


